This profile has been updated. Find the new profile here.
Objective and Strategy
Tributary Balanced Fund seeks capital appreciation and current income. They allocate assets among the three major asset groups: common stocks, bonds and cash equivalents. Based on their assessment of market conditions, they will invest 25% to 75% of the portfolio in stocks and convertible securities, and at least 25% in bonds. The portfolio is typically 70-75 stocks from small- to mega-cap and turnover is about half of the category average. They currently hold about 50 bonds.
Adviser
Tributary Capital Management. At base, Tributary is a subsidiary of First National Bank of Omaha and the Tributary funds were originally branded as the bank’s funds. Tributary advises seven mutual funds, as well as serving high net worth individuals and institutions. As December 31, 2011, they had about $1.1 billion under management.
Managers
Kurt Spieler and John Harris. Mr. Spieler is the lead manager and the Managing Director of Investments for the advisor. In that role, he develops and manages investment strategies for high net worth and institutional clients. He has 24 years of investment experience in fixed income, international and U.S. equities including a stint as Head of International Equities for Principal Global Investors and President of his own asset management firm. Mr. Harris is a Senior Portfolio Manager for the advisor. He joined Tributary in 2007 and this fund’s team in 2010. He has 18 years of investment management experience including analytical roles for Principal Global Investors and American Equity Investment Life Insurance Company.
Management’s Stake in the Fund
Mr. Spieler has over $100,000 in the fund. Mr. Harris has $10,000 in the fund, an amount limited by his “an interest in a more aggressive stock allocation.”
Opening date
August 6, 1996
Minimum investment
$1000, reduced to $100 for accounts opened with an automatic investing plan.
Expense ratio
1.22%, after a minor waiver, on $59 million in assets (as of 2/29/12).
Comments
Tributary Balanced does what you want to “balanced” fund to do. It uses a mix of stocks and bonds to produce returns greater than those associated with bonds with volatility less than that associated with stocks. Morningstar’s “investor returns” research supports the notion that this sort of risk consciousness is probably the most profitable path for the average investor to follow.
What’s remarkable is how very well, very quietly, and very consistently Tributary achieves those objectives. The fund has returned 7.6% per year for the past decade, 50% better than its peer group, but has taken on no additional risk to achieve those returns. Its Morningstar profile, as of 3/28/12, looks like this:
|
Rating |
Returns |
Risk |
Returns relative to peers |
|
| Past three years |
* * * * * |
High |
Average |
Top 1% |
| Past five years |
* * * * * |
High |
Average |
Top 1% |
| Past ten years |
* * * * * |
High |
Average |
Top 2% |
| Overall |
* * * * * |
High |
Average |
n/a |
Its Lipper rankings, as of 3/28/12, parallel Morningstar’s:
|
Total return |
Consistency |
Preservation |
|
| Past three years |
* * * * * |
* * * * * |
* * * * |
| Past five years |
* * * * * |
* * * * * |
* * * * |
| Past ten years |
* * * * * |
* * * * * |
* * * |
| Overall |
* * * * * |
* * * * * |
* * * * |
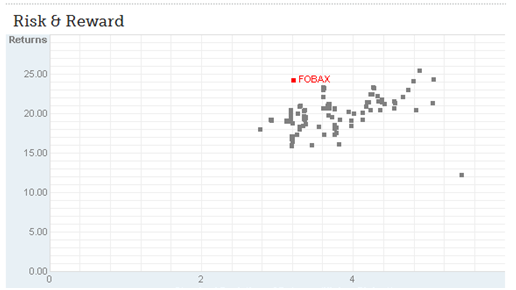
We commissioned an analysis of the fund by the folks at Investment Risk Management Systems (a/k/a FundReveal), who looked at daily volatility and returns, and concluded “FOBAX is a well-managed, safe, low risk Moderate Allocation fund.
- Its low volatility, high return performance is visible in cumulative 5 year, latest cumulative one year and latest quarter analysis results.
- Its Persistence Rating (PR) is 60, indicating that it has maintained an “A-Best” rating over most of last 20 quarters.
- This is also evident from the rolling 20 quarters Risk-Return ratings which have been between “A-Best” and “C-Less Risky.”
Our bottom line opinion is that FOBAX seems to be one of the better managed funds in the Moderate Allocation class.”
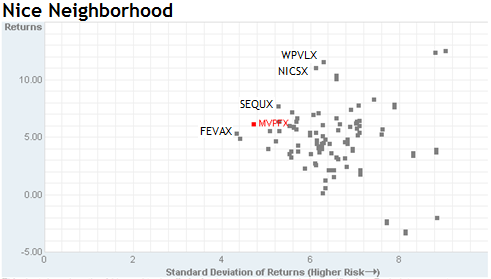
SmartMoney provides a nice visual representation of the risk-return relationships of funds. Below is the three-year scatterplot for the balanced fund universe. In general, an investor wants to be as near the upper-left corner (universe returns, zero risk) as possible. There are three things to notice in this graph:
- Three funds form the group’s northwest boundary; that is, three that have a distinguished risk-return balance. They are Tributary, Vanguard Balanced Index (VBINX) which is virtually unbeatable and Calvert Balanced (CSIFX) which provides middling returns with quite muted risk.
- The only funds with higher returns (Fidelity Asset Manager 85% FAMRX and T. Rowe Price Personal Strategy Growth TRSGX than Tributary have far higher stock allocations (around 85%), far higher volatility and took 70% greater losses in 2008.
- Ken Heebner is sad. His CGM Mutual (LOMMX) is the lonely little dot in the lower right.
 To what could we attribute Tributary’s success? Mr. Spieler claims three sources of alpha, or positive risk-adjusted returns. They are:
To what could we attribute Tributary’s success? Mr. Spieler claims three sources of alpha, or positive risk-adjusted returns. They are:
- They have a flexible asset allocation, which is driven by a macro-economic assessment, profit analysis and valuation analysis. In theory the fund might hold anywhere between 25-75% in equities though the actual allocation tends to sit between 50-70%.
- Stock selection tends to be opportunistic. The portfolio tilts toward growth stocks and the managers are particularly interested in emerging markets growth stocks. The neat trick is they pursue their interest without investing in foreign stocks by looking for US firms whose earnings benefit from emerging markets operations. Pricesmart PSMT, for example, has 100% of its operations in South America while Cognizant Technology Solutions CTSH is a play on outsourcing to South Asia. They’re also agnostic as to market cap. Measured by the percentage of earnings from international sources, Tributary offers considerable international exposure. They etimate that 48% of revenues of for their common stock holdings are from international sales. That compares to an estimated 42% of international sales for the S&P 500.
- Fixed-income selection is sensitive to duration targets and unusual opportunities. About 20% of the portfolio is invested in taxable municipal bonds, such as the Build America Bonds. Those were added to the portfolio when irrational fear gripped the fixed income market and investors were willing to sell such bonds as a substantial discount in order to flee to the safety of Treasuries. Understanding that the fundamentals behind the bonds were solid, the managers snatched them up and booked a solid profit.
The managers are also risk-conscious, which is appropriate everywhere and especially so in a balanced fund. The stock portfolio tends to be sector-neutral, and the number of names (typically 70-75) was based on an assessment of the amount of diversification needed for reasonable risk management.
Bottom Line
The empirical record is pretty clear. Almost no fund offers a consistently better risk-return profile. While it would be reassuring to see somewhat lower expenses or high insider ownership, Tributary has clearly earned a spot on the “due diligence” list for any investor interested in a hybrid fund.
Fund website
Tributary Funds. FundReveal’s complete analysis of the fund is available on their blog.
© Mutual Fund Observer, 2012. All rights reserved. The information here reflects publicly available information current at the time of publication. For reprint/e-rights contact us.