By David Snowball
Dear friends,
They’ve done it again. After 32 years at Augustana, I’m still amazed and delighted each spring. For all that I grumble about their cell phone-addled intellects and inexplicable willingness to drift along sometimes, their energy, bravery and insistence on wanting to do good continue to inspire me. I wish them well and will soon begin to prepare for the challenges posed by my 33rd set of first-year students.

But not right now. Right now, Chip and I are enjoying being in Scotland, being in each other’s company and being without cell service. Grand and languorous adventure awaits on islands and Highlands. While she and I are away, we’ve turned most of this month’s issue over to our colleagues though I did have time to write just a bit. And so…
Funds without fillers
Here are two simple truths:
- Owning stocks makes sense because, over the long run, returns on stocks far outstrip returns on other liquid, publicly-accessible asset classes. Over the past 90 years, large cap stocks have returned 10% a year while government bonds have made 5-6%.
Sadly, that simple observation leads to this sort of silliness:
See? As long as your retirement is at least 87 years off, it’s silly to put your money anywhere other than common stocks. (The article’s author, a pharmacist and active investor, concludes that you shouldn’t trust mutual funds or ETFs but should, instead, be a do-it-yourself value investor. Uhhh … no thanks.) For those of us with a time horizon shorter than 87 years though, there’s a second truth to cope with.
- Owning stocks doesn’t always make sense because the price of higher long-term returns is higher immediate volatility. That’s because stocks are more exciting than bonds. Frankly, no normal human ever said “yup, I got me some 30-year Ginnie Mae jumbos with a coupon of 3.5%” with nearly the same visceral delight as “yup, I got into Google at the IPO.” Maaaagic! That desire to own magic often enough leads investors to spend hundreds of dollars to buy shares which are earning just pennies a year. Good news leads to excitement, excitement leads to a desire to own more, that desire leads to a bidding war for shares, which leads to a soaring stock price, which leads to more bidding … and, eventually, a head-first tumble into a black hole.
GMO’s Ben Inker quantified the magnitude of the hysteria: “the volatility of U.S. since 1881 has been a little over 17% per year. The volatility of the underlying fair value of the market has been a little over 1%. Well over 90% of the volatility of the stock market cannot be explained as a rational response to the changing value of the stream of dividends it embodies” (“Keeping the Faith,” Quarterly Letter, 1Q 2016).
One reasonable conclusion, if you accept the two arguments above, is you should rely on stock managers who are not wedded to stocks. When we enter a period when owning stocks makes less sense, then your manager should be free to … well, own less stock. There are at least three ways of doing that: making bets that the market or particular sectors or securities will fall (long/short equity), shifting assets from overvalued asset classes to undervalued ones (flexible portfolios) or selling stocks as they become overvalued and holding the proceeds in cash until stocks become undervalued again (absolute value investing). Any of the three strategies can work though the first two tend to be expensive and complicated.
So why are long/short and flexible portfolios vastly more popular with investors than straightforward value investing? Two reasons:
- They’re sexy. It’s almost like being invested in a hedge fund which, despite outrageous expenses, illiquidity, frequent closures and deplorable performance, is where all the Cool Kids hang out.
- You demand managers that do something! (Even if it’s something stupid.) Batters who swing at the first pitch, and every pitch thereafter, are exciting. They may go down, but they go down in glory. Batters who wait for a fat pitch, watching balls and marginal strikes go by, are boring. They may get solid hits but fans become impatient and begin screaming “we’re not paying you to stand there, swing!” As the season goes on, batters feel the pressure to produce and end up swinging at more and more bad pitches.
In The Dry Powder Gang, Revisited (May 2016), we concluded:
[B]eing fully invested in stocks all the time is a bad idea. Allowing greed and fear, alternately, to set your market exposure is a worse idea. Believing that you, personally, are magically immune from those first two observations is the worst idea of all.
You should invest in stocks only when you’ll be richly repaid for the astronomical volatility you might be exposed to. Timing in and out of “the market” is, for most of us, far less reliable and far less rewarding than finding a manager who is disciplined and who is willing to sacrifice assets rather than sacrifice you. The dozen teams listed above have demonstrated that they deserve your attention, especially now.
One of those managers, Eric Cinnamond of ASTON River Road Absolute Value (ARIVX) wrote to take issue with our claim that cash necessarily serves as a drag on a portfolio. He writes:
 This is another misconception about not being fully invested. If you have large discounts you can still generate attractive returns without being invested in what I call “fillers.” Just like with processed food, investment fillers are often there just to fill up the portfolio, but often provide little value and in some cases can be hazardous to your health! Open the hood of most fully invested small cap funds and you’ll find plenty of fillers these days, especially in sectors like consumer and health care. The stocks are clearly overvalued but managers think because they’re in lower risk sectors they won’t get destroyed. Good example WD-40 (WDFC) at 30x earnings! Great company but you could lose half your capital if it ever reverted to a more justifiable 7% free cash flow yield.
This is another misconception about not being fully invested. If you have large discounts you can still generate attractive returns without being invested in what I call “fillers.” Just like with processed food, investment fillers are often there just to fill up the portfolio, but often provide little value and in some cases can be hazardous to your health! Open the hood of most fully invested small cap funds and you’ll find plenty of fillers these days, especially in sectors like consumer and health care. The stocks are clearly overvalued but managers think because they’re in lower risk sectors they won’t get destroyed. Good example WD-40 (WDFC) at 30x earnings! Great company but you could lose half your capital if it ever reverted to a more justifiable 7% free cash flow yield.
That led us to the question, “so, how good are absolute value guys as stock-pickers.” That is, if you don’t feel compelling to buy “fillers” just for the optical value of a full-invested portfolio, how well do the stocks you find compelling perform?
Answer: really quite well. In the chart below, we look at the YTD performance of cash-heavy funds through early May. We then calculate how the stock portion of the portfolio performed, assuming that the cash portion was returning zero. For example, if a fund was 10% invested in stocks and had returned 1% YTD, we impute a stock return of 10% for that period.
|
|
Style
|
Cash
|
2016 return, as of 5/6/16
|
Imputed active return
|
|
ASTON / River Road Independent Value ARIVX
|
Small-cap value
|
85
|
8.5
|
56.7
|
|
Intrepid Endurance ICMAX
|
Small-cap value
|
67
|
4.2
|
12.7
|
|
Hennessy Total Return HDOGX
|
Large-cap value, Dogs of the Dow
|
49
|
5.3
|
10.4
|
|
Intrepid Disciplined Value ICMCX
|
Mid-cap value
|
48
|
4.8
|
9.2
|
|
Castle Focus MOATX
|
Global multi-cap core
|
34
|
6.0
|
9.1
|
|
Pinnacle Value PVFIX
|
Small-cap core
|
47
|
4.2
|
8.9
|
|
Frank Value FRNKX
|
Mid-cap core
|
60
|
2.8
|
7.0
|
|
Cook & Bynum COBYX
|
Global large-cap core
|
37
|
4.3
|
6.8
|
|
Centaur Total Return TILDX
|
Equity-income
|
45
|
3.6
|
6.6
|
|
Bruce BRUFX
|
Flexible
|
26
|
2.5
|
3.4
|
|
Bread & Butter BABFX
|
Multi-cap value
|
42
|
1.3
|
2.2
|
|
FPA Crescent FPACX
|
Flexible
|
36
|
0.2
|
0.3
|
|
Chou Opportunity CHOEX
|
Flexible
|
22
|
(16.6)
|
(21.3)
|
|
Two plausible benchmarks
|
|
Vanguard Total Stock Market VTSMX
|
Multi-cap core
|
0
|
1
|
1
|
|
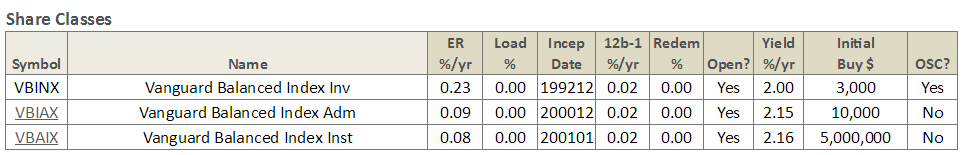
Vanguard Balanced Index VBINX
|
Hybrid
|
2
|
2.3
|
2.3
|
Two things stand out: first, the absolute value guys have, almost without exception, outperformed a fully invested portfolio during the year’s violent ups and downs. Second, the stocks in their portfolios have dramatically outperformed the stocks in a broad market index. Excluding the freakish Chou Opportunity fund, the stocks in the remaining twelve portfolio returned 10.6% on average while the Total Stock Market Index made 1%.
Bottom line: the demand for a fully-invested portfolio forces managers to buy stocks they don’t want to own. Judged by reasonable measures (risk-adjusted returns measured by the Sharpe ratio) over reasonable periods (entire market cycles rather than arbitrary 1/3/5 year snippets), you are better served by portfolios without fillers and by the sorts of managers we characterized as the “we’ve got your back” guys. Go check them out. The clock is ticking and you really don’t do your best work in the midst of a panic.
Wait! You can’t start a new bear market. We’re not done with the last one yet!
Many thoughtful people believe that the bull market that began in March 2009, the second oldest in 70 years, is in its final months. The S&P 500, despite periods of startling volatility, has gone nowhere in the year since reaching its all-time high on May 21, 2015; as I write on May 21, 2016, it sits 1% below that peak. It looks like this:
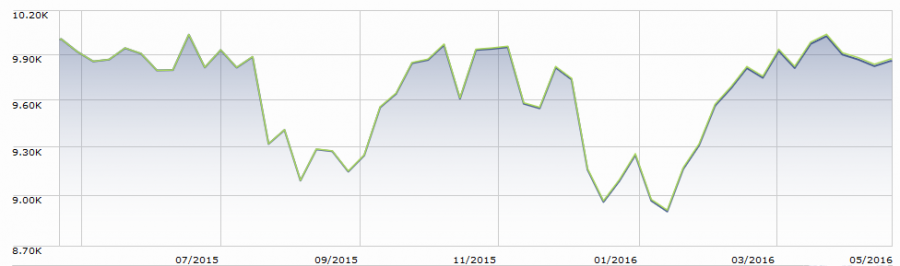
That’s bad: Randall Forsyth reports that no bull market in 30 years has gone so long without a new high (“Stocks Are Stuck in the Twilight Zone,” Barrons, 5/21/16). Of 13 bull markets since 1946 that have gone a year without a high, ten have ended in bear markets (“Clock ticks on bull market,” 5/20/16).
Meanwhile earnings have declined for a fourth consecutive quarter (and are well on their way to a fifth quarter). FactSet (5/20/16) notes we haven’t seen a streak that long or a quarterly drop so great since the financial crisis. The stock market is, in consequence, somewhere between “pricey” and “ridiculously pricey.” A new bear market may not be imminent (check with the Fed), but it will arrive sooner rather than later.
“But wait!” cries one cadre of managers, “we can’t have a new bear market yet. The old one hasn’t finished with us yet.”

That’s right. There are funds that still haven’t recovered their October 2007 levels. We screened the MFO Premium database, looking for funds that have spent the past 101 months still mauled by the bear.
We’ve found 263 funds, collectively holding $507 billion in assets, that haven’t recovered from the financial crisis. Put another way, $10,000 invested in one of these funds 3,150 days ago in October 2007 still isn’t worth $10,000.
Highlights of the list:
- Thirteen funds have managed double-digit annual losses since the start of the crisis. These are ranked from the greatest annualized loss down.
Direxion Monthly Emerging Markets Bull 2x (DXELX)
UltraEmerging Markets ProFund (UUPIX)
Guinness Atkinson Alternative Energy (GAAEX)
Midas (MIDSX)
Direxion Monthly 7-10 Year Treasury Bear 2x (DXKSX)
Mobile Telecommunications UltraSector ProFund (WCPIX)
ProShares Ultra Financials(UYG)
Rising Rates Opportunity ProFund (RRPIX)
Banks UltraSector ProFund (BKPIX)
UltraInt’l ProFund (UNPIX)
UltraJapan ProFund (UJPIX)
Calvert Global Energy Solutions (CAEIX)
Rydex Inverse Government Long Bond Strategy (RYJUX)
Ten of those funds could reasonably claim that they’re simple, mechanical trading vehicles which are designed for sophisticated (hah!) investors to hold for hours or a few days, not years. Three of the funds have no such excuse.
- Sixteen of the funds are double-dippers; they crashed in 2007-09 and then crashed even worse between 2009 and 2016. Technically we’re measuring a fund’s maximum drawdown, the greatest decline registered after it had begun to recover. Most of the double-dippers were leveraged equity, income or currency funds. Four funds managed the feat on (tremendously bad) luck and skill alone. Funds whose maximum drawdowns occurred after March 2009 include
- Midas, down 88%, bottoming in December 2015
- Calvert Global Energy Solutions, down 75% and Guinness Atkinson Alternative Energy, down 85%, both as of July 2012
- Nysa, down 55% as of February 2016.
- One hundred ninety of the funds, around 72%, are international vehicles: 114 diversified international, 47 are emerging markets funds, 13 Europe-centered and 16 variously Asia-centered. There are no Latin American funds on the list.
- 78 of the funds are passive, quasi-passive or smart beta sorts of funds, including ETFs, ETNs, mechanical leveraged equity and enhanced index funds. The advisor that appears most frequently is iShares.

- Five simple domestic equity funds must take the Walk of Shame
AMG Managers Brandywine Advisors Mid Cap Growth (BWAFX), a mid-cap growth fund that’s lost 3.7% annually over the full market cycle.
Schneider Value (SCMLX) is a concentrated $20 million deep value fund that’s lost 1.2% annually, buoyed by a 15% return so far in 2016. It has a maddening tendency to finish way above average one year then crash for the next two.
Stonebridge Small Cap Growth (SBSGX) has lost 2.9% annually over the full market cycle but wins points for consistency: by Morningstar’s assessment, it has trailed at least 99% of its peers for the trailing 3, 5, 10 and 15 year periods.
Nysa (NYSAX), a small cap fund that would appall even Steadman. The fund’s not only lost 7.6% per year over the current market cycle, it’s lost over 50% in the 19 years since inception. In a hopeful move, the fund installed a new manager in February, 2013. He’s down 28% since then.
Jacobs Small Cap Growth (JSCGX) is the product of a bizarre marketing decision. In 2010, Jacob Investment Management decided to acquire Rockland Small Cap Growth Fund, a dying small cap fund with a terrible record and rechristen it as their own. The hybrid product is down 4.7% annually over the full market cycle. Since conversion, the fund has trailed its peers every year and appears to trail, well, all of them.
- 55 are multi-billion dollar funds. The Biggest Losers, all with over $10 billion in assets, are
- Vanguard Total International Stock Index (VGTSX)
- Vanguard Emerging Markets Stock Index (VEIEX)
- iShares MSCI Emerging Markets ETF (EEM)
- Vanguard FTSE All-World ex US Index ETF (VEU)
- Financial Select Sector SPDR (XLF)
- iShares MSCI Eurozone ETF (EZU)
The most famous funds on the list include Janus Overseas (JNSOX), T. Rowe Price Emerging Markets Stock (PRMSX) and Fidelity Overseas (FSOFX), one of 12 Fido funds to earn this sad distinction.
The complete list of Bear Chow Funds is here.
One bit of good news for investors in these funds; others have suffered more. Three funds have waited more than 20 years to recover their previous highs:
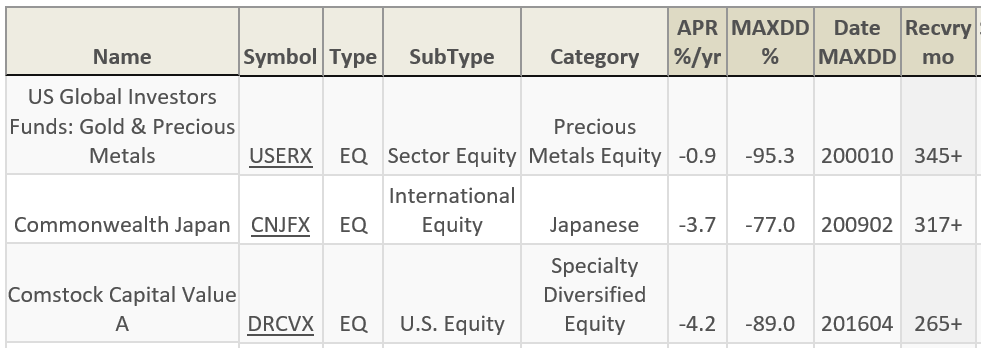
Bottom line: if you own one of these funds, you need to actively pursue an answer to the question “why?” First why: why did I choose to invest in this fund in the first place? Was it something I carefully researched, something pushed on me by a broker, an impulse or what? That’s a question only you can answer. Second why: why does this fund appear to be so bad? There might be a perfectly legitimate reason for its apparent misery. If so, either a fund’s representative or your adviser owes you a damned straight, clear explanation. Do not accept the answer “everyone was down” any more than you’d accept “everyone cheats.” Not everyone was down this much and not everyone stayed down. And if, after listening to them bloviate a bit you start to feel the waft of smoke up your … uhh, nethers, you need to fire them.
Smart people saying interesting stuff
Josh Brown, “The Repudiation Phase of the Bubble,” 05/09/2016:
One of the common threads of every financial or asset bubble throughout human history is that they all have a repudiation phase – a moment where all the lies that had been built up alongside the excess are aired in public. Every reputation companies and players get caught up in it… We’re there now. New shit is coming to light every five minutes. Every reputation you thought was untouchable and every omission you’d accepted because it was already accepted by the crowd – all back on the table for discussion (dissection?).
Snowball’s note: for some reason, an old aphorism popped into my head as I read this. “The function of liberal Republicans (yes, there were such once) is to shoot the wounded after the battle.”
Cullen Roche, “A catastrophe looms over high-fee mutual funds and investment advisers,” 04/28/2016:
Back in 2009 I wrote a very critical piece on mutual funds basically calling them antiquated products that do the American public a disservice. I was generalizing, of course, as there are some fine mutual funds out there. However, as a generalization I think it’s pretty fair to say that the vast majority of mutual funds are closet-indexing leaches that do no one any good (except for the management companies who charge the high fees). But there are smart ways to be active and very silly ways to be active. Mutual funds are usually a silly way to be active as they sell the low probability of market-beating returns in exchange for the guarantee of high fees and taxes.
Dan Loeb is right. A catastrophe is coming. The end of an era is here. And the American public is going to be better off because of it.
Snowball’s note: “the vast majority are …” is absolutely correct. The question for me is whether really worthwhile funds will stubbornly insist on self-destructing because (1) the managers are obsessed about talking about raw performance numbers and (2) firms would rather die on their own terms rather than looking for ways to collaborate with other innovators to redefine the grounds of the debate.
Had I mentioned my impending encounter with Cullen Skink (no relation), a sort of Scottish fish chowder?
Meb Faber, “Which Institution Has the Best Asset Allocation Model?” 05/18/2016. After analyzing the recommended asset allocations of the country’s 40 top brokerages and comparing their results over time, Faber fumes:
There you have it – the difference between the most and least aggressive portfolios is a whopping 0.53% a year. Now, how much do you think all of these institutions charge for their services? How many millions and billions in consulting fees are wasted fretting over asset allocation models?
So all those questions that stress you out…
- “Is it a good time for gold?”
- “What about the next Fed move – should I lighten my equity positions beforehand?”
- “Is the UK going to leave the EU, and what should that mean for my allocation to foreign investments?”
Let them go.
If you’re a professional money manager, go spend your time on value added activities like estate planning, insurance, tax harvesting, prospecting, general time with your clients or family, or even golf.
If you’re a retail investor, go do anything that makes you happy.
Either way, stop reading my blog and go live your life.
Snowball’s note: I found the table of asset allocation recommendations fascinating, in about the way that I might find a 40-car pile-up on the Interstate fascinating. Two things stood out. In a broadly overpriced market, none of these firms had the courage to hold more than trivial amounts of cash. And they do have a devotion to hedge funds and spreading the money into every conceivable nook and cranny. I was mostly impressed with Fidelity’s relatively straightforward 60/40 sort of model.
Mr. Faber’s performance analysis is unpersuasive, if not wrong. He looks at how the brokerages various allocations would have performed from 1973 to the present but it appears that he simply assumes that the current asset allocation (4% to EM debt, 14% to private equity, 25% to hedge funds) can be projected backward to 1973. If so … uh, no.
Finally, his analysis implies that high equity exposures – even over a period of decades – do not materially enhance returns. As a practical matter, you’re doing about as well at 40% equity as at 65%. Given that I’ve argued for stock-light portfolios, I’m prone to agree.
Side note to Mr. Faber: I took your advice and am lounging on the Isle of Skye. Did you, or are you scribbling away at yet another life-wasting blog post?
Bob Cochran’s Thinking beyond funds
 We were delighted to announce last month that Bob Cochran joined MFO’s Board of Directors. Bob is the lead portfolio manager, Chief Compliance Officer, and a principal of PDS Planning in Columbus, Ohio, and a long-time contributor to the FundAlarm and MFO discussion boards.
We were delighted to announce last month that Bob Cochran joined MFO’s Board of Directors. Bob is the lead portfolio manager, Chief Compliance Officer, and a principal of PDS Planning in Columbus, Ohio, and a long-time contributor to the FundAlarm and MFO discussion boards.
The Observer strives to help two underserved groups: small independent investors and small independent managers. In an experiment in outreach to the former group, and most especially to younger, less confident investors, Bob has agreed to write a series of short articles that help people think beyond funds. That aligns nicely with Meg Faber’s recommendation, above, and with both Bob and Sam Lee’s approach to their clients. All agree that your investments are an important part of your financial life, but they don’t drive your success on their own. Here’s Bob’s first reminder of stuff worth knowing but often overlooked.
They Are Just Documents. How Important Can They Be?
Take a moment and think about what could happen if you were to suddenly become physically or mentally unable to handle your affairs. Young, old, single, married, in a committed relationship or not: the fact is unless you have certain documents in place, your financial and health well being could be in limbo. Everyone should have the following documents created, executed, and ready should they be needed.
- Durable Power of Attorney, sometimes called a financial power of attorney. This designates someone to act on your behalf should you be unable to pay bills and make other financial decisions. This allows your designee access to bank accounts, brokerage accounts, and retirement accounts (the latter only if specifically stated in the document), and the authority to make deposits, withdrawals, and pay bills, and allow access to any safe deposit boxes.
- Health Care Power of Attorney, also called a Health Care Directive or Medical Power of Attorney. This document allows your designee the authority to make health care decisions. In some states, this can be what is called a Springing Power of Attorney that takes effect only after your incapacity.
If you do not have these two documents, think of the problems that could arise should you become unable to handle your financial affairs or make health care decisions by yourself. How will your ongoing bills be paid? Who will respond to doctors and health care providers on your behalf? The time and money to have the courts make a ruling could be significant, and that does not ensure it is consistent with your wishes.
Both documents are easily created by your attorney, or you may find them online, specifically for the state in which you live. Generally, your spouse would be named as POA if you are married. If you are single, a parent, relative, or close friend are often selected. Remember the person you name will have broad powers, so be sure it is someone you trust. And be sure you provide a copy of the documents to the person you have named as POA.
Tragedies happen all the time. They are seldom anticipated. We have had clients who have spent money getting these documents created, but have never signed them. This is a huge mistake! Take action today to make sure you live your life on your own terms. After all, it’s your life, plan for it.
On Financial Planners
 A family friend recently asked me to look at his mutual fund investments. He contributes to these investments periodically through his colleague, a Certified Financial Planner at a long-time neighborhood firm that provides investment services. The firm advertises it’s likely more affordable than other firms thanks to changes in how clients are billed, so it does not “charge hefty annual advisor fees of 1% or more.”
A family friend recently asked me to look at his mutual fund investments. He contributes to these investments periodically through his colleague, a Certified Financial Planner at a long-time neighborhood firm that provides investment services. The firm advertises it’s likely more affordable than other firms thanks to changes in how clients are billed, so it does not “charge hefty annual advisor fees of 1% or more.”
I queried the firm and planner on FINRA’s BrokerCheck site and fortunately found nothing of concern. FINRA stands for Financial Industry Regulatory Authority and is a “not-for-profit organization authorized by Congress to protect America’s investors by making sure the securities industry operates fairly and honestly.”
A couple recent examples of its influence: FINRA Fines Raymond James $17 Million for Systemic Anti-Money Laundering Compliance Failures and FINRA Sanctions Barclays Capital, Inc. $13.75 Million for Unsuitable Mutual Fund Transactions and Related Supervisory Failures.
The BrokerCheck site should be part of the due-diligence for all investors. Here for example is the type of allegations and settlements disclosed against the firm Edward Jones in 2015: “The firm was censured and agreed to pay $13.5 million including interest in restitution to eligible customers … that had not received available sales charge waivers … since 2009, approximately 18,000 accounts purchased mutual fund shares for which an available sales charge waiver was not applied.”
And, here an example of experience listed for an “Investment Adviser Representative” …

But I’m getting sidetracked, so back to my friend’s portfolio review. Here’s what I found:
- He has 5 separate accounts – 2 Traditional IRAs, 2 Roth IRAs, and one 529.
- All mutual funds are American Funds, accessed directly through American Funds website.
- He owns 34 funds, across the 5 accounts.
- Adjusting for different share classes (both front-loaded A, and back-loaded B … no longer offered), he owns 8 unique funds.
- The 8 “unique” funds are not all that unique. Many hold the very same stocks. Amazon was held in 6 different funds. Ditto for Phillip Morris, Amgen, UnitedHealth Group, Home Depot, Broadcom, Microsoft, etc.
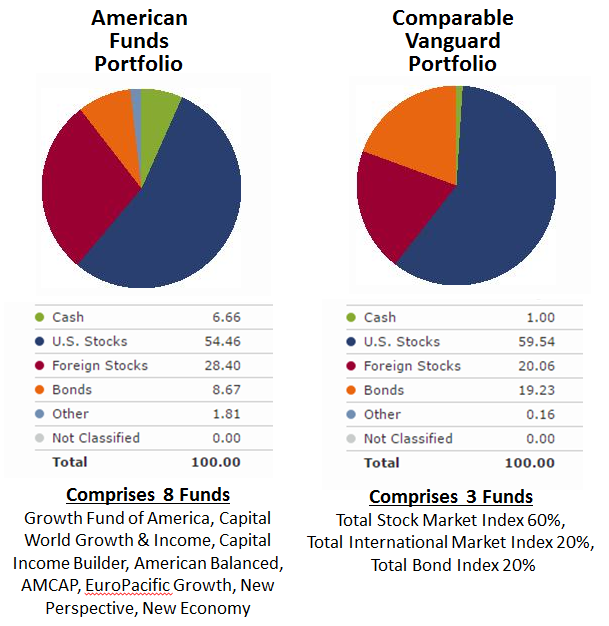
- The 8 funds are, in order of largest allocation (A class symbols for reference): Growth Fund of America (AGTHX), Capital World Growth & Income (CWGIX), Capital Income Builder (CAIBX), American Balanced (ABALX), AMCAP (AMCPX), EuroPacific Growth (AEPGX), New Perspective (ANWPX), and New Economy (CNGAX).
After scratching my head a bit at the sheer number of funds and attendant loads, annual expense ratios, and maintenance fees, I went through the exercise of establishing a comparable portfolio using only Vanguard index funds.
I used Morningstar’s asset allocation tool to set allocations, as depicted below. Not exact, but similar, while exercising a desire to minimize number of funds and maintain simple allocations, like 60/40 or 80/20. I found three Vanguard funds would do the trick: Total Stock Market Index 60%, Total International Market Index 20%, and Total Bond Index 20%.
The following table and corresponding plot shows performance since November 2007, start of current market cycle, through April 2016 (click on image to enlarge):
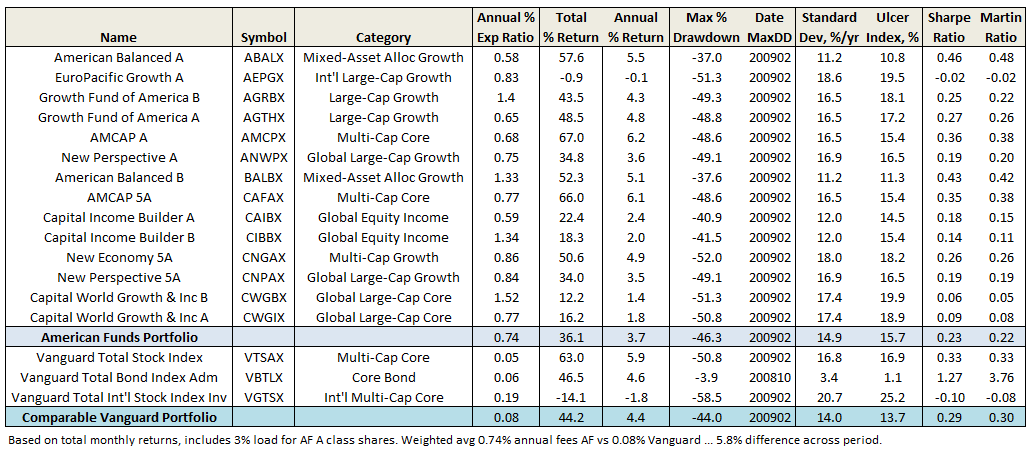
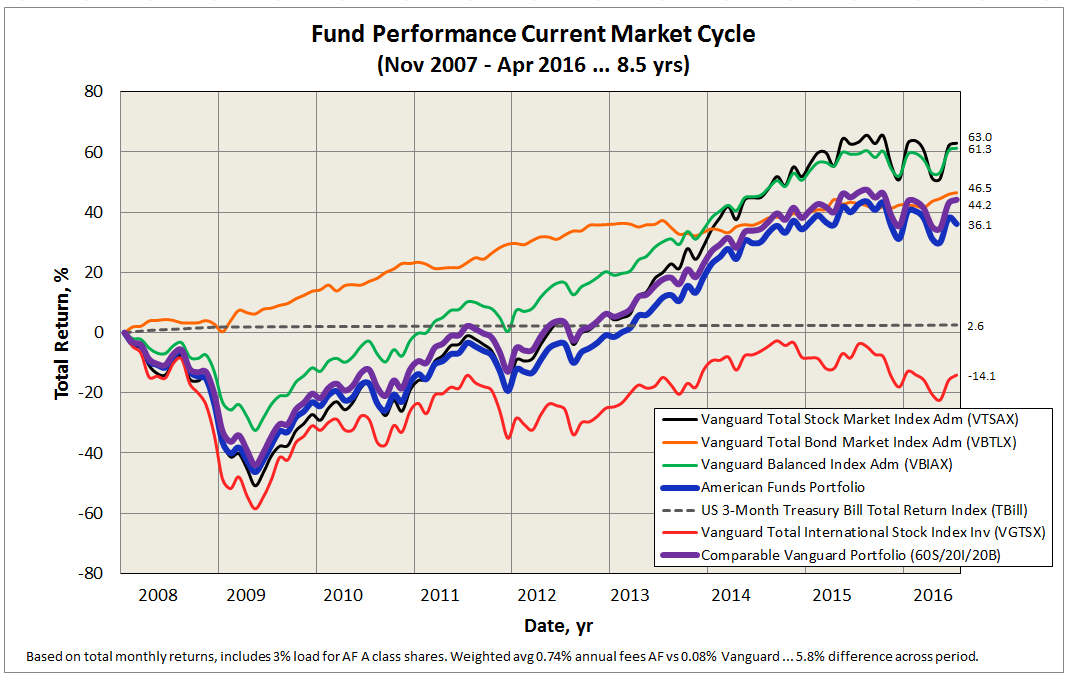
As Mr. Buffet would be quick to point out, those who simply invested in the Total Stock Market Index fund received the largest reward, if suffering gut-wrenching drawdown in 2009. The Total Bond Index rose rather steadily, except for brief period in 2013. The 60/40 Balanced Index performed almost as well as the Total stock index, with about 2/3 the volatility. Suspect such a fund is all most investors ever need and believe Mr. Bogle would agree. Similarly, the Vanguard founder would not invest explicitly in the Total International Stock fund, since US S&P 500 companies generate nearly half their revenue aboard. Over this period anyway, underperformance of international stocks detracted from each portfolio.
The result appears quite satisfying, since returns and volatility between the two portfolios are similar. And while past performance is no guarantee of future performance, the Vanguard portfolio is 66 basis points per year cheaper, representing a 5.8% drag to the American Funds’ portfolio over an 8.5 year period … one of few things an investor can control. And that difference does not include the loads American Funds charges, which in my friend’s case is about 3% on A shares.
My fear, of course, is that while this Certified Financial Planner may not directly “charge hefty annual advisor fees,” my friend is being directed toward fee-heavy funds with attendant loads and 12b-1 expenses that indirectly compensate the planner.
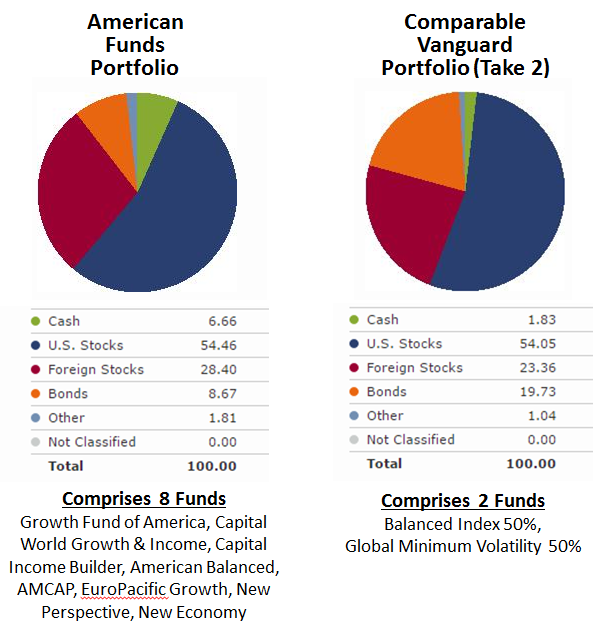
Inspired by David’s 2015 review of Vanguard’s younger Global Minimum Volatility Fund (VMVFX/VMNVX) I made one more attempt to simplify the portfolio even more and reduce volatility, while keeping global exposure similar. This fund’s 50/50 US/international stock split combined with the 60/40 stock/bond split of the Vanguard Balanced Fund, produces an even more satisfying allocation match with the American Funds portfolio. So, just two funds, each held at 50% allocation.
Here is updated allocation comparison:
And here are the performance comparison summary table and plot from January 2014 through April 2016, or 2.33 years (click image to enlarge):
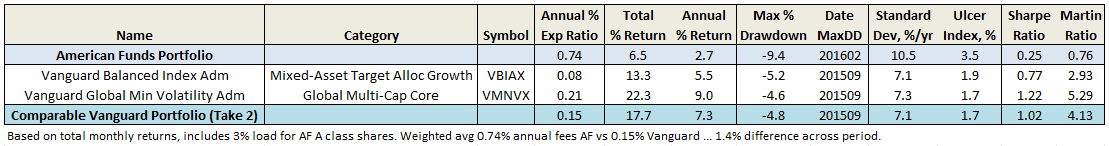
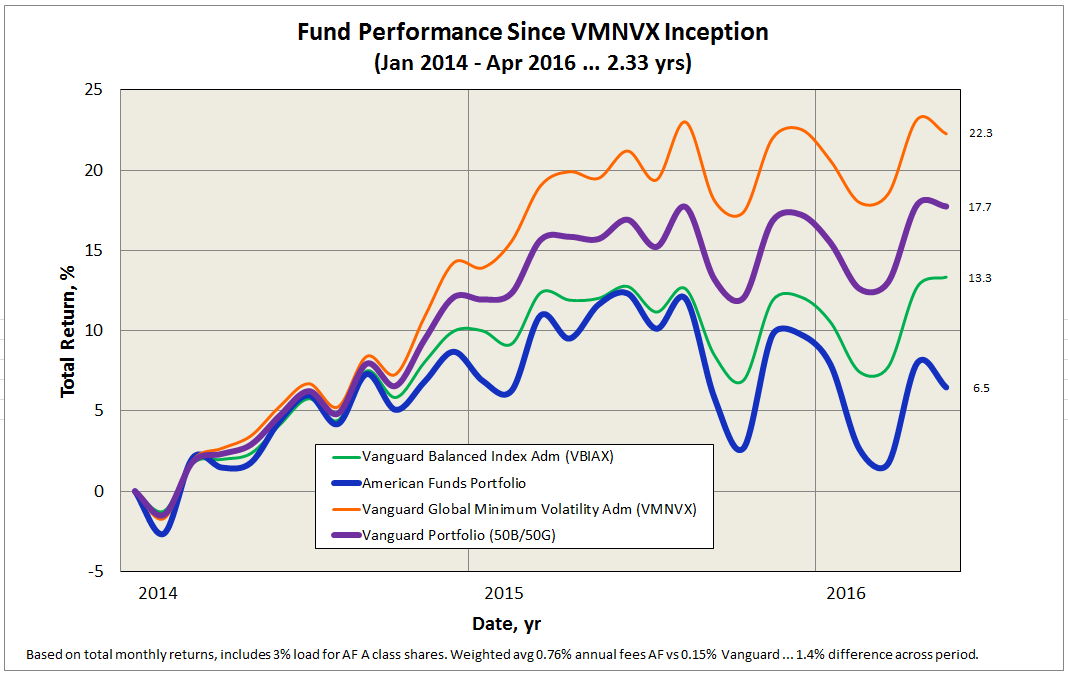
I should note that the Global Volatiliy Fund is not an index fund, but actively managed by Vanguard’s Quantitative Equity Group, so this portfolio is also 50/50 passive/active. While the over-performance may temper, lower volatility will persist, as will the substantially lower fees.
Other satisfying aspects of the two comparable Vanguard portfolios are truly unique underlying holdings in each fund and somewhat broader exposure to value and mid/small cap stocks. Both these characteristics have shown over time to deliver premiums versus growth and large cap stocks.
Given the ease at which average investors can obtain and maintain mutual fund portfolios at Vanguard, like those examined here, it’s hard to see how people like my friend will not migrate away from fee-driven financial planners that direct clients to fee-heavy families like American Funds.
Every Active Fund is a Long-Short Fund: A Simple Framework for Assessing the Quality, Quantity and Cost of Active Management
By Sam Lee
Here’s a chart of the 15-year cumulative excess return (that is, return above cash) of a long-short fund. Over this period, the fund generated an annualized excess return of 0.82% with an annualized standard deviation of 4.35%. The fund charges 0.66% and many advisors who sell it take a 5.75% commission off the top.
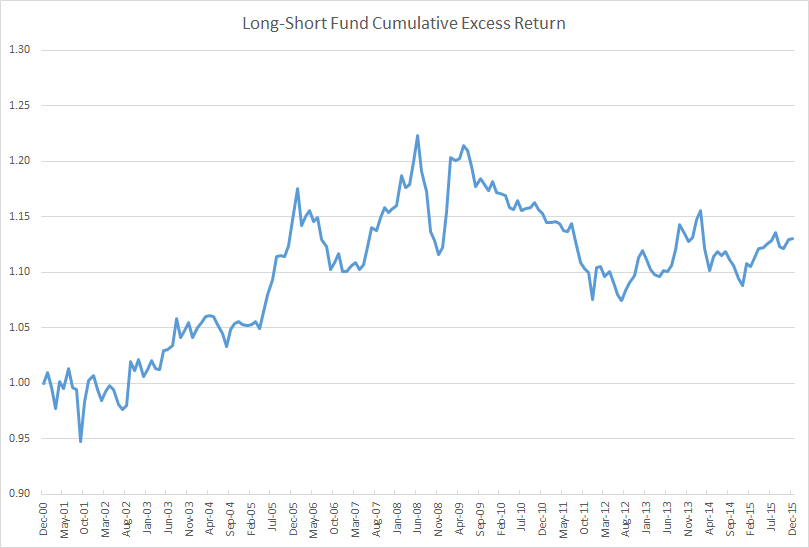
Though its best returns came during the financial crisis, making it a good diversifier, I suspect few would rush out to buy this fund. Its performance is inconsistent, its reward-to-risk ratio of 0.19 is mediocre, and its effective performance fee of 44% is comparable to that of a hedge fund. There are plenty of better-performing market-neutral or long-short funds with lower effective fees.
Despite the unremarkable record, about $140 billion is invested in a version of this strategy under the name of American Funds Growth Fund of America AGTHX. I simply subtracted the Standard & Poor’s 500 Index’s monthly total return from AGTHX’s monthly total return to create the long-short excess return track record (total return would include the return of cash).
This is an unconventional way of viewing a fund’s performance. But I think it is the right way, because, in a real sense, every active fund is a long-short strategy plus its benchmark.
Ignoring regulatory or legal hurdles, a fund manager can convert any long-only fund into a long-short fund by shorting the fund’s benchmark. He can also convert a long-short fund into a long-only fund by buying benchmark exposure on top of it (and closing out any residuals shorts). I could do the same thing to any fund I own through a futures account by overlaying or subtracting benchmark exposure.
Viewing funds this way has three major benefits. First, it allows you to visualize the timing and magnitude of a fund’s excess returns, which can alter your perception of a fund’s returns in major ways versus looking at a total return table or eyeballing a total return chart. Looking at a fund’s three-, five- and ten-year trailing returns tells you precious little about a fund’s consistency and the timing of its returns. The ten-year return contains the five-year return which contains the three-year return which contains the one-year return. (If someone says a fund’s returns are consistent, citing 3-, 5-, and 10-year returns, watch out!) Rolling period returns are a step up, but neither technique has the fidelity and elegance of simply cumulating a fund’s excess returns.
Second, it makes clear the price, historical quantity and historical quality of a fund’s active management. The “quantity” of a fund’s active management is its tracking error, or the volatility of the fund’s returns in excess of its benchmark. The “quality” of a fund’s management is its information ratio, or excess return divided by tracking error. Taking these two factors into consideration, it becomes clearer whether a fund has offered a good value or not. A fund shouldn’t automatically be branded expensive based on its expense ratio observed in isolation. I would happily give up my left pinky for the privilege of investing in Renaissance Technologies’ Medallion fund, which charges up to 5% of assets and 44% of net profits, and I would consider myself lucky.
Finally, it allows you to coherently assess alternative investments such as market-neutral funds on the same footing as long-only active managers. A depressingly common error in assessing long-short or market neutral funds is to compare their returns against the raw returns of long-only funds or benchmarks. A market neutral fund should be compared against the active component of a long-only manager’s returns.
To make these lessons concrete, let’s perform a simple case study with two funds: Vulcan Value Partners Small Cap VVPSX and Vanguard Market Neutral VMNFX. Here’s a total return chart for both funds since the Vulcan fund’s inception on December 30, 2009. (Note that Vanguard Market Neutral was co-managed by AXA Rosenberg until late 2010, after which Vanguard’s Quantitative Equity Group took full control.)
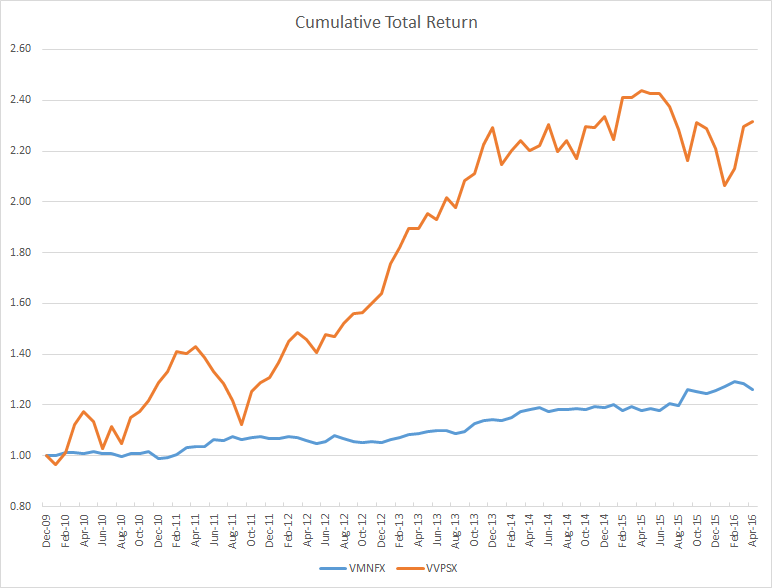
Given the choice between the two funds, which would you include in your portfolio? Over this period the Vanguard fund returned a paltry 3.7% annually and the Vulcan fund a blistering 14.2%. If you could only own one fund in your portfolio, the Vulcan fund is probably the better choice as it benefits from exposure to market risk and therefore has a much higher expected return. However, if you are looking for the fund that enhances the risk-adjusted return of portfolio, there isn’t enough information to say at this point; it is meaningless to compare a fund with market exposure with a market neutral fund on a total return basis.
A good alternative fund usually neutralizes benchmark-like exposure and leave only active, or skilled-based, returns. A fairer comparison of the two funds would strip out market exposure from Vulcan Small Cap (or, equivalently, add benchmark exposure to Vanguard Market Neutral). In the chart below, I subtracted the returns of the Vanguard Small Cap Value ETF VBR, which tracks the CRSP US Small Cap Value Index, from the Vulcan fund’s returns. While the Vulcan fund benchmarks itself against the Russell 2000 Value index, the Russell 2000 is terribly flawed and has historically lost about 1% to 2% a year to index reconstitution costs. Small-cap managers love the Russell 2000 and its variations because it is a much easier benchmark to beat. Technically, I’m also supposed to subtract the cash return (something like the 3-month T-bill or LIBOR rate) from Vanguard Market Neutral, but cash yields have effectively remained 0% over this period.
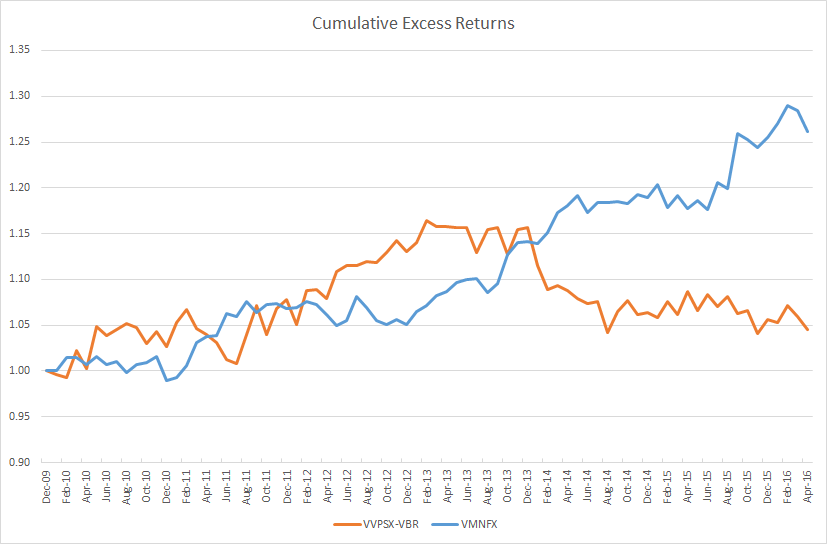
When comparing both funds simply based on their active returns, Vanguard Market Neutral Fund looks outstanding. Investors have paid a remarkably low management fee (0.25%) for strong and consistent outperformance. Even better, the fund’s outperformance was not correlated with broad market movements.
This is not to say that Vanguard has the better fund simply based on past performance. Historical quantitative analysis should supplement, not supplant, qualitative judgment. The quality of the managers and the process have to be taken into account when making a forecast of future outperformance as a fund’s past excess return is very loosely related to its future excess return. There is a short-term correlation, where high recent excess return predicts high future near-term excess return due to a momentum effect, but over longer horizons there is little evidence that high past return predicts high future return. Confusingly, low long-run excess returns predict low future returns, suggesting evidence of persistent negative skill. If a fund has historically displayed a long-term pattern of low active exposure and negative excess returns, its fees should either be extremely low or you shouldn’t own it at all.
—–
There’s a puzzle here. Imagine if Vanguard Market Neutral’s managers simply overlaid static market exposure on their fund. Here’s how their fund would have performed. A long-only fund that has beaten the market by 3.7% a year with minimal downside tracking error over five years would easily attract billions of dollars. But here Vanguard is, wallowing is relative obscurity, despite having remarkably low absolute and relative costs.
Why is this? In theory, the price of active management—in whatever form—should tend to equalize in a competitive market. However, what we see is that long-only active management tends to dominate and is often wildly expensive relative to the true exposures offered, and long-short active management tends to often repackage market beta and overcharge for it, creating pockets of outstanding value among strategies that are truly market neutral and highly active.
I think three forces are at work:
- Investors do not adjust a fund’s returns for its beta exposures. A high return fund, even if it’s almost from beta, tends to attract assets despite extremely high fees for the actively managed portion.
- Investors focus on absolute expense ratios, often ignoring the level of active exposure obtained.
- Investors are uncomfortable with unconventional strategies that use leverage and derivatives and incur high tracking error.
Given these facts, a profit-maximizing fund company will be most rewarded by offering up closet index funds. Alternative managers will offer up market beta in a different form. Active managers that offer truly market neutral exposure will be punished due to their unconventionality and comparisons against forms of active management where beta exposures are baked into the track record.
Investment Implications
When choosing among active strategies, all sources of excess return should be on a level playing field. There is no reason to compare long-only active managers against other long-only active managers. Your portfolio doesn’t care where it gets its excess returns from and neither should you.
However, because investors tend to anchor heavily on absolute expense ratios, the price of active management offered in a long-only format tends to be much more expensive per unit of exposure than in a long-short format. An efficient way to obtain active management while keeping tracking error in check is to construct a barbell of low-cost benchmark-like funds and higher-cost alternative funds.
 Sam Lee and Severian Asset Management
Sam Lee and Severian Asset Management
Sam is the founder of Severian Asset Management, Chicago. He is also former Morningstar analyst and editor of their ETF Investor newsletter. Sam has been celebrated as one of the country’s best financial writers (Morgan Housel: “Really smart takes on ETFs, with an occasional killer piece about general investment wisdom”) and as Morningstar’s best analyst and one of their best writers (John Coumarianos: “ Lee has written two excellent pieces [in the span of a month], and his showing himself to be Morningstar’s finest analyst”). He has been quoted by The Wall Street Journal, Financial Times, Financial Advisor, MarketWatch, Barron’s, and other financial publications.
Severian works with high net-worth partners, but very selectively. “We are organized to minimize conflicts of interest; our only business is providing investment advice and our only source of income is our client fees. We deal with a select clientele we like and admire. Because of our unusual mode of operation, we work hard to figure out whether a potential client, like you, is a mutual fit. The adviser-client relationship we want demands a high level of mutual admiration and trust. We would never want to go into business with someone just for his money, just as we would never marry someone for money—the heartache isn’t worth it.” Sam works from an understanding of his partners’ needs to craft a series of recommendations that might range from the need for better cybersecurity or lower-rate credit cards to portfolio reconstruction.
The Education of a Portfolio Manager
By Leigh Walzer
Like 3 million of his peers, my son will graduate college this spring. In the technology space many of the innovative companies seem to care less about which elite institution is named on his piece of sheepskin and more about the skillset he brings to the role.
Asset management companies and investors entrusting their money to fund managers might wonder if the guys with fancy degrees actually do better than the rest of the pack.
There is an old adage that that the A students work for the C students. I remember working for Michael Price many years ago. Michael was a proud graduate and benefactor of the University of Oklahoma. He sometimes referred to my group (which did primarily distressed debt) as “the Ivy Leaguers.”
Graduates of Stanford and Harvard outperformed their peers by 1% per year for the past three years.
Thanks to the Trapezoid database, we were able to compile information to see if the Ivy Leaguers (like my son) actually perform better. Our laboratory is the mutual fund universe. We looked at 4000 funds managed by graduates of 400 universities around the world. We focused for this study on results for the three years ending April 30, 2016.
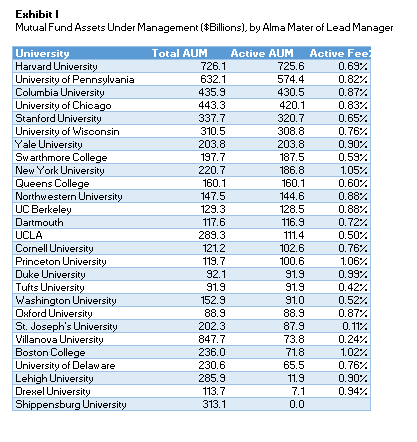
A few caveats: We concede to purists and academics that our study lacks rigor. The mutual fund database does not capture separate accounts, hedge funds, etc. We excluded many funds (comprising 25% of the AUM in our universe) where we lacked biographical data on the manager. Successful active funds rely on a team so it may be unfair to ascribe success to a single individual; in some cases we arbitrarily chose the first named manager. We used the institution associated with the manager’s MBA or highest degree. Some schools are represented by just 1 or 2 graduates. We combined funds from disparate sectors. Active and rules-based funds are sometimes strewn together. We haven’t yet crunched the numbers on the value of CFA certification. And we draw comparisons without testing for statistical validity.
I was a little surprised at the mix of colleges managing the nation’s mutual funds. Villanova has an excellent basketball program. But I didn’t expect it to lead the money manager tables. However, nearly all the funds managed by Villanova were Vanguard index funds. The same is true for Shippensburg, St. Joseph’s, Lehigh, and Drexel.
When we concentrated on active funds, the leading schools were Harvard, Wharton, Columbia University, University of Chicago, and Stanford. Note that Queens College cracks the top 10 – this is attributable almost entirely to one illustrious grad: Dina Perry, a money manager at Capital Re.
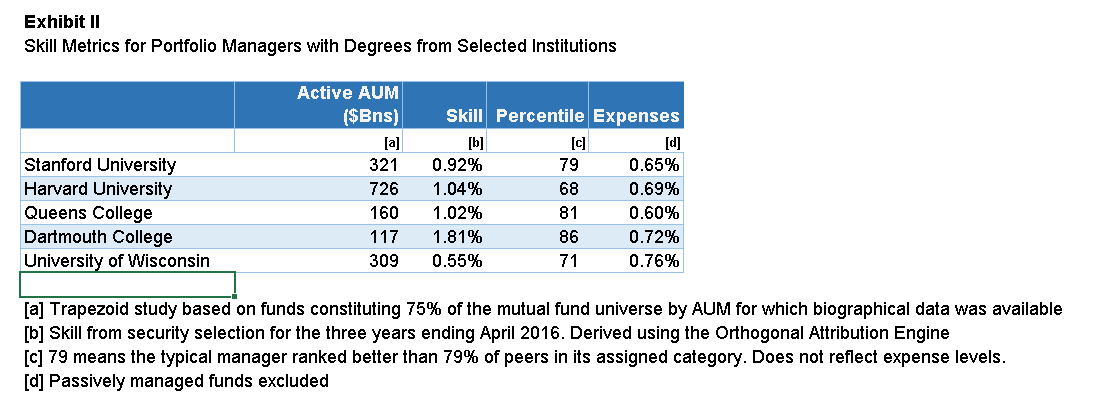
Who performed the best over the last 3 years? By one measure, Stanford graduates did the best followed by Harvard, Queens College, Dartmouth, and University of Wisconsin. Trapezoid looks mainly at each manager’s skill from security selection. Institutions managing fewer assets have a higher bar to clear to make the list. Managers from these top five schools ranked, on average, in the 77th percentile (100 being best) in their respective categories in skill as measured by Trapezoid.
|
Exhibit III: Fund Analysis Report for TRAIX
|
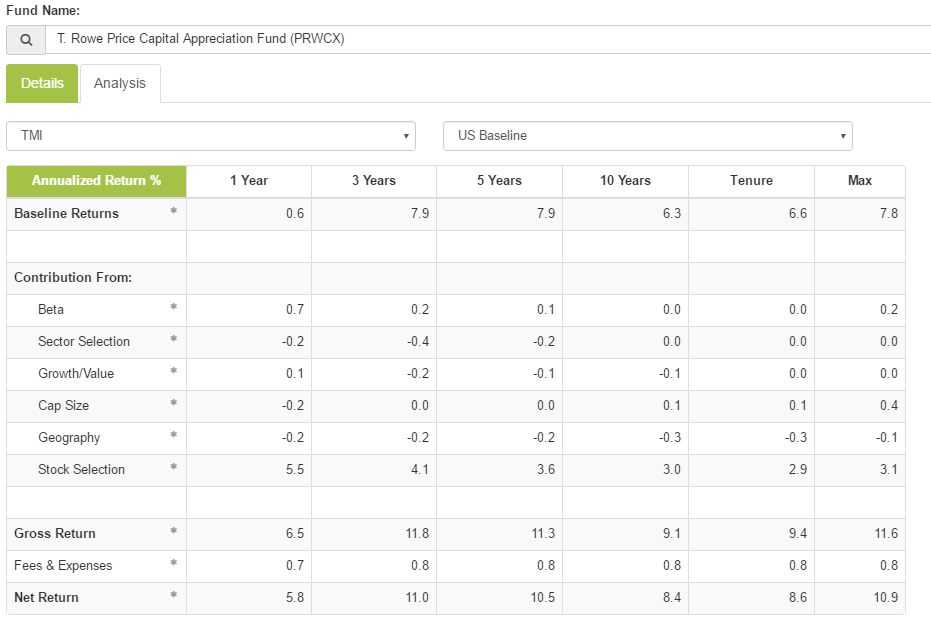
If size and sample size were disregarded, some other colleges would score well. Notably, Hillsdale College benefitted from very strong performance by David Giroux, manager of the T Rowe Price Capital Appreciation Fund (TRAIX – closed to new investors). Wellington’s Jean Hynes lifted Wellesley College to the top echelon. Strong international programs include University of Queensland and CUNEF.
I searched in vain for an alum of Professor Snowball’s Augustana College in our database. Bear in mind though that any Viking who went on to earn a post-graduate degree elsewhere will show up under that school. (Snowball’s note: Augie is a purely undergraduate college and most managers accumulate a grad degree or three, so we’d be invisible. And the only fund manager on our Board of Trustees, Ken Abrams at Vanguard Explorer VEXPX, earned both his degrees at that upstart institution in Palo Alto.)
By and large it doesn’t cost investors more to “hire” graduates of the leading schools. The average fee for active managers at these five schools is 69 bps compared with 87 bps for the overall universe.
It seems remarkable that graduates of Stanford and Harvard outperformed their peers by 1% per year for the past three years. If we add Chicago and Wharton (the next two highest ranked MBA institutions), the advantage for the elite graduates falls to 0.47%. If we expand it to include the 10 universities (as ranked by US News & World Report) the advantage falls to 30bps.
We confess we are a bit surprised by these findings. We wonder how efficient market proponents like Burton Malkiel and Jack Bogle would explain this. (Graduates of their institution, Princeton University, also outperformed the market by 1%.)
If we were recruiting for a mutual fund complex, we would focus on the leading MBA programs. Judging by the numbers many asset managers do precisely that; Over 20% of all active mutual fund managers come from these schools
Does it mean that investors should select managers on the basis of academic credentials? If the choice were between two active funds, the answer is yes. If the choice is between a fund managed actively managed by a Stanford MBA and a passive fund, the answer is less clear. We know for the past 3 years the return produced by a typical Stanford MBA adjusted for the portfolio’s characteristics exceeds expense. But we would need to be fairly confident our stable of well-educated managers would repeat their success over the long haul by a sufficient margin.
Trapezoid’s fundattribution.com website allows registered users to review funds to see whether skill is likely to justify expense for a given fund class. We do this based on a probabilistic analysis which looks at the manager’s entire track record, not just the three-year skill rating. MFO readers may register at www.fundattribution.com for a demo and see the probability for funds in certain investment categories.
Interestingly the school whose fund managers gave us the highest confidence is Dartmouth. But we wouldn’t draw too strong conclusion unless Dartmouth has figured out how to clone its star, Jeff Gundlach of DoubleLine.
Bottom Line:
Graduates of top schools seem to invest better than their peers. Our finding may not be surprising, but it contradicts the precept of efficient market theorists. Knowing the fund manager graduated a top school or MBA program is helpful at the margin but probably not sufficient to choose the fund over a low-cost passive alternative.
 What’s the Trapezoid story? Leigh Walzer has over 25 years of experience in the investment management industry as a portfolio manager and investment analyst. He’s worked with and for some frighteningly good folks. He holds an A.B. in Statistics from Princeton University and an M.B.A. from Harvard University. Leigh is the CEO and founder of Trapezoid, LLC, as well as the creator of the Orthogonal Attribution Engine. The Orthogonal Attribution Engine isolates the skill delivered by fund managers in excess of what is available through investable passive alternatives and other indices. The system aspires to, and already shows encouraging signs of, a fair degree of predictive validity.
What’s the Trapezoid story? Leigh Walzer has over 25 years of experience in the investment management industry as a portfolio manager and investment analyst. He’s worked with and for some frighteningly good folks. He holds an A.B. in Statistics from Princeton University and an M.B.A. from Harvard University. Leigh is the CEO and founder of Trapezoid, LLC, as well as the creator of the Orthogonal Attribution Engine. The Orthogonal Attribution Engine isolates the skill delivered by fund managers in excess of what is available through investable passive alternatives and other indices. The system aspires to, and already shows encouraging signs of, a fair degree of predictive validity.
The stuff Leigh shares here reflects the richness of the analytics available on his site and through Trapezoid’s services. If you’re an independent RIA or an individual investor who need serious data to make serious decisions, Leigh offers something no one else comes close to. More complete information can be found at www.fundattribution.com. MFO readers can sign up for a free demo.
Elevator Talk: Goodwood SMid Cap Discovery (GAMAX/GAMIX)
 Since the number of funds we can cover in-depth is smaller than the number of funds worthy of in-depth coverage, we’ve decided to offer one or two managers each month the opportunity to make a 200 word pitch to you. That’s about the number of words a slightly-manic elevator companion could share in a minute and a half. In each case, I’ve promised to offer a quick capsule of the fund and a link back to the fund’s site. Other than that, they’ve got 200 words and precisely as much of your time and attention as you’re willing to share. These aren’t endorsements; they’re opportunities to learn more.
Since the number of funds we can cover in-depth is smaller than the number of funds worthy of in-depth coverage, we’ve decided to offer one or two managers each month the opportunity to make a 200 word pitch to you. That’s about the number of words a slightly-manic elevator companion could share in a minute and a half. In each case, I’ve promised to offer a quick capsule of the fund and a link back to the fund’s site. Other than that, they’ve got 200 words and precisely as much of your time and attention as you’re willing to share. These aren’t endorsements; they’re opportunities to learn more.
Goodwood SMid Cap isn’t your typical small-to-mid cap fund. In 2013, the manager of Caritas All-Cap Growth Fund (CTSAX) decided he’d had enough and left, leading the Board to order the fund’s closure and liquidation. I paraphrased their logic this way: “our fund is tiny, expensive, bad, and pursues a flawed investment strategy (long stocks, short ETFs). We’ll be going now.” Then, after liquidating all of the fund’s holdings, the Board put a stop to the action, appointed a transition manager and two months later sold the fund (and its record) to Goodwood.
The new manager moved it from all-cap growth with shorting via ETFs to small-to-mid cap value. According to one recent interview, the fund was originally a long-only product which has only recently added several hedging options. Managers Ryan Thibodeaux and Josh Pesses have a portfolio of 50-70 stocks with distinct biases toward smaller cap companies and value rather than growth. They’re able to hedge that portfolio with up to 20 short positions, cash, and a mix of puts and call options. Currently the fund’s net market exposure is 75%, which about 40% of the portfolio invested in small- to micro-cap stocks.
 Mr. Thibodeaux founded Goodwood in 2012 after a nine year stint with Maple Leaf LP, a hedge fund that received a “seed” investment from Julian Robertson’s famous Tiger Management, leading to the informal designation of Maple Leaf as a “Tiger Seed.” Maple Leaf, like Goodwood, was a fundamental, value-biased long/short fund. Mr. Pesses joined Goodwood about a year later. Like Mr. Thibodeaux he was at Maple Leaf, served as a Partner and Senior Equity Research Analyst from 2007 to 2012. Their first products at Goodwood were long/short separate accounts which have done remarkably well. From January 1, 2008 – March 31, 2016, their long/short composite returned 8.6% annually after fees. The average Morningstar peer made 0.7%. That seems like a hopeful sign since those same strategies should help buoy GAMAX.
Mr. Thibodeaux founded Goodwood in 2012 after a nine year stint with Maple Leaf LP, a hedge fund that received a “seed” investment from Julian Robertson’s famous Tiger Management, leading to the informal designation of Maple Leaf as a “Tiger Seed.” Maple Leaf, like Goodwood, was a fundamental, value-biased long/short fund. Mr. Pesses joined Goodwood about a year later. Like Mr. Thibodeaux he was at Maple Leaf, served as a Partner and Senior Equity Research Analyst from 2007 to 2012. Their first products at Goodwood were long/short separate accounts which have done remarkably well. From January 1, 2008 – March 31, 2016, their long/short composite returned 8.6% annually after fees. The average Morningstar peer made 0.7%. That seems like a hopeful sign since those same strategies should help buoy GAMAX.
That said, performance has still been rocky. From the day Goodwood took over the fund (10/01/13) to 05/21/16, GAMAX has lost a bit over 6% while Morningstar’s small-blend category is up 7.3%. In 2015, the fund trailed 100% of its peers but so far in 2016, it’s returned 14.2% and is in the top 1% of its peer group. That sort of divergence led us to ask Messrs. Thibodeaux and Pesses to talk a bit more about what’s up. Here are their 200 (well, okay, 261 but that’s still only 130.5 per manager) words on why you need Goodwood:
There is not much about our firm and the Goodwood SMID Cap Discovery Fund that one would call conventional. From our background, to a geographic location that puts us well off the beaten path, to our atypical entree into the 40 Act world, to our investment strategy – we don’t fit neatly into any one box, Morningstar or otherwise.
When we took an over as manager to an existing mutual fund in October 2013, it was our first foray into the open-end side of the investment business. Up to that point, we’d spent the bulk our careers as analysts at a long/short hedge fund. That experience influences the way we approach stock selection and portfolio construction today and is a differentiator in the 40 Act space.
Our investment process is driven by a fundamental value-based approach, but that is not what sets our work apart. We see flexibility as a hallmark of our more “opportunistic” approach to investing. We invest in the sectors, both long and short, that we have covered for our entire careers – Consumer, Healthcare, Industrials and Technology. We are agnostic to benchmark weightings and when opportunities are scarce, we are comfortable with high cash balances. The Fund is and will always be long-biased, but we actively hedge our exposure using options and look at add alpha where possible through short selling individual securities.
Ultimately, our goal is to achieve superior risk adjusted returns over the intermediate to long term and we believe the Fund can serve as a valuable complement to core or passive Small and Mid cap positions.
The minimum initial investment for GAMAX is $2,500 with an expense ratio of 1.95%. The minimum investment for the institutional shares is $100,000; those shares carry a 1.7% E.R. Here’s the Goodwood website, it’s one of those fancy modern ones that doesn’t facilitate links to individual pages so you’ll have to go and click around a bit. If you’re interested in the strategy, you might choose to read through some of the many articles linked on their homepage.
Launch Alert: Centerstone Investors Fund (CETAX/CENTX)
Centerstone Investors and its sibling Centerstone International (CSIAX/CINTX) launched on May 3, 2016. The Investors fund will be a 60/40-ish global hybrid fund. Their target allocation ranges are 50-80% equity, 20-40% fixed income and 5-20% cash. Up to 20% of the fund might be in high-yield bonds. They anticipate that at least 15% of the total portfolio and at least 30% of their stocks will be non-U.S.
The argument for being excited about Centerstone Investors is pretty straightforward: it’s managed by Abhay Deshpande who worked on the singularly-splendid First Eagle Global (SGENX) fund for 14 years, the last six of them as co-manager. He spent a chunk of that time working alongside the fund’s legendary manager, Jean-Marie Eveillard and eventually oversaw “the vast majority” of First Eagle’s $100 billion. SGENX has a five star rating from Morningstar. Morningstar downgraded the fund from Silver to Bronze as a result of Mr. Deshpande’s departure. Before First Eagle, he was an analyst for Oakmark International and Oakmark International Small Cap and an acquaintance of Ed Studzinski’s. During his callow youth, he was also an analyst for Morningstar.
Here’s the goal: “we hope to address a significant need for investment strategies that effectively seek to manage risk and utilize active reserve management in an effort to preserve value for investors,” says Mr. Deshpande. “It’s our intention to manage Centerstone’s multi-asset strategies in such a way that they can serve as core holdings for patient investors concerned with managing risk.”
Given that he’s running this fund as a near-clone of SGENX, is there any reason to invest here rather than there? I could imagine three:
- Deshpande was seen as the driver of SGENX’s success in the years after Mr. Eveillard’s departure, which is reflected in the Morningstar downgrade when he left. So there’s talent on Centerstone’s side.
- SGENX has $47 billion in assets and is still open, which limits the fund’s investable universe and largely precludes many of the small issues that drove its early success. Centerstone, with $15 million in assets, should be far more maneuverable for far longer.
- First Eagle is in the process of being taken over by two private equity firms after generations as a family-owned business. Centerstone is entirely owned by its founder and employees, so its culture is less at-risk.
The opening expense ratio for “A” shares is 1.36% after waivers and the minimum initial investment is $5000. The “A” shares have a 5% front load but Mr. Deshpande expects that load-waived shares will be widely available. The investment minimum for institutional shares is $100,000 but the e.r. does drop to 1.11%. In lieu of a conventional factsheet, Centerstone provides a thoughtful overview that works through the fund’s strategy and risk-return profile. Centerstone’s homepage is regrettably twitchy but there’s a thoughtful letter from Mr. Deshpande that’s well worth tracking down.
Launch Alert: Matthews Asia Credit Opportunities (MCRDX)
Matthews Asia Credit Opportunities (MCRDX/MICPX) launched on April 29, 2016.
Matthews International Capital Management, LLC, the Investment Advisor to the Matthews Asia Funds, was founded in 1991 by Paul Matthews. Since then they’ve been the only U.S. fund complex devoted to Asia. They have about $21 billion in fund assets and advise18 funds. Of those, two focus on Asian credit markets: Strategic Income (MAINX) and Credit Opportunities.
Both of the credit-oriented funds are managed by Teresa Kong and Satya Patel. Ms. Kong joined Matthews in 2010 after serving as Head of E.M. Investments for BlackRock, then called Barclays Global. She founded their Emerging Markets Fixed Income Group and managed a bunch of portfolios. Her degrees are both from Stanford, she’s fluent in Cantonese and okay at Mandarin. Mr. Patel joined Matthews in 2011 from Concerto Asset Management where he was an investment analyst. He’s also earned degrees from Georgia (B.A.), the London School of Economics (M.A. in accounting and finance) and the University of Chicago (M.B.A. ). The state of his Mandarin is undisclosed.
The fund invests primarily in dollar-denominated Asian credit securities. The fund’s managers want their returns driven by security selection rather than the vagaries of the international currency market. And so “credit” excludes all local currency bonds. At least 80% of the portfolio will be invested in traditional sorts of credit securities – mostly “sub-investment grade securities” – while up to 20% might be placed in convertibles or hybrid securities.
Four things stand out about the fund:
The manager is really good. In our conversations, Ms. Kong has been consistently sharp, clear and thoughtful. Her Strategic Income fund has returned 4.2% annually since inception, in line with its EM Hard Currency Debt peer group, but it has done it with substantially less volatility.
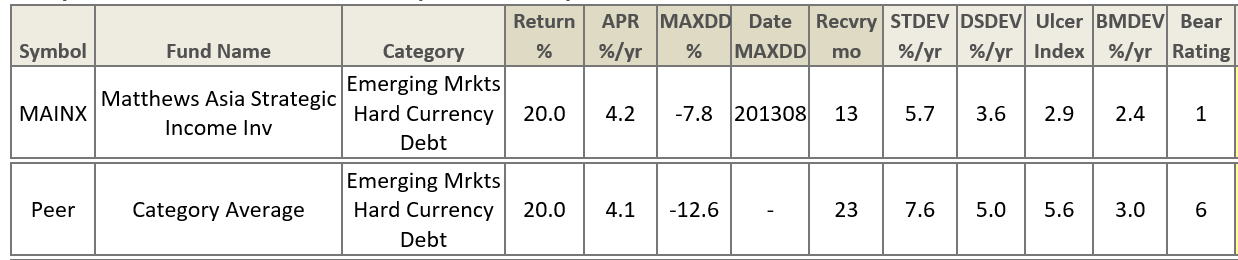
The fund’s targets are reasonable and clearly expressed. “The objective of the strategy,” Ms. Kong reports, “is to deliver 6-9% return with 6-9% volatility over the long term.”
Their opportunity set is substantial and attractive. The Asia credit market is over $600 billion and the sub-investment grade slice which they’ll target is $130 billion. For a variety of reasons, “about a quarter of Asian bonds are not rated by one of the Big Three US rating agencies anymore,” which limits competition for the bonds since many U.S. investors can only invest in rated bonds. That also increases the prospect for mispricing, which adds the Matthews’ advantage. “Over the past 15 years,” they report, “Asia high yield has a cumulative return double that of European, LATAM and US high yield, with less risk than Europe and LATAM.” Here’s the picture of it all:
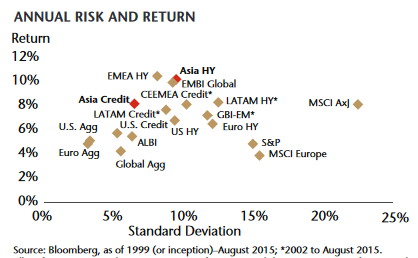
You might draw a line between Asia Credit and Asia HY then assume that the fund will fall on that line rather nearer to Asia HY.
The fund’s returns are independent of the Fed. U.S. investors are rightly concerned about the effect of the Fed’s next couple tightening moves. The correlation between the Asia HY market and the Barclays US Aggregate is only 0.39. Beyond that, the managers have the ability to use U.S. interest rate futures to hedge U.S. interest rate risk.
The opening expense ratio for Investor shares is 1.1% and the minimum initial investment is $2500, reduced to $500 for IRAs. The investment minimum for institutional shares is $3 million but the e.r. does drop to 0.90%. Matthews has provide a thoughtful introduction that works through the fund’s strategy and risk-return profile. The fund’s homepage is understandably thin on content but Matthews, institutionally, is a pretty content-rich site.
Manager Changes
It’s been a singularly quiet month so far, with changes in the management teams at just 32 funds (tabulated below). In truth, none of the additions or subtractions appears to be game-changers.
Because bond fund managers, traditionally, had made relatively modest impacts of their funds’ absolute returns, Manager Changes typically highlights changes in equity and hybrid funds.
| Ticker |
Fund |
Out with the old |
In with the new |
Date |
| ARDWX |
Aberdeen Multi-Manager Alternative Strategies Fund II |
Santa Fe Partners LLC no longer serves as a sub-adviser to the fund, and Henry Davis is no longer listed as a portfolio manager for the fund. |
Ian McDonald, Averell Mortimer, Darren Wolf, Russell Barlow, Vicky Hudson, Peter Wasko and Kevin Lyons remain on the management team |
5/16 |
| ASTYX |
AllianzGI Best Styles International Equity |
No one, but … |
Erik Mulder joined Michael Heldmann and Karsten Niemann in managing the fund. |
5/16 |
| AZDAX |
AllianzGI Global Fundamental Strategy Fund |
Andreas Utermann is no longer listed as a portfolio manager for the fund. |
Neil Dwane joins the management team of Armin Kayser, Karl Happe, Eric Boess, and Steven Berexa. |
5/16 |
| BGEIX |
American Century Global Gold Fund |
William Martin and Lynette Pang are no longer listed as portfolio managers for the fund. |
Yulin Long and Elizabeth Xie are now managing the fund. |
5/16 |
| BDMAX |
BlackRock Global Long/Short Equity Fund |
Paul Ebner is no longer listed as a portfolio manager for the fund. |
Richard Mathieson joins Raffaele Savi and Kevin Franklin in managing the fund. |
5/16 |
| BMSAX |
BlackRock Secured Credit Portfolio |
Carly Wilson and C. Adrian Marshall are gone. |
Mitchell Garfin remains and is joined by James Keenan, Jeff Cucunato, Jose Aguilar and Artur Piasecki. |
5/16 |
| BIALX |
Brown Advisory Global Leaders Fund |
No one, but … |
Bertie Thomson joins Michael Dillon in managing the fund. |
5/16 |
| CSIBX |
Calvert Bond Portfolio |
Matthew Duch will no longer serve as a portfolio manager for the fund. |
Vishal Khanduja and Brian Ellis will remain on the portfolio management team. |
5/16 |
| CGAFX |
Calvert Green Bond Fund |
Matthew Duch will no longer serve as a portfolio manager for the fund. |
Vishal Khanduja and Brian Ellis will remain on the portfolio management team. |
5/16 |
| CYBAX |
Calvert High Yield Bond Fund |
Matthew Duch will no longer serve as a portfolio manager for the fund. |
Vishal Khanduja and Brian Ellis will remain on the portfolio management team and will be joined by Patrick Faul. |
5/16 |
| CFICX |
Calvert Income Fund |
Matthew Duch will no longer serve as a portfolio manager for the fund. |
Vishal Khanduja and Brian Ellis will remain on the portfolio management team. |
5/16 |
| CLDAX |
Calvert Long-Term Income Fund |
Matthew Duch will no longer serve as a portfolio manager for the fund. |
Vishal Khanduja and Brian Ellis will remain on the portfolio management team. |
5/16 |
| CSDAX |
Calvert Short Duration Income Fund |
Matthew Duch will no longer serve as a portfolio manager for the fund. |
Vishal Khanduja and Brian Ellis will remain on the portfolio management team. |
5/16 |
| CULAX |
Calvert Ultra-Short Income Fund |
Matthew Duch will no longer serve as a portfolio manager for the fund. |
Vishal Khanduja and Brian Ellis will remain on the portfolio management team. |
5/16 |
| SDUAX |
Deutsche Ultra Short Duration Bond Fund, soon to be the Deutsche Fixed Income Opportunities Fund |
As of August 31, Eric Meyer will no longer serve as a portfolio manager for the fund. |
John Ryan is joined by Roger Douglas and Rahmila Nadi in managing the fund. |
5/16 |
| DGANX |
Dreyfus Global Infrastructure Fund |
Joshua Kohn is no longer listed as a portfolio manager for the fund. |
Maneesh Chhabria is joined by Theodore Brooks on the management team. |
5/16 |
| ETMGX |
Eaton Vance Tax-Managed Small-Cap Fund |
Nancy Took, lead portfolio manager, announced her intention to retire at the end of October, 2016. |
Michael McLean and J. Griffith Noble will continue with the fund. |
5/16 |
| GSBFX |
Goldman Sachs Income Builder Fund |
Effective immediately, Lale Topcuoglu no longer serves as a portfolio manager for the fund. |
Daniel Lochner, Charles Dane, Colin Bell, Ronald Arons, Andrew Braun and David Beers will continue to manage the fund. |
5/16 |
| HBIAX |
HSBC Global High Income Bond Fund |
Lisa Chua is no longer listed as a portfolio manager for the fund. |
Nishant Upadhyay joins Rick Liu and Jerry Samet in managing the fund. |
5/16 |
| HBYAX |
HSBC Global High Yield Bond Fund |
Lisa Chua is no longer listed as a portfolio manager for the fund. |
Nishant Upadhyay joins Rick Liu and Mary Gottshall Bowers in managing the fund. |
5/16 |
| WASAX |
Ivy Asset Strategy Fund |
Mike Avery will no longer manage the fund, effective June 30, 2016. |
F. Chace Brundige and Cynthia Prince-Fox will continue to co-manager the fund. |
5/16 |
| IVTAX |
Ivy Managed International Opportunities Fund |
Mike Avery will no longer manage the fund, effective June 30, 2016. |
At that time, F. Chace Brundige and Cynthia Prince-Fox will become co-managers of the fund. |
5/16 |
| JMMAX |
JPMorgan Multi-Manager Alternatives Fund |
No one, but … |
P/E Global LLC has been added as an eleventh subadvisor to the fund. |
5/16 |
| SCGLX |
Scout Global Equity Fund |
James Moffett and founding manager James Reed are no longer listed as portfolio managers for the fund. |
Charles John is joined by John Indellicate and Derek Smashey. Somehow the combination of “indelicate” and “smashy” seems like fodder for a bunch of in-jokes. |
5/16 |
| UMBWX |
Scout International Fund |
Michael P. Fogarty no longer serves as a portfolio manager of the fund. |
Michael Stack and Angel Luperico will continue to manage the fund. |
5/16 |
| SEQUX |
Sequoia Fund |
No one, but … |
John Harris, Arman Gokgol-Kline, Trevor Magyar, and David Sheridan join David Poppe as co-managers. |
5/16 |
| TVOAX |
Touchstone Small Cap Value Fund |
DePrince Race & Zollo, Inc. will no longer subadvise the fund. Gregory Ramsby and Randy Renfrow will no longer serve as portfolio managers for the fund. |
Russell Implementation Services will subadvise the fund, with Wayne Holister as portfolio manager, until June 30, 2016. After June 30, LMCG Investments will become the subadvisor to the fund. |
5/16 |
| USIFX |
USAA International Fund |
No one, but … |
Filipe Benzinho is joining Susanne Willumsen, James Shakin, Craig Scholl, Paul Moghtader, Ciprian Marin, Taras Ivanenko, Andrew Corry, Daniel Ling and Marcus Smith to manage the fund. |
5/16 |
| HEMZX |
Virtus Emerging Markets Opportunities Fund |
No one, but … |
Brian Bandsma and Jin Zhang join Matthew Benkendorf in managing the fund |
5/16 |
| JVIAX |
Virtus Foreign Opportunities Fund |
No one, but … |
Daniel Kranson and David Souccar will join Matthew Benkendorf in managing the fund |
5/16 |
| NWWOX |
Virtus Global Opportunities Fund |
No one, but … |
Ramiz Chelat will join Matthew Benkendorf in managing the fund |
5/16 |
| UNASX |
Waddell & Reed Advisors Asset Strategy Fund |
Mike Avery will no longer manage the fund, effective June 30, 2016. |
F. Chace Brundige and Cynthia Prince-Fox will continue to co-manager the fund. |
5/16 |
A Road Trip to Seafarer
Ben Peters, a CFP and chief compliance officer for Burton Enright Welch in the Bay Area, reported on his field trip to Seafarer in his Q1 shareholder letter. Ben had first learned of Seafarer through the Observer and was kind enough to share these reflections on his trip to Larkspur.
The more we communicated with Seafarer the more confidence we gained. Seafarer’s managers are undeniably, overwhelmingly smart. They have a deep understanding of EM investing and are serious and forthright about the risks. And as with most upper echelon managers, they leave you so impressed as to be uneasy: your impulse is to hand over your last dime.
Our visit to Seafarer’s Larkspur headquarters hammered home our conviction. Many fund managers want to be seen as the masters of the universe. Their offices usually have the downtown location, sweeping views, and fancy artwork to match.
Seafarer’s HQ is refreshing. Seafarer resides in a 3-story, non-descript office park in a quaint Bay-side town. There was no receptionist, flat screen TVs, or abstract paintings … the grand tour didn’t require any walking because the whole office is visible from the middle of the room …
The humble setting is symbolic. Seafarer is one of the lowest fee active emerging markets managers available even though it is relatively small.
Updates
Execution postponed: back in February 2016, the Board of $95 million ASTON Small Cap Fund (ATASX) moved to appoint GW&K Investment Management, LLC as subadviser to the fund in anticipation merging it into the year-old, $1.5 million AMG GW&K Small Cap Growth Fund (GWGIX). In May the board reversed course on the merger, though it still hopes to have GW&K run the fund permanently.
With the same enthusiasm that Republican leaders bring to their belated embrace of Donald Trump, mutual fund advisers are buying active/smart/tilted ETFs to stanch the bleeding. Garth Freisen, a principal at III Capital Management, reports:
[Contining movement of assets from funds to ETFs] helps explain recent moves by traditional asset management companies to acquire ETF-focused firms specializing in the construction of low-cost, active indexing portfolios:
In addition, he notes that Goldman Sachs and Fido are launching their own quant-driven ETFs (“Active Management Is Worth It When The Price Is Right,” 5/23/2016).
Briefly Noted . . .
Boston Partners Emerging Markets Long/Short Fund (BDMAX) has announced that “the Adviser expects that the Fund’s long positions will not exceed approximately 50% of the Fund’s net assets with an average of 30% to 70% net long.” Heretofore the extent of the fund’s market exposure wasn’t constrained in the prospectus.
Stonebridge Capital Management has announced they no longer intend to advise the Stonebridge Small-Cap Growth Fund (SBSGX). “The Board is considering alternative plans with respect to the Fund, which may include closure and liquidation of the Fund.” Here’s what the Board has to wrestle with: an utterly dismal track record that will haunt any future manager, $12 million in assets and expenses north of 2.1% per year. One of the two managers has been with the fund for 16 years and still has not invested a penny in it. The only bright side is that the fund has a substantial embedded tax loss (Morningstar estimates about 17%) so liquidation would partially offset taxable gains elsewhere in an investor’s portfolio.
From the file labeled “I learn something new every month.” Touchstone Small Cap Value Fund (TVOAX) is switching managers. On May 20, 2016, DePrince, Race & Zollo, Inc. are out. On June 30, 2016, LMCG steps in. And what happens during the six week interregnum? Russell happens. Russell Implementation Services provides caretaker management in the window between the departure of one manager or team and the arrival of the next. Touchstone’s SEC filing reports:
Russell will make investment decisions for the Fund and also ensure compliance with the Fund’s investment policies and guidelines. Russell has been providing transition management services to clients since 1992. Russell has transitioned nearly $2.3 trillion in assets for clients in over 2,300 transition events in the last three calendar years. As of December 2015, Russell was managing 17 mandates with $1.7 billion in assets across a broad range of asset classes.
That implies $800 billion/year in assets temporarily managed by a caretaker. Who knew?
SMALL WINS FOR INVESTORS
All eight share classes of AB Small Cap Growth (QUASX) re-opened to new investors on June 1, 2016.
Effective June 3, 2016, Dreyfus International Stock Fund (DISAX) will be re-opened to new investors.
Touchstone Sands Capital Select Growth Fund (TSNAX) closed to new accounts, with certain exceptions, on April 8, 2013. With due consideration, the Advisor has determined to re-open the Fund for sales to investors making purchases in an account or relationship related to a fee-based, advisory platform.
CLOSINGS (and related inconveniences)
Undiscovered Managers Behavioral Value Fund (UBVAX) appears to be closing a bit more tightly. The fund is currently closed to new investors which eight classes of exceptions. As of June 27, 2016, the number of exceptions decreases to six and the wording on some of those six seems a bit more restrictive. It appears from the filing that the two lost exceptions will be:
- Approved brokerage platforms where the Fund is on a recommended list compiled by a Financial Intermediary’s research department as of the Closing Date may continue to utilize the Fund for new and existing accounts.
- Approved Section 529 college savings plans utilizing the Fund as of the Closing Date may do so for new and existing accounts.
OLD WINE, NEW BOTTLES
On July 1, 2016, BlackRock Managed Volatility Portfolio (PBAIX) will be renamed BlackRock Tactical Opportunities Fund. The revised statement of investment strategy doesn’t mention volatility but, instead, talks about “an appropriate return-to-risk trade-off” and warns of the prospect of frequent trading.
Also on July 1, BlackRock Secured Credit Portfolio (BMSAX) gets renamed BlackRock Credit Strategies Income Fund. Up until now it has invested, quite successfully, in “secured instruments, including bank loans and bonds, issued primarily, but not exclusively, by below investment grade issuers.” Going forward it will have one of those “invest in any danged thing we want to” strategies. Pursuant thereunto, two of the three current managers get sacked and four new managers get added. After the dust settles, four of the fund’s five managers will bear the rank “Managing Director.” The fifth, poor Artur Piasecki, is merely “Director.”
That same exhausting day, BlackRock Managed Volatility Portfolio (PCBAX) becomes BlackRock Tactical Opportunities Fund. The new investment strategy highlights frequent trading and the use of derivatives. It also abandons the old 50% global stocks / 50% global bonds benchmark.
As of August 1, 2016, Deutsche Ultra-Short Duration Fund (SDUAX) will be renamed Deutsche Fixed Income Opportunities Fund. Following the fund’s name change, its amorphous investment goal (“current income consistent with total return”) remains but its strategy changes from allowing up to 50% non-investment grade plus up to 20% cash to 30% non-investment grade with no reference to cash. Its principal benchmark becomes a 3-month LIBOR index.
Effective June 14, 2016, “Fidelity” will replace “Spartan” in the fund name for each Spartan Index Fund a/k/a each Fidelity Index fund.
On July 5, 2016, Victory CEMP Multi-Asset Growth Fund (LTGCX) will be renamed the Victory CEMP Global High Dividend Defensive Fund and its investment objective will change to reflect a dividend income component. This will be the fund’s second name in a year; up until November it was Compass EMP Multi-Asset Growth Fund. It’s a fund of Victory CEMP’s volatility-weighted ETFs. At 2.12% in expenses for 1.46% in long-term annual returns, one might suspect that it’s overpriced.
The sub-adviser to SilverPepper Merger Arbitrage Fund (SPABX/SPAIX) has changed its name from Brown Trout Management, LLC to Chicago Capital Management, LLC.
OFF TO THE DUSTBIN OF HISTORY
AAM/HIMCO Unconstrained Bond Fund (AHUAX) will undergo “termination, liquidation and dissolution” on June 28, 2016.
Eaton Vance Richard Bernstein Market Opportunities Fund (ERMAX) has closed and will liquidate on June 29, 2016. This is another “well, we gave it almost two years (!) before pulling the plug” fund.
Eaton Vance Currency Income Advantage Fund (ECIAX) will return its $1 million in assets to investors and vanish, after almost three years of operation, on June 29, 2016.
Goldman Sachs Financial Square Tax-Exempt California Fund (ITCXX) and Goldman Sachs Financial Square Tax-Exempt New York Fund (IYAXX) were slated for liquidation on August 31, 2016 but the Board and advisor got twitchy. Each fund now faces execution on June 10, 2016.
Harbor Funds’ Board of Trustees has determined to liquidate and dissolve the Harbor Unconstrained Bond Fund (HRUBX), which is roughly but not perfectly a clone of PIMCO Unconstrained Bond (PUBDX). The liquidation of the Fund is expected to occur on July 29, 2016.
Little Harbor Multi-Strategy Composite Fund (LHMSX), which you didn’t know existed, now no longer exists.
The Board of Trustees of Northern Funds has decreed that Multi-Manager Large Cap Fund (NMMLX), Multi-Manager Small Cap Fund (NMMSX), and Multi-Manager Mid Cap Fund (NMMCX) be liquidated on July 22, 2016. About that “multi-manager” thing: each of the funds is run by same two Northern Trust managers. They haven’t been noticeably “multi” since about 2012. They have about $900 million in assets between them with the smallest, Small Cap, posted the best relative returns.
Oppenheimer Commodity Strategy Total Return Fund (QRAAX) will liquidate on July 15, 2016. Why, you ask? Uhhhh …
The Board of Trustees of The Purisima Funds has determined that it is advisable “to liquidate, dissolve and terminate the legal existence” of The Purisima Total Return Fund (PURIX) and The Purisima All-Purpose Fund (PURLX). Their departure is notable primarily because of their manager, Kenneth Fisher, America’s largest investment advisor and source of, oh, I don’t know, one-third of all of the pop-up ads on the internet.
As of May 9, PURLX had $46,374 and PURIX has $257 million. Whether you judge PURIX as “unimpressive” or “almost freakishly bad” depends on whether you ask Lipper or Morningstar. Lipper benchmarks it against the Flexible Portfolio group, which it trails only modestly since inception. Morningstar categorizes it as domestic large-blend, and it trails the vast majority of such funds over every period from one-year to fifteen. In reality, Lipper is probably a truer fit. The fund is about 65% US large caps, 20% international large caps and 10% “other,” which includes two exchange-traded notes in its top 10 holdings. Regardless of the rater, the funds’ record suggests that Mr. Fisher – son of Phil Fisher (author of Common Stocks and Uncommon Profits, 1958, and “one of the great investors of all time,” according to Morningstar) – seems better suited to marketing than managing.
The month’s oddest closure announcement: “On May 6, 2016, at the recommendation of SF Advisors, LLC, the investment adviser to the Trust, the Trust’s Board of Trustees approved the closing and subsequent liquidation of the Funds. Accordingly, the Funds are expected to cease operations, liquidate any assets, and distribute the liquidation proceeds to shareholders of record on June 6, 2016.” Uhhh … no such funds were ever launched. This raises the same philosophical question as the speculation that near black holes, particles could be destroyed the moment before they’re created. Can funds that have never commenced operations cease them?
Pending shareholder approval (which is a lot like saying “pending the rising of the sun”), Stratus Government Securities (STGSX) and Stratus Growth (STWAX) will liquidate on June 10, 2016. How much suspense is there about the outcome of the vote? Well, the vote is Tuesday, June 7and liquidation is scheduled (tentatively, of course) for Friday of that same week.
Thomson Horstmann & Bryant Small Cap Value Fund (THBSX) will liquidate on June 24, 2016.
Effective May 6, 2016, Virtus Alternative Income Solution Fund, Virtus Alternative Inflation Solution Fund and Virtus Alternative Total Solution Fund were liquidated. Lest that phrase confuse us, the adviser clarifies: “The funds have ceased to exist.”
In Closing . . .
If you own an Android smart phone, you should go download and use the Ampere app. As you’re reading this, Chip and I will be in Scotland, likely in the vicinity of Inverness. One of the great annoyances of modern travel is the phenomenal rate at which phones drain their batteries and the subsequent need to search for charging options in airports and rail stations. What I didn’t know is how much of a different your charging cable makes in how much time it will take to regain a reasonable charge. Ampere is an app which measures, among other useful things, how quickly your phone is recharging.
It turns out that the quality of charging cable makes a huge difference. Below are two screencaps. I started with same charger and the phone then worked my way through a set of four different charging cables. The charge rates varied greatly from cable to cable.
 In the instance above, it would take nearly four times as long to recharge my phone using the cable on the left. Every cable I tested produced a different charge rate, from a low of 300 mA to a high of 1200 mA.
In the instance above, it would take nearly four times as long to recharge my phone using the cable on the left. Every cable I tested produced a different charge rate, from a low of 300 mA to a high of 1200 mA.
My suggestion for travelers: download Ampere, use it to identify your best-performing cables then ditch the rest, and remember to switch to “airplane mode” for faster charging.
You’re welcome.
As ever, we want to take a moment to offer a sincere xei xei to all the folks who’ve supported us this month in thought, word and deed. To our faithful friends, Deb (still hoping to make it to Albuquerque) and Greg, thank you. Thanks, too, to Andrew, William, Robert, and Jason (all the way from Surrey, UK). We appreciate your generosity.
We’ll look for you at Morningstar! We’re hopeful of catching up with a number of folks at the conference including folks from Centerstone, Evermore, FPA, Intrepid, Matthews and Seafarer … with maybe just a hint of Poplar Forest, a glimpse of Polaris and the teasing possibility of ride down Queens Road. We’ll post synopses to our discussion board each day and we’ll offer some more-refined prose when you come by for our July issue.

Remember, as you’re reading this, Chip and I are chillin’ in Scotland. If you’ve got questions or concerns about this month’s issue and you’d like them addressed before my return on June 7th, please drop a note to our colleague and data wizard, Charles Boccadoro. He’s got the keys to the back door.
As ever,


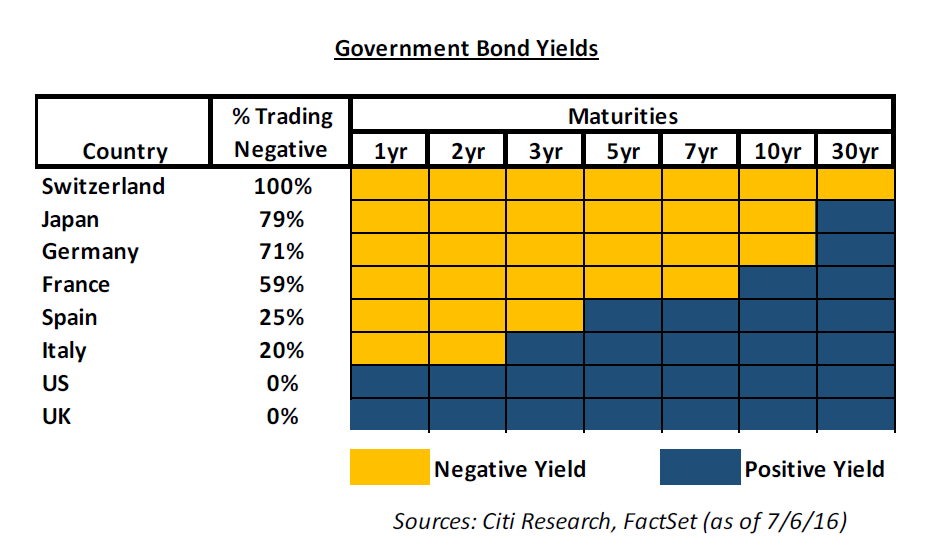




 This is another misconception about not being fully invested. If you have large discounts you can still generate attractive returns without being invested in what I call “fillers.” Just like with processed food, investment fillers are often there just to fill up the portfolio, but often provide little value and in some cases can be hazardous to your health! Open the hood of most fully invested small cap funds and you’ll find plenty of fillers these days, especially in sectors like consumer and health care. The stocks are clearly overvalued but managers think because they’re in lower risk sectors they won’t get destroyed. Good example WD-40 (WDFC) at 30x earnings! Great company but you could lose half your capital if it ever reverted to a more justifiable 7% free cash flow yield.
This is another misconception about not being fully invested. If you have large discounts you can still generate attractive returns without being invested in what I call “fillers.” Just like with processed food, investment fillers are often there just to fill up the portfolio, but often provide little value and in some cases can be hazardous to your health! Open the hood of most fully invested small cap funds and you’ll find plenty of fillers these days, especially in sectors like consumer and health care. The stocks are clearly overvalued but managers think because they’re in lower risk sectors they won’t get destroyed. Good example WD-40 (WDFC) at 30x earnings! Great company but you could lose half your capital if it ever reverted to a more justifiable 7% free cash flow yield. 



 We were delighted to announce last month that Bob Cochran joined MFO’s Board of Directors. Bob is the lead portfolio manager, Chief Compliance Officer, and a principal of PDS Planning in Columbus, Ohio, and a long-time contributor to the FundAlarm and MFO discussion boards.
We were delighted to announce last month that Bob Cochran joined MFO’s Board of Directors. Bob is the lead portfolio manager, Chief Compliance Officer, and a principal of PDS Planning in Columbus, Ohio, and a long-time contributor to the FundAlarm and MFO discussion boards. A family friend recently asked me to look at his mutual fund investments. He contributes to these investments periodically through his colleague, a
A family friend recently asked me to look at his mutual fund investments. He contributes to these investments periodically through his colleague, a 









 Sam Lee and
Sam Lee and 


 What’s the Trapezoid story? Leigh Walzer has over 25 years of experience in the investment management industry as a portfolio manager and investment analyst. He’s worked with and for some frighteningly good folks. He holds an A.B. in Statistics from Princeton University and an M.B.A. from Harvard University. Leigh is the CEO and founder of Trapezoid, LLC, as well as the creator of the Orthogonal Attribution Engine. The Orthogonal Attribution Engine isolates the skill delivered by fund managers in excess of what is available through investable passive alternatives and other indices. The system aspires to, and already shows encouraging signs of, a fair degree of predictive validity.
What’s the Trapezoid story? Leigh Walzer has over 25 years of experience in the investment management industry as a portfolio manager and investment analyst. He’s worked with and for some frighteningly good folks. He holds an A.B. in Statistics from Princeton University and an M.B.A. from Harvard University. Leigh is the CEO and founder of Trapezoid, LLC, as well as the creator of the Orthogonal Attribution Engine. The Orthogonal Attribution Engine isolates the skill delivered by fund managers in excess of what is available through investable passive alternatives and other indices. The system aspires to, and already shows encouraging signs of, a fair degree of predictive validity. Since the number of funds we can cover in-depth is smaller than the number of funds worthy of in-depth coverage, we’ve decided to offer one or two managers each month the opportunity to make a 200 word pitch to you. That’s about the number of words a slightly-manic elevator companion could share in a minute and a half. In each case, I’ve promised to offer a quick capsule of the fund and a link back to the fund’s site. Other than that, they’ve got 200 words and precisely as much of your time and attention as you’re willing to share. These aren’t endorsements; they’re opportunities to learn more.
Since the number of funds we can cover in-depth is smaller than the number of funds worthy of in-depth coverage, we’ve decided to offer one or two managers each month the opportunity to make a 200 word pitch to you. That’s about the number of words a slightly-manic elevator companion could share in a minute and a half. In each case, I’ve promised to offer a quick capsule of the fund and a link back to the fund’s site. Other than that, they’ve got 200 words and precisely as much of your time and attention as you’re willing to share. These aren’t endorsements; they’re opportunities to learn more. Mr. Thibodeaux founded Goodwood in 2012 after a nine year stint with Maple Leaf LP, a hedge fund that received a “seed” investment from Julian Robertson’s famous Tiger Management, leading to the informal designation of Maple Leaf as a “Tiger Seed.” Maple Leaf, like Goodwood, was a fundamental, value-biased long/short fund. Mr. Pesses joined Goodwood about a year later. Like Mr. Thibodeaux he was at Maple Leaf, served as a Partner and Senior Equity Research Analyst from 2007 to 2012. Their first products at Goodwood were long/short separate accounts which have done remarkably well. From January 1, 2008 – March 31, 2016, their long/short composite returned 8.6% annually after fees. The average Morningstar peer made 0.7%. That seems like a hopeful sign since those same strategies should help buoy GAMAX.
Mr. Thibodeaux founded Goodwood in 2012 after a nine year stint with Maple Leaf LP, a hedge fund that received a “seed” investment from Julian Robertson’s famous Tiger Management, leading to the informal designation of Maple Leaf as a “Tiger Seed.” Maple Leaf, like Goodwood, was a fundamental, value-biased long/short fund. Mr. Pesses joined Goodwood about a year later. Like Mr. Thibodeaux he was at Maple Leaf, served as a Partner and Senior Equity Research Analyst from 2007 to 2012. Their first products at Goodwood were long/short separate accounts which have done remarkably well. From January 1, 2008 – March 31, 2016, their long/short composite returned 8.6% annually after fees. The average Morningstar peer made 0.7%. That seems like a hopeful sign since those same strategies should help buoy GAMAX.



 In the instance above, it would take nearly four times as long to recharge my phone using the cable on the left. Every cable I tested produced a different charge rate, from a low of 300 mA to a high of 1200 mA.
In the instance above, it would take nearly four times as long to recharge my phone using the cable on the left. Every cable I tested produced a different charge rate, from a low of 300 mA to a high of 1200 mA.


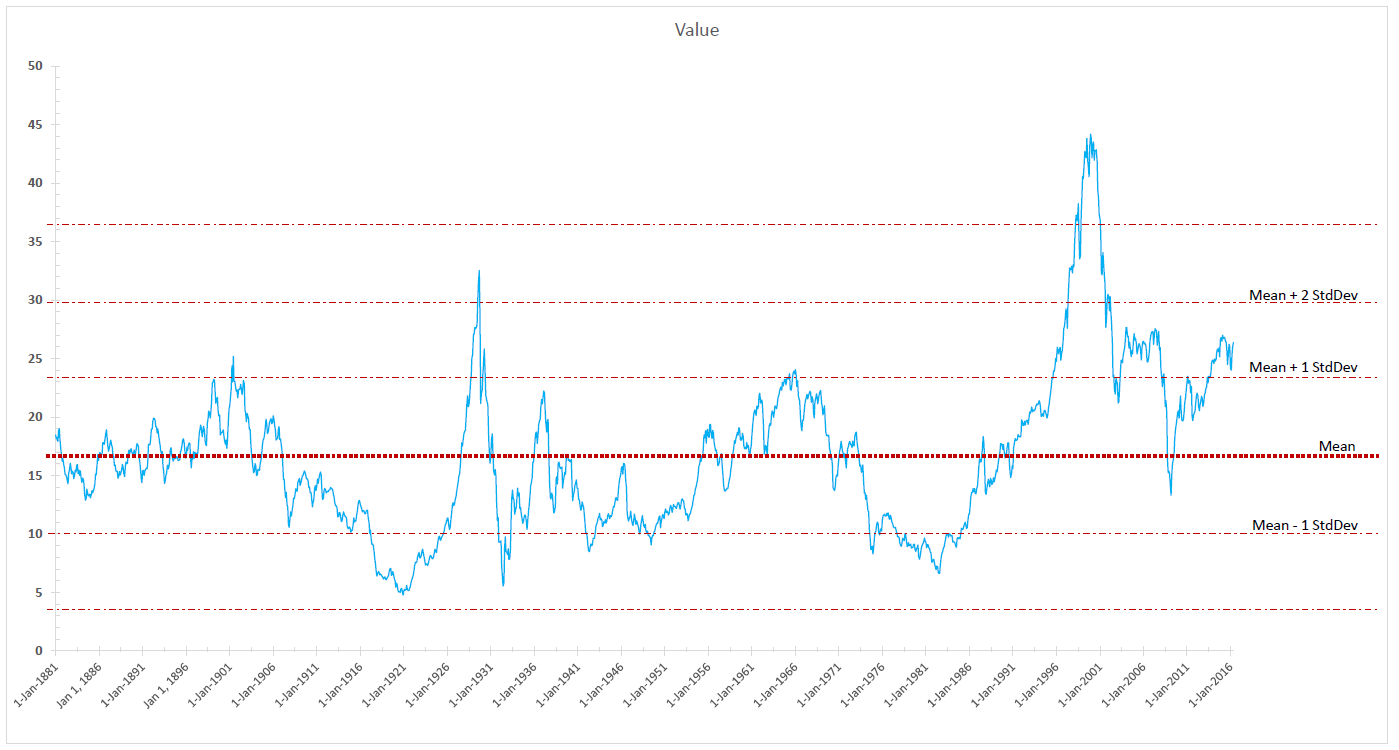
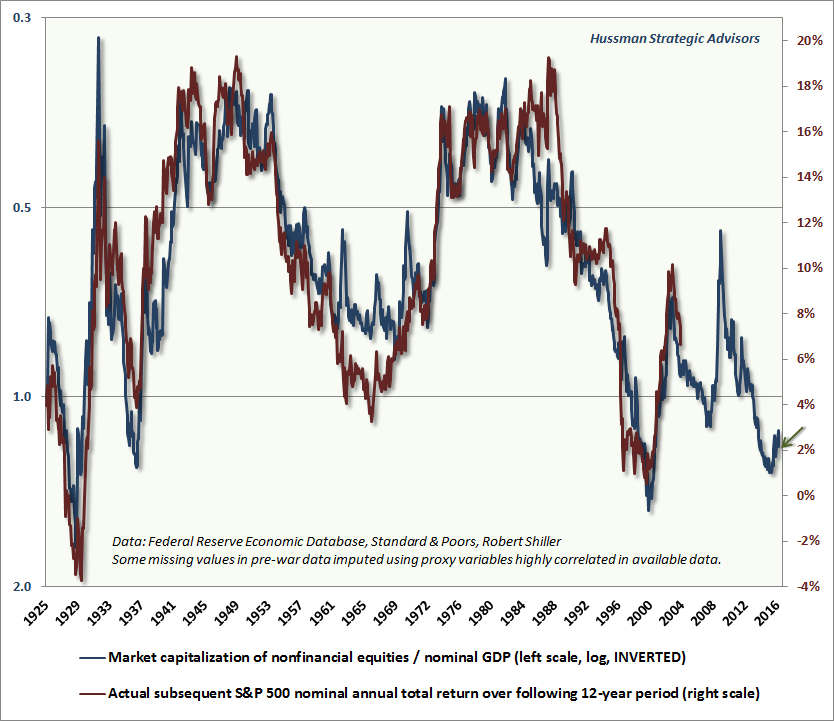
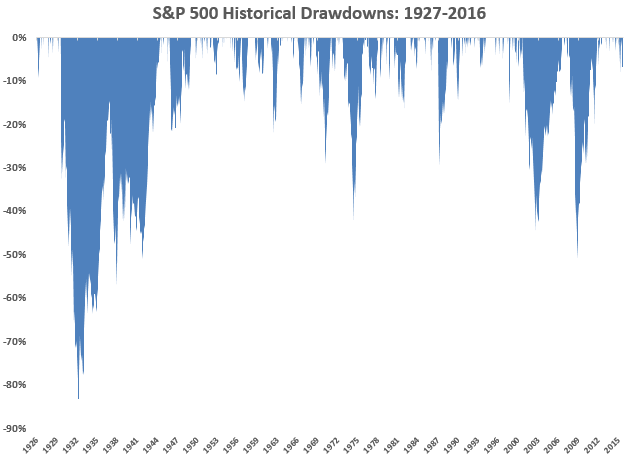 I think of this as “the icicle chart.” Ben Carlson, one of the Ritholtz managers, wrote a really thoughtful essay, rich in visuals, in April. He posted it on his Wealth of Commonsense blog under the name “
I think of this as “the icicle chart.” Ben Carlson, one of the Ritholtz managers, wrote a really thoughtful essay, rich in visuals, in April. He posted it on his Wealth of Commonsense blog under the name “

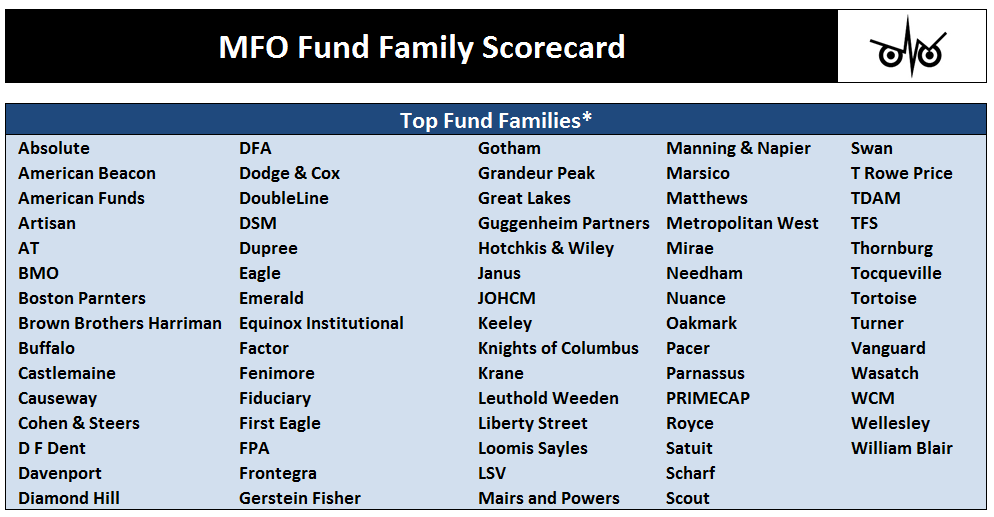

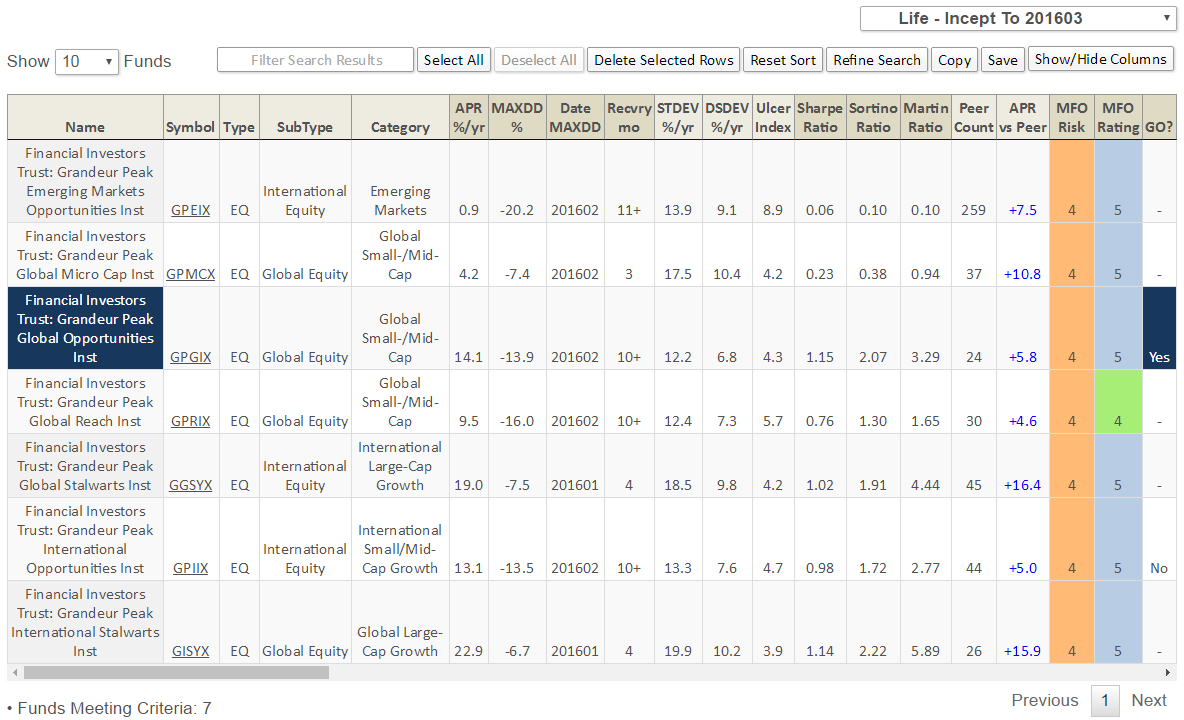
 One should forgive one’s enemies, but not before they are hanged.
One should forgive one’s enemies, but not before they are hanged. The best performing asset class in this quarter has been – gold. Actually the best performing asset class has been the gold miners, with silver not too far behind. We have had gold with a mid-teen’s total return. And depending on which previous metals vehicle you have invested in, you may have seen as much as a 60%+ total return (looking at the germane Vanguard fund). Probably the second best area generically has been energy, but again, you had to choose your spots, and also distinguish between levered and unlevered investments, as well as proven reserves versus hopes and prayers.
The best performing asset class in this quarter has been – gold. Actually the best performing asset class has been the gold miners, with silver not too far behind. We have had gold with a mid-teen’s total return. And depending on which previous metals vehicle you have invested in, you may have seen as much as a 60%+ total return (looking at the germane Vanguard fund). Probably the second best area generically has been energy, but again, you had to choose your spots, and also distinguish between levered and unlevered investments, as well as proven reserves versus hopes and prayers.
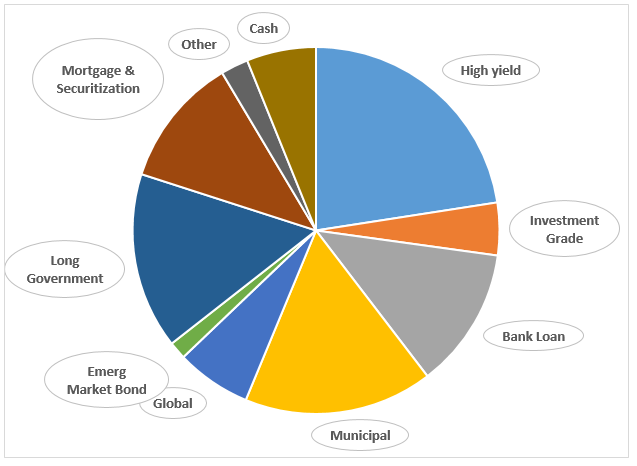
 April has come to a close and another Fed meeting has passed without a rate rise. At the same time, markets have continued to rally with the equity market, as measured by the S&P 500 Index, gaining another 0.39% in April, bringing the 3-month total return to 7.05%. Bonds also rallied as the Barclays U.S. Aggregated Bond Index gained 0.38% in April, and 2.02% over the past 3-months. Not bad for traditional asset classes.
April has come to a close and another Fed meeting has passed without a rate rise. At the same time, markets have continued to rally with the equity market, as measured by the S&P 500 Index, gaining another 0.39% in April, bringing the 3-month total return to 7.05%. Bonds also rallied as the Barclays U.S. Aggregated Bond Index gained 0.38% in April, and 2.02% over the past 3-months. Not bad for traditional asset classes.
 The
The  We’ve been following Bob’s posts for the past 10 or 15 years where, as BobC, he’s been one of the most respected, thoughtful and generous contributors to our discussion board and the FundAlarm’s before that. The Observer aspires to serve two communities: the small, independent managers who are willing to stray from the herd and who are passionate about what they do (rather than about how much they can make) and the individual investors who deserve better than the timid, marketing-driven pap they’re so often fed. As we begin our sixth year, we thought that finding someone who is both active in the industry and broad in mind and spirit would allow us to serve folks better.
We’ve been following Bob’s posts for the past 10 or 15 years where, as BobC, he’s been one of the most respected, thoughtful and generous contributors to our discussion board and the FundAlarm’s before that. The Observer aspires to serve two communities: the small, independent managers who are willing to stray from the herd and who are passionate about what they do (rather than about how much they can make) and the individual investors who deserve better than the timid, marketing-driven pap they’re so often fed. As we begin our sixth year, we thought that finding someone who is both active in the industry and broad in mind and spirit would allow us to serve folks better.
 A queer and wonderful ride. Bernie Klawans – an aerospace engineer – ran it for decades, from 1971-2011, likely out of his garage. One-page website, no 800-number, no reports or newsletters or commentaries. Also an incredibly blurry logo that might well have been run through a mimeograph machine once or twice. Mr. Klawans brought on a successor when he was in his late 80s, worked with him for a couple years, retired in April and passed away within about six months. Then his chosen successor, Craig Arnholt, died unexpectedly within a year. The Board of Trustees actually managed the fund for six months (quite successful – they beat both their LV peers and the S&P) before finding a manager who’d run the fund for a pittance. The new guy was doing fine then … kapow! He lost 22% in September and October of 2014, when the rest of the market was essentially flat. That was a combination of a big stake in Fannie and Freddie – adverse court ruling cut their market value by half in a month – and energy exposure. He’s been staggering toward the cliff ever since.
A queer and wonderful ride. Bernie Klawans – an aerospace engineer – ran it for decades, from 1971-2011, likely out of his garage. One-page website, no 800-number, no reports or newsletters or commentaries. Also an incredibly blurry logo that might well have been run through a mimeograph machine once or twice. Mr. Klawans brought on a successor when he was in his late 80s, worked with him for a couple years, retired in April and passed away within about six months. Then his chosen successor, Craig Arnholt, died unexpectedly within a year. The Board of Trustees actually managed the fund for six months (quite successful – they beat both their LV peers and the S&P) before finding a manager who’d run the fund for a pittance. The new guy was doing fine then … kapow! He lost 22% in September and October of 2014, when the rest of the market was essentially flat. That was a combination of a big stake in Fannie and Freddie – adverse court ruling cut their market value by half in a month – and energy exposure. He’s been staggering toward the cliff ever since.



 Here’s the brief version of recent events:
Here’s the brief version of recent events:
 “Advertising is the modern substitute for argument; its function is to make the worse appear the better.”
“Advertising is the modern substitute for argument; its function is to make the worse appear the better.”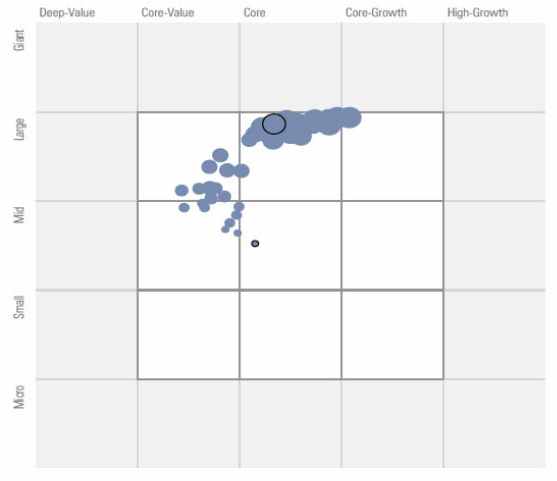
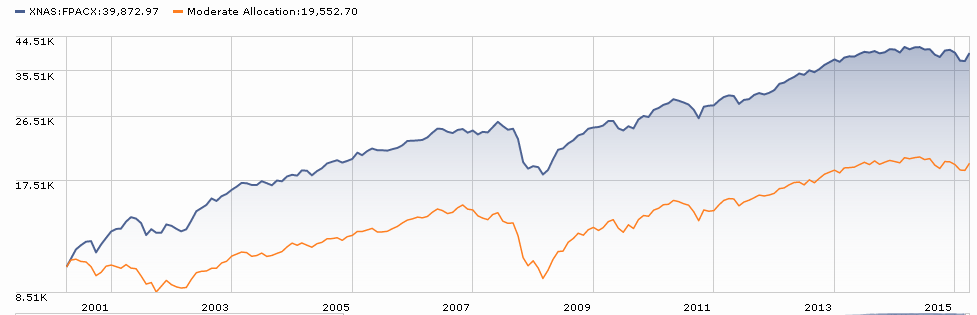
 Last month, David
Last month, David