Last week the Wall Street Journal published a story slamming Morningstar (“The Morningstar Mirage”), arguing the firm’s star ratings were virtually useless as predictors of performance. The Journal showed that both five-star funds and one-star funds regressed toward the mean over time. But it overstated its case because the funds didn’t regress all the way: five-star funds ended up doing much better than one star funds three, five and even ten years on. The pattern is striking: higher stars predicted higher future star ratings over all the Continue reading →
Category Archives: Mutual Fund Commentary
Launch Alert: Northern Funds U.S. Quality ESG Fund (NUESX)
On October 02, 2017, Northern Trust Asset Management launched Northern U.S. Quality ESG Fund. It strikes me as a particularly interesting fund which combines two separately valuable commitments in a single low-cost platform.
The case for investing in high quality companies is almost definitional. No sensible person buys low quality anything when, for about the same price, they can get a high quality alternative. The key is having a viable definition of “quality” and a clear sense of how much of a premium a quality company might charge. Northern has done a Continue reading →
Launch Alert: American Beacon Shapiro Equity Opportunities Fund (SHXPX) and American Beacon Shapiro SMID Cap Equity Fund (SHDPX) Investor Class
On September 12, 2017, American Beacon launched two funds using Shapiro Capital Management, an institutional, value-oriented firm, as its sub-advisor. This alert focuses on the Equity Opportunities Fund, its all-cap value product. The SMID fund applies the same strategy in the mid cap space.
Established in 1990, Shapiro is known for deep fundamental research and concentrated portfolios. As of 2017, its managers — Samuel Shapiro, Michael McCarthy, Louis Shapiro, and Harry Shapiro — have 141 years of collective investment experience and head a team without turnover for 27 years, a continuity that confirms their ability to outperform their peers Continue reading →
Predicting 2017’s Capital Gain Distributions
Warren Buffet once quipped: “Forecasts usually tell us more of the forecaster than of the forecast.” This is one reason I hesitate to forecast what we might see this year for capital gains distributions from mutual funds. Nonetheless, I’ll reveal a little about myself and will make an educated guess.
Looking Back
I don’t track absolute dollars of fund distributions, but for the Continue reading →
Fuller & Thaler Behavioral Small-Cap Equity (FTHNX), November 2017
Objective and strategy
FTHNX pursues long-term capital appreciation. The managers invest in a diversified US small cap equity portfolio. The managers seek out stocks where other investors are likely to make behavioral mistakes. If they conclude that an investor mistake is likely and the company has solid fundamentals, the portfolio managers generally buy the stock. They sell when the misbehavior has run its course, which tends to lead to a high turnover portfolio. That said, they do not automatically buy or sell based on a single security’s characteristics; they impose a risk management overlay that helps control exposures to sectors, size, and other characteristics. The fund currently holds Continue reading →
Briefly Noted …
The $12 million Global Strategic Income Fund (VEEEX) has a couple upgrades planned for the next month. “These changes included the appointment of a new adviser and sub-adviser to the Fund; revisions to the Fund’s investment objective; revisions to the Fund’s investment strategy; a change to the name of the Fund; changes to certain service provider agreements; and the addition of new share classes as well as the conversion of Class C Shares into Class A Shares.” Nominally the current version of the fund had a global, all-asset strategy; practically, it was a global equity fund with a 30-day SEC yield of 0.00%. The new fund will be Continue reading →
October 1, 2017
Dear friends,
It’s finally fall, my favorite season of the year. The heat abates, the garden quiets, the apples ripen. Chip and I will soon venture north to Wisconsin for leaf peeking and visits to orchards. You’d be amazed at the variety of flavors found in apples; there are about 200 varieties grown in the US, with the average grocery store stocking just a half dozen (including that flavorless favorite, Red Delicious). You’ve still got time to do better. In the Midwest, anyway, October is the month for Haralson and King David, Golden Russet and Creston, Enterprise and Voyager. Heck, you might find a few Lura Red or Wolf Rivers left, if you’re Continue reading →
The Story without a title
In journalism, the headlines you read are generally an afterthought, crafted by a headline writer – not the story’s author – to fit the available space and grab attention. For us, story titles function differently: they’re “framing devices,” which we write early and which help us figure out how to explain the entire story.
This is “the story without a title,” because I’ve got Continue reading →
The wise reader’s two most important words. “Uh, no.”
Having concluded that we’re not willing to pay for the services of professional journalists and editors, we’re increasingly getting what we paid for: stories written by robots, amateurs, dilettantes and self-interested parties posing as journalists. Here’s my monthly roundup of stories that made my head hurt, plus one opening note on Continue reading →
Launch Alert: Artisan Global Discovery Fund (APFDX)
On August 21, 2017, Artisan Partners launched a near-clone of their very successful Artisan Global Opportunities Fund (ARTRX). Artisan organizes their managers into eight autonomous teams, with each team supported by an analyst corps and responsible for one or more funds. Global Discovery will be managed by the Growth team, which is also responsible for Global Opportunities, Mid Cap (ARTMX) and Continue reading →
Briefly noted
I’ve lost track of many of the funds that we profiled back in the FundAlarm days. This month one surfaced, Capital Advisors Growth Fund (CIAOX), and it was awfully nice to see that (a) they’re still providing exactly what they promised long ago – cautious equity exposure with no glitz – and (b) we were right, nine years ago, in assessing it as an exceptionally solid citizen for equity investors interested in sleeping well at night.
Briefly the number of mutual funds liquidating matched the number of ETFs liquidating, then September 29th came around and Continue reading →
September 1, 2017
Dear friends,
Our thoughts and prayers go out to the people in Houston and the surrounding Gulf Coast. The receding flood waters end one phase of the disaster and exposes the next.

Several mutual fund families have headquarters, or significant presence, in the Houston area. Those include Ascendant, Bridgeway, Crossmark Global (formerly Capstone), Invesco, Kerns Capital, Salient, Sarofim and Continue reading →
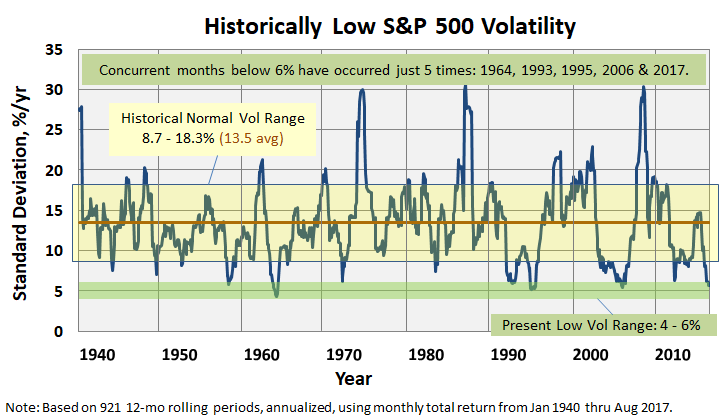
Historically Low Volatility
“Experts often possess more data than judgment.”
Colin Powell
The S&P 500 closed August yesterday with an annualized standard deviation below 6%. Typically, since about 1940, which marked the end of The Great Depression, annualized standard deviation runs between 13 and 14%. It was the second consecutive month to break the 6% threshold; in fact, only five times has volatility remained this low for consecutive months: 1964, 1993, 1995, 2006 and 2017.
The Land of the Investment Dervishes
America’s best-selling poet is a Muslim theologian who died 750 years ago. Jalal ad-Din Muhammad Rumi (alternately, Mevlana Jalaluddin Rumi) is not only namesake to Beyonce’s new child, but also founder of Sufism, a branch of Islam. Sufism is both mystical and ecstatic. Rumi was given to a whirling dance that reflects the boundless joy and energy that overwhelms a believer; it helped believers express and achieve ecstasy, was codified by his son and practiced by dervishes, literally “poor monks.” They became famous as whirling dervishes, who spun with an almost unhuman grace, energy and tenacity.
I thought of them as Continue reading →
Launch Alert: Driehaus Small Cap Growth (DVSMX)
On August 21, 2017, Driehaus Capital launched Driehaus Small Cap Growth (DVSMX/DNSMX). There’s reason to pay attention.
The fund will target U.S. small cap (sub $6 billion market cap) growth stocks. The “name rule” obliges them to keep at least 80% in small caps; they allow that the other 20% might be in international stocks that trade on U.S. exchanges or larger cap equities. As is common with Driehaus, it’s a growth-centered fund likely with a fairly high portfolio turnover rate.
They’re attempting to find “fundamentally strong companies,” which obliges them to evaluate the company’s competitive position, industry dynamics, potential growth catalysts and its financial strength. They also account for comparative stock valuations and external factors (behavioral and macro-economic) likely to impact the Continue reading →
Briefly Noted
Updates
PIMCO fee roulette. PIMCO is changing the advisory fees on a bunch of their funds, some up, some down, and some both. Here’s the snapshot:
PIMCO All Asset Fund (PASAX), management fees go up 0.05% for D shares.
PIMCO All Asset All Authority Fund (PAUAX) up 0.05% for D shares
PIMCO Total Return Fund (PTTAX) up 0.05% for D shares, down 0.05% for A shares.
PIMCO Unconstrained Bond Fund (PUBAX), down 0.11% for all asset Continue reading →
August 1, 2017
Dear friends,
 For those of us who teach, August is a bittersweet month. Each year we approach summer like a gaggle of penitent drunks. This time, we promise, it’ll be different. We’ll do better. Trust us: we will revise all of our courses for fall. We will catch up on that mountain of books heaped beside the chair. We will finish that book manuscript (Miscommunication in the Workplace, 2d ed., in my case.). On top of which, we’ll see our children without the use of small electronic devices, we’ll be out there running at 6:00 each morning, we’ll get our roughage and Continue reading →
For those of us who teach, August is a bittersweet month. Each year we approach summer like a gaggle of penitent drunks. This time, we promise, it’ll be different. We’ll do better. Trust us: we will revise all of our courses for fall. We will catch up on that mountain of books heaped beside the chair. We will finish that book manuscript (Miscommunication in the Workplace, 2d ed., in my case.). On top of which, we’ll see our children without the use of small electronic devices, we’ll be out there running at 6:00 each morning, we’ll get our roughage and Continue reading →
Morningstar’s universe
We regularly lament the fact that several hundred consistently four- and five-star funds have lost Morningstar analyst coverage over the years. Our almost-monthly feature “Left Behind by Morningstar” profiles a fund that once received analyst coverage but has now been ignored for five or more years. This month we profile Evermore Global Value (EVGBX / EVGIX), rated four-star for the past three years, past five years and overall. It’s a Euro-centric special situations fund run by David Marcus, whose roots are in the Mutual Series funds from the days of Michael Price’s reign. It’s both good and a good diversifier.
At the same time, we want to celebrate funds that have Continue reading →
Briefly noted
The industry appears to be in full summer-beach mode, or its doing so splendidly that there’s no need to even think about changing anything. In any case, July saw the smallest number of announced changes in about five years.
Updates
Our July 2017 profile of Matthews Asia Credit Opportunities (MCRDX/MICPX) described it as investing in high-yield bonds. That’s correct but incomplete. Manager Satya Patel reminded us that the fund’s core investments can include “convertibles, hybrids and derivatives with fixed income characteristics.” Indeed, since inception convertible bonds have represented 20-25% of the portfolio. We’ve corrected the profile to reflect that. The fund has built a substantial performance advantage over its peers since inception, similar to the consistent success of its older Continue reading →
July 1, 2017
Dear friends,
It’s summer time, an especially blessed and cursed interval for those of us who teach. On the one hand, we’re mostly freed from the day-to-day obligation to be in the classroom. Some of us write, some travel, some undertake “such other duties as may from time to time be assigned” by our colleges. On the other hand, we hear the clock ticking. All year long, as we try to face down a stack of 32 variably-literate essays at 11 p.m. Sunday night, we think “if I can just make it to summer, I’ll recharge and it’ll be great!” About the first thing we notice when summer does arrive, is that Continue reading →