Dear friends,
Welcome to the New Year. At least as we calculate it. The Year of the Horse begins January 31, a date the Vietnamese share. The Iranians, like the ancient Romans, sensibly celebrate the New Year at the beginning of spring. A bunch of cultures in South Asia pick mid-April. Rosh Hashanah (“head of the year”) rolls around in September. My Celtic ancestors (and a bunch of modern Druidic wannabees) preferred Samhain, at the start of November.
Whatever your culture, the New Year is bittersweet. We seem obsessed with looking back in regret at all the stuff we didn’t do, as much as we look forward to all of the stuff we might yet do.
My suggestion: can the regrets, get off yer butt, and do the stuff now that you know you need to do. One small start: get rid of that mutual fund. You know the one. You’ve been regretting it for years. You keep thinking “maybe I’ll wait to let it come back a bit.” The one that you tend to forget to mention whenever you talk about investments.
Good gravy. Dump it! It takes about 30 seconds on the phone and no one is going to hassle you about it; it’s not like the manager is going to grab the line and begin pleading for a bit more time. Pick up a lower cost replacement. Maybe look into a nice ETF or index fund. Track down a really good fund whose manager is willing to put his own fortune and honor at risk along with yours.
You’ll feel a lot better once you do.
We can talk about your gym membership later.
Voices from the bottom of the well
THESE are the times that try men’s souls. The summer soldier and the sunshine patriot will, in this crisis, shrink from the service of their country; but he that stands by it now, deserves the love and thanks of man and woman. Tyranny, like hell, is not easily conquered; yet we have this consolation with us, that the harder the conflict, the more glorious the triumph. What we obtain too cheap, we esteem too lightly: it is dearness only that gives every thing its value. Heaven knows how to put a proper price upon its goods; and it would be strange indeed if so celestial an article as FREEDOM should not be highly rated.
Thos. Paine, The Crisis, 23 December 1776
Investors highly value managers who are principled, decisive, independent, active and contrarian. Right up to the moment that they have one.
Then they’re appalled.
There are two honorable approaches to investing: relative value and absolute value. Relative value investors tend to buy the best-priced securities available, even if the price quoted isn’t very good. They tend to remain fully invested even when the market is pricey and have, as their mantra, “there’s always a bull market in something.” They’re optimistic by nature, enjoy fruity wines and rarely wear bowties.
Absolute value investors tend to buy equities only when they’re selling for cheap. Schooled in the works of Graham and Dodd, they’re adamant about having “a margin of safety” when investing in an inherently risk asset class like stocks. They tend to calculate the fair value of a company and they tend to use cautious assumptions in making those calculations. They tend to look for investments selling at a 30% discount to fair value, or to firms likely to produce 10% internal returns of return even if things turn ugly. They’re often found sniffing around the piles that trendier investors have fled. And when they find no compelling values, they raise cash. Sometimes lots of cash, sometimes for quite a while. Their mantra is, “it’s not ‘different this time’.” They’re slightly-mournful by nature, contemplate Scotch, and rather enjoyed Andy Rooney’s commentaries on “60 Minutes.”
If you’re looking for a shortcut to finding absolute value investors today, it’s a safe bet you’ll find them atop the “%age portfolio cash” list. And at the bottom of the “YTD relative return” list. They are, in short, the guys you’re now railing against.
But should you be?
I spent a chunk of December talking with guys who’ve managed five-star funds and who were loved by the crowds but who are now suspected of having doubled-up on their intake of Stupid Pills. They are, on whole, stoic.
Take-aways from those conversations:
- They hate cash. As a matter of fact, it’s second on their most-hated list behind only “risking permanent impairment of capital”.
- They’re not perma-bears. They love owning stocks. These are, by and large, guys who sat around reading The Intelligent Investor during recess and get tingly at the thought of visiting Omaha. But they love them for the prospect of the substantial, compounded returns they might generate. The price of those outsized returns, though, is waiting for one of the market’s periodic mad sales.
- They bought stocks like mad in early 2009, around the time that the rest of us were becoming nauseated at the thought of opening our 401(k) statements. Richard Cook and Dowe Bynum, for example, were at 2% cash in March 2009. Eric Cinnamond was, likewise, fully invested then.
- They’ve been through this before though, as Mr. Cinnamond notes, “it isn’t very fun.” The market moves in multi-year cycles, generally five years long more or less. While each cycle is different in composition, they all have similar features: the macro environment turns accommodative, stocks rise, the fearful finally rush in, stocks overshoot fair value by a lot, there’s an “oops” and a mass exit for the door. Typically, the folks who arrived late inherit the bulk of the pain.
- And they know you’re disgusted with them. Mr. Cinnamond, whose fund has compounded at 12% annually for the past 15 years, allows “we get those long-term returns by looking very stupid.” Richard Cook agrees, “we’re going to look silly, sometimes for three to five years at a stretch.” Zac Wydra admits that he sometimes looks at himself in the mirror and asks “how can you be so stupid?”
And to those investors who declare, “but the market is reasonably priced,” they reply: “we don’t buy ‘the market.’ We buy stocks. Find the individual stocks that meet the criteria that you hired us to apply, and we’ll buy them.”
What do they think you should do now? In general, be patient. Mr. Cook points to Charlie Munger’s observation:
I think the [Berkshire Hathaway’s] record shows the advantage of a peculiar mind-set – not seeking action for its own sake, but instead combining extreme patience with extreme decisiveness. It takes character to sit there with all that cash and do nothing. I didn’t get to where I am by going after mediocre opportunities.
Which is hard. Several of the guys pointed to Seth Klarman’s decision to return $4 billion in capital to his hedge fund investors this month. Klarman made the decision in principle back in September, arguing that if there were no compelling investment opportunities, he’d start mailing out checks. Two things are worth noting about Klarman: (1) his hedge funds have posted returns in the high teens for over 30 years and (2) he’s willing to sit at 33-50% cash for a long time if that’s what it takes to generate big long-term returns.
Few managers have Klarman’s record or ability to wait out markets. Mr. Cinnamond noted, “there aren’t many fund managers with a long track record doing this because you’re so apt to get fired.” Jeremy Grantham of GMO nods, declaring that “career risk” is often a greater driver of a manager’s decisions than market risk is.
In general, the absolute value guys suggest you think differently about their funds than you think about fully-invested relative value ones. Cook and Bynum’s institutional partners think of them as “alternative asset managers,” rather than equity guys and they regard value-leaning hedge funds as their natural peer group. John Deysher, manager of Pinnacle Value (PVFIX), recommends considering “cash-adjusted returns” as a viable measure, though Mr. Cinnamond disagrees since a manager investing in unpopular, undervalued sectors in a momentum driven market is still going to look inept.
Our bottom line: investors need to take a lot more responsibility if they’re going to thrive. That means we’ve got to look beyond simple return numbers and ask, instead, about what decisions led to those returns. That means actually reading your managers’ commentaries, contacting the fund reps with specific questions (if your questions are thoughtful rather more than knee-jerk, you’d be surprised at the quality of answers you receive) and asking the all-important question, “is my manager doing precisely what I hired him to do: to be stubbornly independent, fearful when others are greedy and greedy when others are fearful?”
Alternately: buy a suite of broadly diversified, low-cost index funds. There are several really solid funds-of-index-funds that give you broad exposure to market risk with no exposure to manager risk. The only thing that you need to avoid at all costs is the herd: do not pay active management prices for the services of managers whose only goal is to be no different than every other timid soul out there.
The Absolute Value Guys
|
|
Cash
|
Absolute 2013 return
|
Relative 2013 return
|
|
ASTON River Road Independent Value ARIVX
|
67%
|
7%
|
bottom 1%
|
|
Beck, Mack & Oliver Partners BMPEX
|
18
|
20
|
bottom 3%
|
|
Cook & Bynum COBYX
|
44
|
11
|
bottom 1%
|
|
FPA Crescent FPACX *
|
35
|
22
|
top 5%
|
|
FPA International Value FPIVX
|
40
|
18
|
bottom 20%
|
|
Longleaf Partners Small-Cap LLSCX
|
45
|
30
|
bottom 23%
|
|
Oakseed SEEDX
|
21
|
24
|
bottom 8%
|
|
Pinnacle Value PVFIX
|
44
|
17
|
bottom 2%
|
|
Yacktman YACKX
|
22
|
28
|
bottom 17%
|
* FPACX’s “moderate allocation” competitors were caught holding bonds this year, dumber even than holding cash.
Don’t worry, relative value guys. Morningstar’s got your back.
Earnings at S&P500 companies grew by 11% in 2013, through late December, and they paid out a couple percent in dividends. Arguably, then, stocks are worth about 13% more than they were in January. Unfortunately, the prices paid for those stocks rose by more than twice that amount. Stocks rose by 32.4% in 2013, with the Dow setting 50 all-time record highs in the process. One might imagine that if prices started at around fair value and then rose 2.5 times as much as earnings did, valuations would be getting stretched. Perhaps overvalued by 19% (simple subtraction of the earnings + dividend rise from the price + dividend rise)?
Not to worry, Morningstar’s got you covered. By their estimation, valuations are up only 5% on the year – from fully valued in January to 5% high at year’s end. They concluded that it’s certainly not time to reconsider your mad rush into US equities. (Our outlook for the stock market, 12/27/2013.) While the author, Matthew Coffina, did approvingly quote Warren Buffett on market timing:
Charlie and I believe it’s a terrible mistake to try to dance in and out of it based upon the turn of tarot cards, the predictions of “experts,” or the ebb and flow of business activity. The risks of being out of the game are huge compared to the risks of being in it.
He didn’t, however, invoke what Warren Buffett terms “the three most important words in all of investing,” margin of safety. Because you can’t be sure of a firm’s exact value, you always need to pay less than you think it’s worth – ideally 30 or 40% less – in order to protect your investors against your own fallible judgment.
Quo Vadis Japan
 I go out of the darkness
I go out of the darkness
Onto a road of darkness
Lit only by the far off
Moon on the edge of the mountains.
Izumi
One of the benefits of having had multiple careers and a plethora of interests is that friends and associates always stand ready with suggestions for you to occupy your time. In January of 2012, a former colleague and good friend from my days with the Navy’s long-range strategic planning group suggested that I might find it interesting to attend the Second China Defense and Security Conference at the Jamestown Foundation. That is how I found myself seated in a conference room in February with roughly a hundred other people. My fellow attendees were primarily from the various alphabet soup governmental agencies and mid-level military officers.
The morning’s presentations might best be summed up as grudging praise about the transformation of the Chinese military, especially their navy, from a regional force to one increasingly able to project power throughout Asia and beyond to carry out China’s national interests. When I finally could not stand it any longer, after a presentation during Q&A, I stuck my hand up and asked why there was absolutely no mention of the 600 pound gorilla in the corner of the room, namely Japan and the Japanese Maritime Self-Defense Force. The JMSDF was and is either the second or third largest navy in the world. It is considered by many professional observers to be extraordinarily capable. The silence that greeted my question was akin to what one would observe if I had brought in a dog that had peed on the floor. The moderator muttered a few comments about the JMSDF having fine capabilities. We then went on with no mention of Japan again. At that point I realized I had just learned the most important thing that I was going to take from the conference, that Japan (and its military) had become the invisible country of Asia.
The New Year is when as an investor you reflect back on successes and mistakes. And if one is especially introspective, one can ponder why. For most of 2013, I was banging the drum on two investment themes that made sense to me: (a) the Japanese equity market and (b) the Japanese currency – the yen – hedged back into U.S. dollars. The broad Japanese market touched highs this month not seen before this century. The dollar – yen exchange rate moved from 89.5 at the beginning of the year to 105.5. In tandem, the themes have proven to be quite profitable. Had an investment been made solely in the Wisdom Tree: Japan Hedged Equity ETF, a total return of 41.8% would have been achieved by the U.S. dollar investor. So, is this another false start for both the Japanese stock market and economy? Or is Japan on the cusp of an economic and political transformation?
 When I mention to institutional investors that I think the change in Japan is real, the most common response I get is a concern about “Abenomics.” This is usually expressed as “They are printing an awful lot of money.” Give me a break. Ben Bernanke and his little band of merry Fed governors have effectively been printing money with their various QE efforts. Who thinks that money will be repaid or the devaluation of the U.S. dollar will be reversed? The same can be said of the EU central bankers. If anything, the U.S. has been pursuing a policy of beggar thy creditor, since much of our debt is owed to others. At least in Japan, they owe the money to themselves. They have also gone through years of deflation without the social order and fabric of society breaking down. One wonders how the U.S. would fare in a similar long-term deflationary environment.
When I mention to institutional investors that I think the change in Japan is real, the most common response I get is a concern about “Abenomics.” This is usually expressed as “They are printing an awful lot of money.” Give me a break. Ben Bernanke and his little band of merry Fed governors have effectively been printing money with their various QE efforts. Who thinks that money will be repaid or the devaluation of the U.S. dollar will be reversed? The same can be said of the EU central bankers. If anything, the U.S. has been pursuing a policy of beggar thy creditor, since much of our debt is owed to others. At least in Japan, they owe the money to themselves. They have also gone through years of deflation without the social order and fabric of society breaking down. One wonders how the U.S. would fare in a similar long-term deflationary environment.
I think the more important distinction is to emphasize what “Abenomics” is not. It is not a one-off program of purchasing government bonds with a view towards going from a multi-year deflationary spiral to generating a few points of inflation. It is a comprehensive program aimed at reversing Japan’s economic, political, and strategic slide of the past twenty years. Subsumed under the rubric of “Abenomics” are efforts to increase and widen the acceptance of child care facilities to enable more of Japan’s female talent pool to actively participate in the workforce, a shift in policy for the investments permitted in pension funds to dramatically increase domestic equity exposure, and incentives to transform the Japanese universities into research and resource engines. Similarly, the Japanese economy is beginning to open from a closed economy to one of free trade, especially in agriculture, as Japan has joined the Trans Pacific Partnership. Finally, public opinion has shifted dramatically to a willingness to contemplate revision of Japan’s American-drafted post-war Constitution. This would permit a standing military and a more active military posture. It would normalize Japan as a global nation, and restore a balance of interests and power in East Asia. The ultimate goal then is to restore the self-confidence of the Japanese nation. So, what awakened Japan and the Japanese?
Strangely enough, the Chinese did it. I have been in Japan four times in the last twenty-two months, which does not make me an expert on anything. But it has allowed me to discern a shift in the mood of the country. Long-time Japan hands had told me that when public opinion in Japan shifts, it shifts all at once and moves together in the same direction. Several months ago, I asked a friend and investment manager who is a long-time resident of Tokyo what had caused that shift in opinion. His response was that most individuals, he as well, traced it to the arrest and detention by the Japanese Coast Guard, of a Chinese fishing vessel and its captain who had strayed into Japanese waters. China responded aggressively, embargoing rare earth materials that the Japanese electronics and automobile industries needed, and made other public bellicose noises. Riots and torching of Japanese plants in China followed, with what seemed to be the tacit approval of the Chinese government. Japan released the ship and its captain, and in Asian parlance, lost face. As my friend explained it, the Japanese public came to the conclusion that the Chinese government was composed of bad people whose behavior was unacceptable. Concurrently, Japan Inc. began to relocate its overseas investment away from China and into countries such as Vietnam, Indonesia, Thailand, and Singapore.
From an investment point of view, what does it all mean? First, one should not look at Prime Minister Abe, Act II (remember that he was briefly in office for 12 months in 2006-2007) in a vacuum. Like Reagan and Churchill, he used his time in the “wilderness years” to rethink what he wanted to achieve for Japan and how he would set about doing it. Second, one of the things one learns about Japan and the Japanese is that they believe in their country and generally trust their government, and are prepared to invest in Japan. This is in stark contrast to China, where if the rumors of capital flows are to be believed, vast sums of money are flowing out of the country through Hong Kong and Singapore. So, after the above events involving China, Abe’s timing in return to office was timely.
While Japanese equities have surged this year, that surge has been primarily in the large cap liquid issues that are easily studied and invested in by global firms. Most U.S. firms follow the fly-by approach. Go to Tokyo for a week of company meetings, and invest accordingly. Few firms make the commitment of having resources on the ground. That is why if you look at most U.S.-based Japan specialist mutual funds, they all own pretty much the same large cap liquid names, with only the percentages and sector weightings varying. There are tiers of small and mid-cap companies that are under-researched and under-invested in. If this is the beginning of a secular bull market, as we saw start in the U.S. in 1982, Japan will just be at the beginnings of eliminating the value gap between intrinsic value and the market price of securities, especially in the more inefficiently-traded and under-researched companies.
So, as Lenin once famously asked, “What is to be done?” For most individuals, individual stock investments are out of the question, given the currency, custody, language, trading, and tax issues. For exposure to the asset class, there is a lot to be said for a passive approach through an index fund or exchange-traded fund, of which there are a number with relatively low expense ratios. Finally, there are the fifteen or so Japan-only mutual funds. I am only aware of three that are small-cap vehicles – DFA, Fidelity, and Hennessy. There are also two actively-managed closed end funds. I will look to others to put together performance numbers and information that will allow you to research the area and draw your own conclusions.
Finally, it should be obvious that Japan does not lend itself to simple explanations. As Americans, we are often in a time-warp, thinking that with the atomic bombs, American Occupation and force-fed Constitution, we successfully transformed Japan into a pacifist democratically-styled Asian theme park. My conclusion is rather that what you see in Japan is not reality (whatever that is) but what they are comfortable with you seeing. I think for instance of the cultural differences with China in a business sense. With the Chinese businessman, a signed contract is in effect the beginning of the negotiation. For the Japanese businessman, a signed contract is a commitment to be honored to the letter.
I will leave you with one thing to ponder shared with me by a Japanese friend. She told me that the samurai have been gone for a long time in Japan. But, everyone in Japan still knows who the samurai families are and everyone knows who is of those families and who is not. And she said, everyone from those families still tends to marry into other samurai families. So I thought, perhaps they are not gone after all.
Edward Studzinski
From Day One …
… the Observer’s readers were anxious to have us publish lists of Great Funds, as FundAlarm did with its Honor Roll funds. For a long time I demurred because I was afraid folks would take such a list too seriously. That is, rather than viewing it as a collection of historical observations, they’d see it as a shopping list.
After two years and unrelenting inquires, I prevailed upon my colleague Charles to look at whether we could produce a list of funds that had great track records but, at the same time, highlight the often-hidden data concerning those funds’ risks. With that request and Charles’s initiative, the Great Owl Funds were launched.
And now Charles returns to that troubling original question: what can we actually learn about the future from a fund’s past?
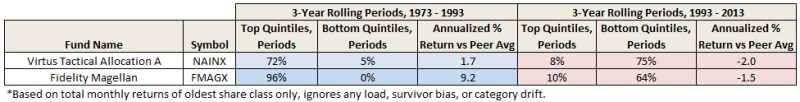
In Search of Persistence
It’s 1993. Ten moderate allocation funds are available that have existed for 20 years or more. A diligent, well intended investor wants to purchase one of them based on persistent superior performance. The investor examines rolling 3-year risk-adjusted returns every month during the preceding 20 years, which amounts to 205 evaluation periods, and delightfully discovers Virtus Tactical Allocation (NAINX).
It outperformed nearly 3/4ths of the time, while it under-performed only 5%. NAINX essentially equaled or beat its peers 194 out of 205 periods. Encouraged, the investor purchases the fund making a long-term commitment to buy-and-hold.
It’s now 2013, twenty years later. How has NAINX performed? To the investor’s horror, Virtus Tactical Allocation underperformed 3/4ths of the time since purchased! And the fund that outperformed most persistently? Mairs & Power Balanced (MAPOX), of course.
Back to 1993. This time a more aggressive investor applies the same methodology to the large growth category and finds an extraordinary fund, named Fidelity Magellan (FMAGX). This fund outperformed nearly 100% of the time across 205 rolling 3-year periods over 20 years versus 31 other long-time peers. But during the next 20 years…? Not well, unfortunately. This investor would have done better choosing Fidelity Contrafund (FCNTX). How can this be? Most industry experts would attribute the colossal shift in FMAGX performance to the resignation of legendary fund manager Peter Lynch in 1990.
MJG, one of the heavy contributors to MFO’s discussion board, posts regularly about the difficulty of staying on top of one’s peer group, often citing results from Standard & Poor’s Index Versus Active Indexing (SPIVA) reports. Here is the top lesson-learned from ten years of these reports:
“Over a five-year horizon…a majority of active funds in most categories fail to outperform indexes. If an investing horizon is five years or longer, a passive approach may be preferable.”
The December 2013 SPIVA “Persistence Scorecard” has just been published, which Joshua Brown writes insightfully about in “Persistence is a Killer.” The scorecard once again shows that only a small fraction of top performing domestic equity mutual funds remain on top across any 2, 3, or 5 year period.
What does mutual fund non-persistence look like across 40 years? Here’s one depiction:
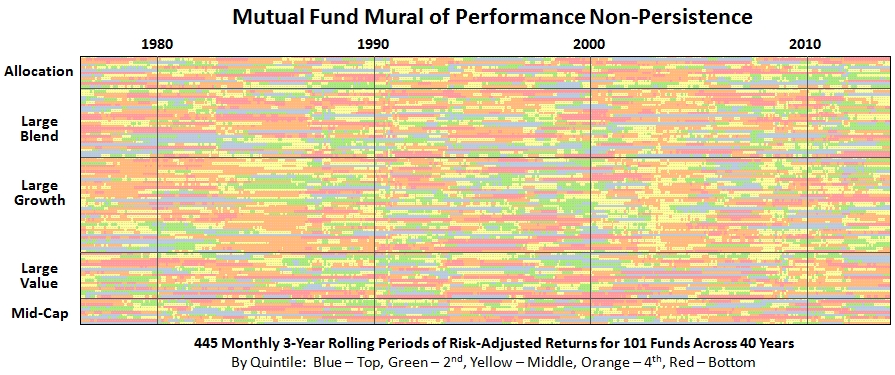
The image (or “mural”) represents monthly rank by color-coded quintiles of risk-adjusted returns, specifically Martin Ratio, for 101 funds across five categories. The funds have existed for 40 years through September 2013. The calculations use total monthly returns of oldest share class only, ignoring any load, survivor bias, and category drift. Within each category, the funds are listed alphabetically.
There are no long blue/green horizontal streaks. If anything, there seem to be more extended orange/red streaks, suggesting that if mutual fund persistence does exist, it’s in the wrong quintiles! (SPIVA actually finds similar result and such bottom funds tend to end-up merged or liquated.)
Looking across the 40 years of 3-year rolling risk-adjusted returns, some observations:
- 98% of funds spent some periods in every rank level…top, bottom, and all in-between
- 35% landed in the bottom two quintiles most of the time…that’s more than 1/3rd of all funds
- 13% were in the top two bottom quintiles…apparently harder to be persistently good than bad
- Sequoia (SEQUX) was the most persistent top performer…one of greatest mutual funds ever
- Wall Street (WALLX) was the most persistent cellar dweller…how can it still exist?
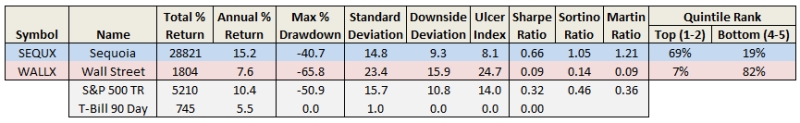
The difference in overall return between the most persistent winner and loser is breathtaking: SEQUX delivered 5.5 times more than SP500 and 16 times more than WALLX. Put another way, $10K invested in SEQUX in October 1973 is worth nearly $3M today. Here’s how the comparison looks:
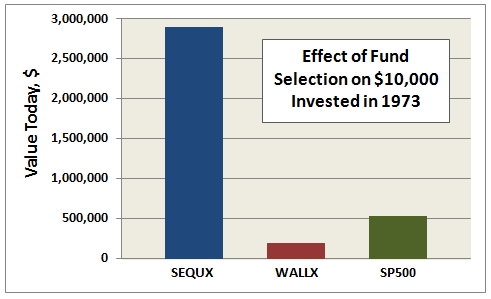
So, while attaining persistence may be elusive, the motivation to achieve it is clear and present.
The implication of a lack of persistence strikes at the core of all fund rating methodologies that investors try to use to predict future returns, at least those based only on historical returns. It is, of course, why Kiplinger, Money, and Morningstar all try to incorporate additional factors, like shareholder friendliness, experience, and strategy, when compiling their Best Funds lists. An attempt, as Morningstar well states, to identify “funds with the highest potential of success.”
The MFO rating system was introduced in June 2013. The current 20-year Great Owls, shown below for moderate allocation and large growth categories, include funds that have achieved top performance rank over the past 20, 10, 5, and 3 year evaluation periods. (See Rating Definitions.)
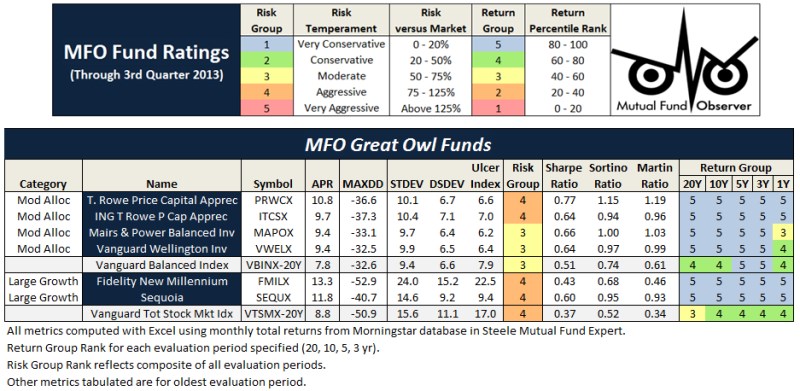
But will they be Great Owls next year? The system is strictly quantitative based on past returns, which means, alas, a gentle and all too ubiquitous reminder that past performance is not a guarantee of future results. (More qualitative assessments of fund strategy, stewardship, and promise are provided monthly in David’s fund profiles.) In any case and in the spirit of SPIVA, we will plan to publish periodically a Great Owl “Persistence Scorecard.”
31Dec2013/Charles
It’s not exciting just because the marketers say it is
Most mutual funds don’t really have any investment reason to exist: they’re mostly asset gathering tools that some advisor created in support of its business model. Even the funds that do have a compelling case to make often have trouble receiving a fair hearing, so I’m sympathetic to the need to find new angles and new pitches to try to get journalists’ and investors’ attention.
But the fact that a marketer announces it doesn’t mean that journalists need to validate it through repetition. And it doesn’t mean that you should just take in what we’ve written.
Case in point: BlackRock Emerging Markets Long/Short Fund (BLSAX). Here’s the combination of reasonable and silly statements offered in a BlackRock article justifying long/short investing:
For example, our access to information relies on cutting edge infrastructure to compile vast amounts of obvious and less-obvious sources of publicly available information. In fact, we consume a massive amount of data from more than 25 countries, with a storage capacity 4 times the Library of Congress and 8 times the size of Wikipedia. We take that vast quantity of publicly available information and filter and identify relevant pieces.
Reasonable statement: we do lots of research. Silly statement: we have a really big hard drive on our computer (“a storage capacity of…”). Why on earth would we care? And what on earth does it mean? “4 times the Library of Congress”? The LoC digital collection – a small fraction of its total collection – holds three petabytes of data, a statement that folks immediately recognize as nonsensical. 3,000,000 gigabytes. So the BlackRock team has a 12 petabyte hard drive? 12 petabytes of data? How’s it used? How much is reliable, consistent, contradictory or outdated? How much value do you get from data so vast that you’ll never comprehend it?
NSA’s biggest “data farm” consumes 65 megawatts of power, has melted down 10 times, and – by the fed’s own reckoning – still hasn’t produced demonstrable security gains. Data ≠ knowledge.
The Google, by the way, processes 20 petabytes of user-generated content per day.
Nonetheless, Investment News promptly and uncritically gloms onto the factoid, and then gets it twice wrong:
The Scientific Active Equity team takes quantitative investing to a whole new level. In fact, the team has amassed so much data on publicly traded companies that its database is now four times the size of Wikipedia and eight times the size of the Library of Congress (Jason Kephart, Beyond black box investing: Fund uses database four times the size of Wikipedia, 12/26/13).
Error 1: reversing the LoC and the Wikipedia. Error 2: conflating “storage capacity” with “data.” (And, of course, confusing “pile o’ data” with “something meaningful.”)
MFWire promptly grabs the bullhorn to share the errors and the credulity:
This Fund Uses the Data of Eight Libraries of Congress (12/26/13, Boxing Day for our British friends)
The team managing the fund uses gigantic amounts of data — four times the size of Wikipedia and eight times the size of the Library of Congress — on public company earnings, analyst calls, news releases, what have you, to gain on insights into different stocks, according to Kephart.
Our second, perhaps larger, point of disagreement with Jason (who, in fairness, generally does exceptionally solid work) comes in his enthusiasm for one particular statistic:
That brings us to perhaps the fund’s most impressive stat, and the one advisers really need to keep their eyes on: its correlation to global equities.
Based on weekly returns through the third quarter, the most recent data available, the fund has a correlation of just 0.38 to the MSCI World Index and a correlation of 0.36 to the S&P 500. Correlations lower than 0.5 lead to better diversification and can lead to better risk-adjusted returns for the entire portfolio.
Uhhh. No?
Why, exactly, is correlation The Golden Number? And why is BlackRock’s correlation enough to make you tingle? The BlackRock fund has been around just one year, so we don’t know its long-term correlation. In December, it had a net market exposure of just 9% which actually makes a .36 correlation seem oddly high. BlackRock’s correlation is not distinctively low (Whitebox Long/Short WBLSX has a three-year correlation of 0.33, for instance).
Nor is low correlation the hallmark of the best long-term funds in the group. By almost any measure, the best long/short fund in existence is the closed Robeco Boston Partners L/S Equity Fund (BPLEX). BPLEX is a five-star fund, a Lipper Leader, a Great Owl fund, with returns in the top 4% of its peer group over the past decade. And its long term correlation to the market: 75. Wasatch Long/Short (FMLSX), another great fund with a long track record: 90. Marketfield (MFLDX), four-star, Great Owl: 67.
The case for BlackRock EM L/S is it’s open. It’s got a good record, though a short one. In comparison to other, more-established funds, it substantially trails Long-Short Opportunity (LSOFX) since inception, is comparable to ASTON River Road (ARLSX) and Wasatch Long Short (FMLSX), while it leads Whitebox Long-Short (WBLSX), Robeco Boston Partners (BPLEX) and RiverPark Long/Short Opportunity (RLSFX). The fund has nearly $400 million in assets after one year and charges 2% expenses plus a 5.25% front load. That’s more than ARLSX, WBLSX or FMLSX, though cheaper than LSOFX.
Bottom Line: as writers, we need to guard against the pressures created by deadlines and the desire for “clicks.” As readers, you need to realize we have good days and bad and you need to keep asking the questions we should be asking: what’s the context of this number? What does it mean? Why am I being given it? How does it compare? And, as investors, we all need to remember that magic is more common in the world of Harry Potter than in the world we’re stuck with.
Wells Fargo and the Roll Call of the Wretched
Our Annual Roll Call of the Wretched highlights those funds which consistently, over a period of many years, trail their benchmark. We noted that inclusion on the list signaled one of two problems:
- Bad fund or
- Bad benchmark.
The former problem is obvious. The latter takes a word of explanation. There are 7055 distinct mutual funds, each claiming – more or less legitimately – to be different from all of the others. For the purpose of comparison, Morningstar and Lipper assign them to one of 108 categories. Some funds fit easily and well, others are laughably misfit. One example is RiverPark Short-Term High Yield Fund (RPHYX), which is a splendid cash management fund whose performance is being compared to the High-Yield group which is dominated by longer-duration bonds that carry equity-like risks and returns.
You get a sense of the mismatch – and of the reason that RPHYX was assigned one-star – when you compare the movements of the fund to the high-yield group.
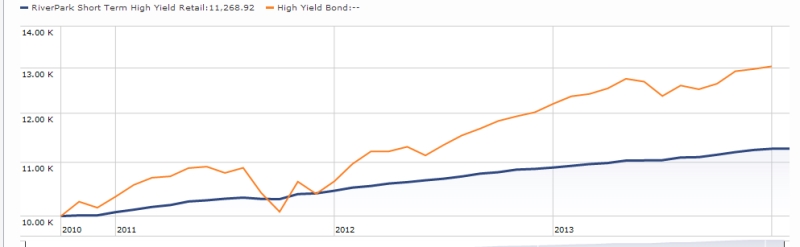
That same problem afflicts Wells Fargo Advantage Short-Term High Yield Bond (SSTHX), an entirely admirable fund that returns around 4% per year over the long term in a category that delivers 50% greater returns with 150% greater volatility. In Morningstar’s eyes, one star.
Joel Talish, one of the managing directors at Wells Fargo Advisors, raised the entirely reasonable objection that SSTHX isn’t wretched – it’s misclassified – and it shouldn’t be in the Roll Call at all. He might well be right. Our strategy has been to report all of the funds that pass the statistical screen, then to highlight those whose performance is better than the peer data suggest. We don’t tend to remove funds from the list just because we believe that the ratings agencies are wrong. We’ve made that decision consciously: investors need to read these ubiquitous statistical screens more closely and more skeptically. A pattern of results arises from a series of actions, and they’re meaningful only if you take the time to understand what’s going on. By highlighting solid funds that look bad because of a rater’s unexplained assignments, we’re trying to help folks learn how to look past the stars.
It might well be the case that highlighting and explaining SSTHX’s consistently one-star performance did a substantial disservice to the management team. It was a judgment call on our part and we’ll revisit it as we prepare future features. For now, we’re hopeful that the point we highlighted at the start of the list:
Use lists like the Roll Call of the Wretched or the Three Alarm Funds as a first step, not a final answer. If you see a fund of yours on either list, find out why. Call the adviser, read the prospectus, try the manager’s letter, post a question on our board. There might be a perfectly good reason for their performance, there might be a perfectly awful one. In either case, you need to know.
Observer Fund Profile
Each month the Observer provides in-depth profiles of notable funds that you’d otherwise not hear of. Our “Most Intriguing New Funds” are funds launched within the past couple years that most frequently feature experienced managers leading innovative newer funds. “Stars in the Shadows” are older funds that have attracted far less attention than they deserve.
RiverPark Strategic Income (RSIVX): RSIVX sits at the core of Cohanzick’s competence, a conservative yet opportunistic strategy that they’ve pursued for two decades and that offers the prospect of doubling the returns of its very fine Short-Term High Yield Fund.
Elevator Talk: Oliver Pursche, GMG Defensive Beta Fund (MPDAX)
 Since the number of funds we can cover in-depth is smaller than the number of funds worthy of in-depth coverage, we’ve decided to offer one or two managers each month the opportunity to make a 200 word pitch to you. That’s about the number of words a slightly-manic elevator companion could share in a minute and a half. In each case, I’ve promised to offer a quick capsule of the fund and a link back to the fund’s site. Other than that, they’ve got 200 words and precisely as much of your time and attention as you’re willing to share. These aren’t endorsements; they’re opportunities to learn more.
Since the number of funds we can cover in-depth is smaller than the number of funds worthy of in-depth coverage, we’ve decided to offer one or two managers each month the opportunity to make a 200 word pitch to you. That’s about the number of words a slightly-manic elevator companion could share in a minute and a half. In each case, I’ve promised to offer a quick capsule of the fund and a link back to the fund’s site. Other than that, they’ve got 200 words and precisely as much of your time and attention as you’re willing to share. These aren’t endorsements; they’re opportunities to learn more.
 The traditional approach to buffering the stock market’s volatility without entirely surrendering the prospect of adequate returns was to divide the portfolio between (domestic, large cap) stocks and (domestic, investment grade) bonds, at a ratio of roughly 60/40. That strategy worked passably well as long as stocks could be counted on to produce robust returns and bonds could be counted on to post solid though smaller gains without fail. As the wheels began falling off that strategy, advisors began casting about for alternative strategies.
The traditional approach to buffering the stock market’s volatility without entirely surrendering the prospect of adequate returns was to divide the portfolio between (domestic, large cap) stocks and (domestic, investment grade) bonds, at a ratio of roughly 60/40. That strategy worked passably well as long as stocks could be counted on to produce robust returns and bonds could be counted on to post solid though smaller gains without fail. As the wheels began falling off that strategy, advisors began casting about for alternative strategies.
Some, like the folks at Montebello Partners, began drawing lessons from the experience of hedge funds and institutional alternatives managers. Their conclusion was that each asset class had one or two vital contributions to make to the health of the portfolio, but that exposure to those assets had to be actively managed if they were going to have a chance of producing equity-like (perhaps “equity-lite”) returns with substantial downside protection.
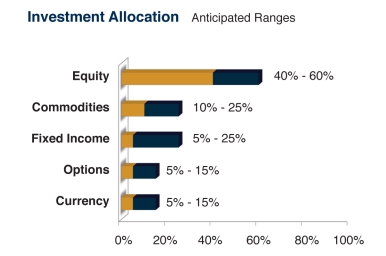
Their strategy is manifested in GMG Defensive Beta, which launched in the summer of 2009. Its returns have generally overwhelmed those of its multi-alternative peers (top 3% over the past three years, substantially higher returns since inception) though at the cost of substantially higher volatility. Morningstar rates it as a five-star fund, while Lipper gives it four stars for both Total Return and Consistency of Return and five stars for Capital Preservation.
Oliver Pursche is the president of Gary M Goldberg Financial Services (hence GMG) one of the four founding co-managers of MPDAX. Here are his 218 words (on whole, durn close to target) on why you should consider a multi alternative strategy:
Markets are up, and as a result, so are the risks of a correction. I don’t think that a 2008-like crash is in the cards, but we could certainly see a 20% correction at some point. If you agree with me, protecting your hard fought gains makes all the sense in the world, which is why I believe low-volatility and multi-alternative funds like our GMG Defensive Beta Fund will continue to gain favor with investors. The problem is that most of these new funds have no, or only a short track-record, so it’s difficult to know how they will actually perform in a prolonged downturn. One thing is certain, in the absence of a longer-term track record, low fees and low turnover tend to be advantageous to investors. This is why our fund is a no-load fund and we cap our fees at 1.49%, well below most of our peers, and our cap gain distributions have been minimal.
From my perspective, if you’re looking to continue to have market exposure, but don’t want all of the risks associated with investing in the S&P 500, our fund is ideally suited. We’re strategic and tactical at the same time and have demonstrated our ability to remain disciplined, which is (I think) why Morningstar has awarded us a 5 Star ranking.
MPDAX is a no-load fund with a single share class. The minimum initial investment is $1,000. Expenses are 1.49% on about $27 million in assets.
The fund’s website is functional but spare. You get the essential information, but there’s no particular wealth of insight or commentary on this strategy. There’s a Morningstar reprint available but you should be aware that the file contains one page of data reporting and five pages of definitions and disclaimers.
Our earlier Elevator Talks were:
- February 2013: Tom Kerr, Rocky Peak Small Cap Value (RPCSX), whose manager has a 14 year track record in small cap investing and a passion for discovering “value” in the intersection of many measures. We’re saddened to report that Tom chose to liquidate the fund.
- March 2013: Dale Harvey, Poplar Forest Partners (PFPFX and IPFPX), a concentrated, contrarian value stock fund that offers “a once-in-a-generation opportunity to invest with a successful American Funds manager who went out on his own.”
- April 2013: Bayard Closser, Vertical Capital Income Fund (VCAPX), “a closed-end interval fund, VCAPX invests in whole mortgage loans and first deeds of trust. We purchase the loans from lenders at a deep discount and service them ourselves.”
- May 2013: Jim Hillary, LS Opportunity Fund (LSOFX), a co-founder of Marsico Capital Management whose worry that “the quality of research on Wall Street continues to decline and investors are becoming increasingly concerned about short-term performance” led to his faith in “in-depth research and long-term orientation in our high conviction ideas.”
- July 2013: Casey Frazier, Versus Capital Multi-Manager Real Estate Income Fund (VCMRX), a second closed-end interval fund whose portfolio “includes real estate private equity and debt, public equity and debt, and broad exposure across asset types and geographies. We target a mix of 70% private real estate with 30% public real estate to enhance liquidity, and our objective is to produce total returns in the 7 – 9% range net of fees.”
- August 2013: Brian Frank, Frank Value Fund (FRNKX), a truly all-cap value fund with a simple, successful discipline: if one part of the market is overpriced, shop elsewhere.
- August 2013: Ian Mortimer and Matthew Page of Guinness Atkinson Inflation Managed Dividend (GAINX), a global equity fund that pursues firms with “sustainable and potentially rising dividends,” which also translates to firms with robust business models and consistently high return on capital.
- September 2013: Steven Vannelli of GaveKal Knowledge Leaders (GAVAX), which looks to invest in “the best among global companies that are tapping a deep reservoir of intangible capital to generate earnings growth,” where “R&D, design, brand and channel” are markers of robust intangible capital. From launch through the end of June, 2013, the fund modestly outperformed the MSCI World Index and did so with two-thirds less volatility
- October 2013: Bashar Qasem of Wise Capital (WISEX), which provides investors with an opportunity for global diversification in a fund category (short term bonds) mostly distinguished by bland uniformity.
- November 2013: Jeffrey Ringdahl of American Beacon Flexible Bond (AFXAX) gives teams from Brandywine Global, GAM and PIMCO incredible leeway wth which to pursue “positive total return regardless of market conditions.” Since inception the fund has noticeably outrun its “nontraditional bond” peers with reasonable volatility.
Conference Call Highlights
 On December 9th, about 50 of us spent a rollicking hour with David Sherman of Cohanzick Asset Management, discussing his new fund: RiverPark Strategic Income Fund (RSIVX). I’m always amazed at how excited folks can get about short-term bonds and dented credits. It’s sort of contagious.
On December 9th, about 50 of us spent a rollicking hour with David Sherman of Cohanzick Asset Management, discussing his new fund: RiverPark Strategic Income Fund (RSIVX). I’m always amazed at how excited folks can get about short-term bonds and dented credits. It’s sort of contagious.
David’s first fund with RiverPark, the now-closed Short Term High Yield (RPHYX), was built around Cohanzick’s strategy for managing its excess cash. Strategic Income represents their seminal, and core, strategy to fixed-income investing. Before launching Cohanzick in 1996, David was a Vice President of Leucadia National Corporation, a holding company that might be thought of as a mini-Berkshire Hathaway. His responsibilities there included helping to manage a $3 billion investment portfolio which had an opportunistic distressed securities flair. When he founded Cohanzick, Leucadia was his first client. They entrusted him with $150 million, this was the strategy he used to invest it.
Rather than review the fund’s portfolio, which we cover in this month’s profile of it (below), we’ll highlight strategy and his response to listener questions.
The fund focuses on “money good” securities. Those are securities where, if held to maturity, he’s confident that he’ll get his entire principal and all of the interest due to him. They’re the sorts of securities where, if the issuer files for bankruptcy, he still anticipates eventually receiving his principal and interest plus interest on his interest. Because he expects to be able to hold securities to maturity, he doesn’t care about “the taper” and its effects – he’ll simply hold on through any kerfuffle and benefit from regular payments that flow in much like an annuity stream. These are, he says, bonds that he’d have his mother hold.
Given that David’s mother was one of the early investors in the fund, these are bonds his mother holds. He joked that he serves as a sort of financial guarantor for her standard of living (if her portfolio doesn’t produce sufficient returns to cover her expenses, he has to reach for his checkbook), he’s very motivated to get this right.
While the fund might hold a variety of securities, they hold little international exposure and no emerging markets debt. They’re primarily invested in North American (77%) and European(14%) corporate debt, in firms where the accounting is clear and nations where the laws are. The fund’s investment mandate is very flexible, so they can actively hedge portfolio positions (and might) and they can buy income-producing equities (but won’t).
The portfolio focuses on non-investment grade securities, mostly in the B – BB range, but that’s consistent with his intention not to lose his investors’ money. He values liquidity in his investments; that is to say, he doesn’t get into investments that he can’t quickly get out of. The fund has been letting cash build, and it’s now about 30% of the portfolio. David’s general preference is to get out too early and lose some potential returns, rather than linger too long and suffer the risk of permanent impairment.
There were rather more questions from callers than we had time to field. Some of the points we did get to talk about:
David is not impressed with the values available in one- to three-year bonds, they’ve been subject to too much buying by the anxious herd. He’s currently finding better values in three- to five-year bonds, especially those which are not included in the major bond indexes. There is, he says, “a lot of high yield value outside of indexed issues.”
About 50% of the corporate bond market qualifies as “high yield,” which gives him lots of opportunities.
This could function as one’s core bond portfolio. While there will be more NAV volatility because of mark-to-market rules (that is, you have to ask “what would I get if I stupidly decided to sell my entire portfolio in the midst of a particular day’s market panic”), the risk of permanent impairment of capital occurs only if he’s made a mistake.
Munis are a possibility, but they’re not currently cheap enough to be attractive.
If there’s a limited supply of a security that would be appropriate for both Short-Term and here, Short-Term gets dibs.
Cohanzick is really good at pricing their portfolio securities. At one level, they use an independent pricing service. At another, getting the price right has been a central discipline since the firm’s founding and he’s comfortable with his ability to do so even with relatively illiquid names.
At base, David believes the fund can generate returns in the 7-8% range with minimal risk of capital loss. Given his record with Cohanzick and RPHYX, we are confident that he’s capable of delivering on that promise. By way of full disclosure: In aligning our mouths and our money, both Chip and I added RSIVX to our personal portfolios this fall. Once we work out all of the Observer’s year-end finances, we also intend to transfer a portion of the money now in MFO’s credit union savings account into an investment in this fund.
For folks interested but unable to join us, here’s the complete audio of the hour-long conversation.
The RSIVX conference call
As with all of these funds, we’ve created a new featured funds page for the RiverPark Strategic Income Fund, pulling together all of the best resources we have for the fund.
January Conference Call: Matt Moran, ASTON River Road Long/Short
 Last winter we spent time talking with the managers of really promising hedged funds, including a couple who joined us on conference calls. The fund that best matched my own predilections was ASTON River Road Long/Short (ARLSX), extensive details on which appear on our ARLSX Featured Fund Page. In our December 2012 call, manager Matt Moran argued that:
Last winter we spent time talking with the managers of really promising hedged funds, including a couple who joined us on conference calls. The fund that best matched my own predilections was ASTON River Road Long/Short (ARLSX), extensive details on which appear on our ARLSX Featured Fund Page. In our December 2012 call, manager Matt Moran argued that:
- The fund might outperform the stock market by 200 bps/year over a full, 3-5 year market cycle.
- The fund can maintain a beta at 0.3 to 0.5, in part because of their systematic Drawdown Plan.
- Risk management is more important than return management, so all three of their disciplines are risk-tuned.
I was sufficiently impressed that I chose to invest in the fund. That does not say that we believe this is “the best” long/short fund (an entirely pointless designation), just that it’s the fund that best matched my own concerns and interests. The fund returned 18% in 2013, placing it in the top third of all long/short funds.
Matt and co-manager Dan Johnson have agreed to join us for a second conversation. That call is scheduled for Wednesday, January 15, from 7:00 – 8:00 Eastern. Please note that this is one day later than our original announcement. Matt has been kicking around ideas for what he’d like to talk about. His short-list includes:
- How we think about our performance in 2013 and, in particular, why we’re satisfied with it given our three mandates (equity-like returns, reduced volatility, capital preservation)
- Where we are finding value on the long side. It’s a struggle…
- How we’re surviving on the short side. It’s a huge challenge. Really, how many marginal businesses can keep hanging on because of the Fed’s historic generosity? Stocks must ultimately earn what underlying business earns and a slug of these firms are earning …
- But, too, our desire not to be carried out in body bags on short side.
- The fact that we sleep better at night with Drawdown Plan in place.
HOW CAN YOU JOIN IN?
 If you’d like to join in, just click on register and you’ll be taken to the Chorus Call site. In exchange for your name and email, you’ll receive a toll-free number, a PIN and instructions on joining the call. If you register, I’ll send you a reminder email on the morning of the call.
If you’d like to join in, just click on register and you’ll be taken to the Chorus Call site. In exchange for your name and email, you’ll receive a toll-free number, a PIN and instructions on joining the call. If you register, I’ll send you a reminder email on the morning of the call.
Remember: registering for one call does not automatically register you for another. You need to click each separately. Likewise, registering for the conference call mailing list doesn’t register you for a call; it just lets you know when an opportunity comes up.
For those of you new to our conference calls, here’s the short version: we set up an audio-only phone conversation, you register and receive an 800-number and a PIN, our guest talks for about 20 minutes on his fund’s genesis and strategy, I ask questions for about 20, and then our listeners get to chime in with questions of their own. A couple days later we post an .mp3 of the call and highlights of the conversation.
WOULD AN ADDITIONAL HEADS UP HELP?
Over two hundred readers have signed up for a conference call mailing list. About a week ahead of each call, I write to everyone on the list to remind them of what might make the call special and how to register. If you’d like to be added to the conference call list, just drop me a line.
February Conference Call: Joshua B. Parker and Alan Salzbank, RiverPark / Gargoyle Hedged Value
We extend our conversation with hedged fund managers in a conversation with Messrs. Parker and Salzbank, whose RiverPark / Gargoyle Hedged Value (RGHVX) we profiled last June, but with whom we’ve never spoken.

Gargoyle is a converted hedge fund. The hedge fund launched in 1999 and the strategy was converted to a mutual fund on April 30, 2012. Rather than shorting stocks, the strategy is to hold a diversified portfolio mid- to large-cap value stocks, mostly domestic, and to hedge part of the stock market risk by selling a blend of index call options. That value focus is both distinctive and sensible; the strategy’s stock portfolio has outperformed the S&P500 by 4.5% per year over the past 23 years. The options overlay generates 1.5 – 2% in premium income per month. The fund ended 2013 with a 29% gain, which beat 88% of its long/short peers.
That call is scheduled for Wednesday, February 12, from 7:00 – 8:00 Eastern. We’ll provide additional details in our February issue.
HOW CAN YOU JOIN IN?
 If you’d like to join in, just click on register and you’ll be taken to the Chorus Call site. In exchange for your name and email, you’ll receive a toll-free number, a PIN and instructions on joining the call. If you register, I’ll send you a reminder email on the morning of the call.
If you’d like to join in, just click on register and you’ll be taken to the Chorus Call site. In exchange for your name and email, you’ll receive a toll-free number, a PIN and instructions on joining the call. If you register, I’ll send you a reminder email on the morning of the call.
Launch Alert: Vanguard Global Minimum Volatility Fund (VMVFX)
 Vanguard Global Minimum Volatility Fund (VMVFX) launched on December 12, 2013. It’s Vanguard’s answer to the craze for “smart beta,” a strategy that seemingly promises both higher returns and lower risk over time. Vanguard dismisses the possibility with terms like “new-age investment alchemy,” and promise instead to provide reasonable returns with lower risk than an equity investor would otherwise be subject to. They are, they say, “trying to deliver broadly diversified exposure to the equity asset class, with lower average volatility over time than the market. We will use quantitative models to assess the expected volatility of stocks and correlation to one another.” They also intend to hedge currency risk in order to further dampen volatility.
Vanguard Global Minimum Volatility Fund (VMVFX) launched on December 12, 2013. It’s Vanguard’s answer to the craze for “smart beta,” a strategy that seemingly promises both higher returns and lower risk over time. Vanguard dismisses the possibility with terms like “new-age investment alchemy,” and promise instead to provide reasonable returns with lower risk than an equity investor would otherwise be subject to. They are, they say, “trying to deliver broadly diversified exposure to the equity asset class, with lower average volatility over time than the market. We will use quantitative models to assess the expected volatility of stocks and correlation to one another.” They also intend to hedge currency risk in order to further dampen volatility.
Most portfolios are constructed with an eye to maximizing returns within a set of secondary constraints (for example, market cap). Volatility is then a sort of fallout from the system. Vanguard reverses the process here by working to minimize the volatility of an all-equity portfolio within a set of secondary constraints dealing with diversification and liquidity. Returns are then a sort of fallout from the design. Vanguard recently explained the fund’s distinctiveness in Our new fund offering: What it is and what it isn’t.
The fund will be managed by James D. Troyer, James P. Stetler, and Michael R. Roach. They are members of the management teams for about a dozen other Vanguard funds.
The Investor share class has a $3,000 minimum initial investment. The opening expense ratio is 0.30%.
MFS made its first foray into low-volatility investing this month, launching MFS Low Volatility Equity (MLVAX) and MFS Low Volatility Global Equity (MVGAX) just one week before Vanguard. The former will target a volatility level that is 20% lower than that of the S&P 500 Index over a full market cycle, while the latter will target 30% less volatility than the MSCI All Country World Index. The MFS funds charge about four times what Vanguard does.
Launch Alert II: Meridian Small Cap Growth Advisor (MSGAX)
 Meridian Small Cap Growth Fund launched on December 16th. The prospectus says very little about what the managers will be doing: “The portfolio managers apply a ‘bottom up’ fundamental research process in selecting investments. In other words, the portfolio managers analyze individual companies to determine if a company presents an attractive investment opportunity and if it is consistent with the Fund’s investment strategies and policies.”
Meridian Small Cap Growth Fund launched on December 16th. The prospectus says very little about what the managers will be doing: “The portfolio managers apply a ‘bottom up’ fundamental research process in selecting investments. In other words, the portfolio managers analyze individual companies to determine if a company presents an attractive investment opportunity and if it is consistent with the Fund’s investment strategies and policies.”
Nevertheless, the fund warrants – and will receive – considerable attention because of the pedigree of its managers. Chad Meade and Brian Schaub managed Janus Triton (JATTX) together from 2006 – May 2013. During their tenure, they managed to turn an initial $10,000 investment into $21,400 by the time they departed; their peers would have parlayed $10,000 into just over $14,000. The more remarkable fact is that the managed it with a low turnover (39%, half the group average), relatively low risk (beta = .80, S.D. about 3 points below their peers) strategy. Understandably, the fund’s assets soared to $6 billion and it morphed from focused on small caps to slightly larger names. Regrettably, Janus decided that wasn’t grounds for closing the fund.
Messrs Meade and Schaub joined Arrowpoint Partners in May 2013. Arrowpoint famously is the home of a cadre of Janus alumni (or escapees, depending): David Corkins, Karen Reidy, Tony Yao, Minyoung Sohn and Rick Grove. Together they managed over $2 billion. In June, they purchased Aster Investment Management, advisor to the Meridian funds, adding nearly $3 billion more in assets. We’ll reach out to the Arrowpoint folks early in the new year.
The Advisor share class is available no-load and NTF through brokerages like Scottrade, with a $2,500 minimum initial investment. The opening expense ratio is 1.60%.
Funds in Registration
New mutual funds must be registered with the Securities and Exchange Commission before they can be offered for sale to the public. The SEC has a 75-day window during which to call for revisions of a prospectus; fund companies sometimes use that same time to tweak a fund’s fee structure or operating details.
Funds in registration this month are eligible to launch in March, 2014 and some of the prospectuses do highlight that date.
And there were a lot of funds targeting a year-end launch. Every day David Welsch, firefighter/EMT/fund researcher, scours new SEC filings to see what opportunities might be about to present themselves. This month he tracked down 15 no-load retail funds in registration, which represents our core interest. That number is down from what we’d normally see because these funds won’t launch until February 2014; whenever possible, firms prefer to launch by December 30th and so force a lot of funds into the pipeline in October.
Interesting entries this month include:
Artisan High Income Fund will invest in high yield corporate bonds and debt. There are two major distinctions here. First, it is Artisan’s first fixed-income fund. Second, Artisan has always claimed that they’re only willing to hire managers who will be “category-killers.” If you look at Artisan’s returns, you’ll get a sense of how very good they are at that task. Their new high-yield manager, and eventual head of a new, autonomous high-yield team, is Bryan C. Krug who ran the $10 billion, five star Ivy High Income Fund (WHIYX) for the past seven years. The minimum initial investment will be $1000 for Investor shares and $250,000 for Advisor shares. The initial expense ratio will be 1.25% for both Investor and Advisor shares.
Brown Advisory Japan Alpha Opportunities Fund will pursue total return by investing principally in Japanese stocks. The fund will be constructed around a series of distinct “sleeves,” each with its own distinct risk profile but they don’t explain what they might be. They may invest in common and preferred stock, futures, convertibles, options, ADRs and GDR, REITs and ETFs. While they advertise an all-cap portfolio, they do flag small cap and EM risks. The fund will be managed by a team from Wellington Management. The minimum initial investment will be $5000. The initial expense ratio will be 1.36%.
Perritt Low Priced Stock Fund will pursue long-term capital appreciation by investing in small cap stocks priced at $15 or less. I’m a bit ambivalent but could be talked into liking it. The lead manager also runs Perritt Microcap (PRCGX) and Ultra MicroCap (PREOX), both of which are very solid funds with good risk profiles. Doubtless he can do it here. That said, the whole “under $15” thing strikes me as a marketing ploy and a modestly regrettable one. What benefit does that stipulation really offer the investors? The minimum initial investment will be $1000, reduced to $250 for all sorts of good reasons, and the initial expense ratio will be 1.5%.
Manager Changes
On a related note, we also tracked down 40 fund manager changes. The most intriguing of those include what appears to be the abrupt dismissal of Ken Feinberg, one of the longest-serving managers in the Davis/Selected Funds, and PIMCO’s decision to add to Bill Gross’s workload by having him fill in for a manager on sabbatical.
Updates
There are really very few emerging markets investors which whom I’d trust my money. Robert Gardiner and Andrew Foster are at the top of the list. There are notable updates on both this month.
 Grandeur Peak Emerging Opportunities (GPEOX) launched two weeks ago, hasn’t released a word about its portfolio, has earned one half of one percent for its investors . . . and has drawn nearly $100 million in assets. Mr. Gardiner and company have a long-established plan to close the fund at $200 million. I’d encourage interested parties to (quickly!) read our review of Grandeur Peak’s flagship Global Reach fund. If you’re interested in a reasonably assertive, small- to mid-cap fund, you may have just a few weeks to establish your account before the fund closes. The advisor does not intend to market the fund to the general public until February 1, by which time it might well be at capacity.
Grandeur Peak Emerging Opportunities (GPEOX) launched two weeks ago, hasn’t released a word about its portfolio, has earned one half of one percent for its investors . . . and has drawn nearly $100 million in assets. Mr. Gardiner and company have a long-established plan to close the fund at $200 million. I’d encourage interested parties to (quickly!) read our review of Grandeur Peak’s flagship Global Reach fund. If you’re interested in a reasonably assertive, small- to mid-cap fund, you may have just a few weeks to establish your account before the fund closes. The advisor does not intend to market the fund to the general public until February 1, by which time it might well be at capacity.
Investors understandably assume that an e.m. small cap fund is necessarily, and probably substantially, riskier than a more-diversified e.m. fund. That assumption might be faulty. By most measures (standard deviation and beta, for example) it’s about 15% more volatile than the average e.m. fund, but part of that volatility is on the upside. In the past five years, emerging markets equities have fallen in six of 20 quarters. We can look at the performance of DFA’s semi-passive Emerging Markets Small Cap Fund (DEMSX) to gauge the downside of these funds.
|
DFA E.M. Small Cap …
|
No. of quarters
|
|
Falls more
|
2
|
|
Fall equally (+/- 25 bps)
|
1
|
|
Falls less
|
2
|
|
Rises
|
1
|
The same pattern is demonstrated by Templeton E.M. Small Cap (TEMMX): higher beta but surprising resilience in declining quarters. For aggressive investors, a $2,000 foot-in-the-door position might well represent a rational balance between the need for more information and the desire to maintain their options.
Happily, there’s an entirely-excellent alternative to GPEOX and it’s not (yet) near closing to new investors.
 Seafarer Overseas Growth & Income (SFGIX and SIGIX) is beginning to draw well-earned attention. Seafarer offers a particularly risk-conscious approach to emerging markets investing. It offers a compact (40 names), all-cap portfolio (20% in small- and microcap names and 28% in mid-caps, both vastly higher than its peers) that includes both firms domiciled in the emerging markets (about 70%) and those headquartered in the developing world but profiting from the emerging one (30%). It finished 2013 up 5.5%, which puts it in the top tier of all emerging markets funds.
Seafarer Overseas Growth & Income (SFGIX and SIGIX) is beginning to draw well-earned attention. Seafarer offers a particularly risk-conscious approach to emerging markets investing. It offers a compact (40 names), all-cap portfolio (20% in small- and microcap names and 28% in mid-caps, both vastly higher than its peers) that includes both firms domiciled in the emerging markets (about 70%) and those headquartered in the developing world but profiting from the emerging one (30%). It finished 2013 up 5.5%, which puts it in the top tier of all emerging markets funds.
That’s consistent with both manager Andrew Foster’s record at his former charge (Matthews Asian Growth & Income MACSX which was one of the two top Asian funds in existence through his time there) and Seafarer’s record since launch (it has returned 20% since February 2012 while its average peer made less than 4%). Assets had been growing briskly through the fund’s first full year, plateaued for much of 2013 then popped in December: the fund moved from about $40 million in AUM to $55 million in a very short period. That presumably signals a rising recognition of Seafarer’s strength among larger investors, which strikes me as a very good thing for both Seafarer and the investors.
On an unrelated note, Oakseed Opportunity (SEEDX) has added master limited partnerships to its list of investable securities. The guys continue negotiating distribution arrangements; the fund became available on the Fidelity platform in the second week of December, 2013. They were already available through Schwab, Scottrade, TDAmeritrade and Vanguard.
Briefly Noted . . .
The Gold Bullion Strategy Fund (QGLDX) has added a redemption fee of 2.00% for shares sold within seven days of purchase because, really, how could you consider yourself a long-term investor if you’re not willing to hold for at least eight days?
Legg Mason Capital Management Special Investment Trust (LMSAX) will transition from being a small- and mid-cap fund to a small cap and special situations fund. The advisor warns that this will involve an abnormal turnover in the portfolio and higher-than-usual capital gains distributions. The fund has beaten its peers precisely twice in the past decade, cratered in 2007-09, got a new manager in 2011 and has ascended to … uh, mediocrity since then. Apparently “unstable” and “mediocre” is sufficient to justify someone’s decision to keep $750 million in the fund.
PIMCO’s RealRetirement funds just got a bit more aggressive. In an SEC filing on December 30, PIMCO shifted the target asset allocations to increase equity exposure and decrease real estate, commodities and fixed income. Here’s the allocation for an individual with 40 years until retirement
|
|
New allocation
|
Old allocation
|
|
Stocks
|
62.5%, with a range of 40-70%
|
55%, same range
|
|
Commodities & real estate
|
20, range 10-40%
|
25, same range
|
|
Fixed income
|
17.5, range 10-60%
|
20, same range
|
Real estate and commodities are an inflation hedge (that’s the “real” part of RealRetirement) and PIMCO’s commitment to them has been (1) unusually high and (2) unusually detrimental to performance.
SMALL WINS FOR INVESTORS
Effective January 2, 2014, BlackRock U.S. Opportunities Portfolio (BMEAX) reopened to new investors. Skeptics might note that the fund is large ($1.6 billion), overpriced (1.47%) and under-performing (having trailed its peers in four of the past five years), which makes its renewed availability a distinctly small win.
Speaking of “small wins,” the Board of Trustees of Buffalo Funds has approved a series of management fees breakpoints for the very solid Buffalo Small Cap Fund (BUFSX). The fund, with remains open to new investors despite having nearly $4 billion in assets, currently pays a 1.0% management fee to its advisor. Under the new arrangement, the fee drops by five basis points for assets from $6 to $7 billion, another five for assets from $7-8 and $8-9 then it levels out at 80 bps for assets over $9 billion. Those gains are fairly minor (the net fee on the fund at $7 billion is $69.5 million under the new arrangement versus $70 million under the old) and the implication that the fund might remain open as it swells is worrisome.
Effective January 1, 2014, Polaris Global Value Fund (PGVFX) has agreed to cap operating expenses at 0.99%. Polaris, a four-star fund with a quarter billion in assets, currently charges 1.39% so the drop will be substantial.
The investment minimum for Institutional Class shares of Yacktman Focused Fund (YAFFX) has dropped from $1,000,000 to $100,000.
Vanguard High-Yield Corporate Fund (VWEHX) has reopened to new investors. Wellington Management, the fund’s advisor, reports that “Cash flow to the fund has subsided, which, along with a change in market conditions, has enabled us to reopen the fund.”
CLOSINGS (and related inconveniences)
Driehaus Select Credit Fund (DRSLX) will close to most new investors on January 31, 2014. The strategy capacity is about $1.5 billion and the fund already holds $1 billion, with more flowing in, so they decided to close it just as they closed its sibling, Driehaus Active Income (LCMAX). You might think of it as a high-conviction, high-volatility fixed income hedge fund.
Hotchkis & Wiley Mid-Cap Value (HWMIX) is slated to close to new investors on March 1, 2014. Ted, our board’s most senior member, opines “Top notch MCV fund, 2.8 Billion in assets, and superior returns.” I nod.
Sequoia (SEQUX) closed to new investors on December 10th. Their last closure lasted 25 years.
Vanguard Capital Opportunity Fund (VHCOX), managed by PRIMECAP Management Company, has closed again. It closed in 2004, opened the door a crack in 2007 and fully reopened in 2009. Apparently the $2 billion in new assets generated a sense of concern, prompting the reclosure.
OLD WINE, NEW BOTTLES
Aberdeen Diversified Income Fund (GMAAX), a tiny fund distinguished more for volatility than for great returns, can now invest in closed-end funds. Two other Aberdeen funds, Dynamic Allocation (GMMAX) and Diversified Alternatives (GASAX), are also now permitted to invest, to a limited extent, in “certain direct investments” and so if you’ve always wanted exposure to certain direct investments (as opposed to uncertain ones), they’ve got the funds for you.
American Independence Core Plus Fund (IBFSX) has changed its name to the American Independence Boyd Watterson Core Plus Fund, presumably in the hope that the Boyd Watterson name will work marketing magic. Not entirely sure why that would be the case, but there it is.
Effective December 31, 2013, FAMCO MLP & Energy Income Fund became Advisory Research MLP & Energy Income Fund. Oddly, the announcement lists two separate “A” shares with two separate ticker symbols (INFIX and INFRX).
In February Compass EMP Long/Short Fixed Income Fund (CBHAX) gets rechristened Compass EMP Market Neutral Income Fund and it will no longer be required to invest at least 80% in fixed income securities. The change likely reflects the fact that the fund is underwater since its November 2013 inception (its late December NAV was $9.67) and no one cares (AUM is $28 million).
In yet another test of my assertion that giving yourself an obscure and nonsensical name is a bad way to build a following (think “Artio”), ING reiterated its plan to rebrand itself as Voya Financial. The name change will roll out over the first half of 2014.
As of early December, Gabelli Value Fund became Gabelli Value 25 Fund (GABVX). And no, it does not hold 25 stocks (the portfolio has nearly 200 names). Here’s their explanation: “The name change highlights the Fund’s overweighting of its core 25 equity positions and underscores the upcoming 25th anniversary of the Fund’s inception.” And yes, that does strike me as something that The Mario came up with and no one dared contradict.
GMO, as part of a far larger fund shakeup (see below), has renamed and repurposed four of its institutional funds. GMO International Core Equity Fund becomes GMO International Large/Mid Cap Equity Fund, GMO International Intrinsic Value Fund becomes GMO International Equity Fund, GMO International Opportunities Equity Allocation Fund becomes GMO International Developed Equity Allocation Fund, and GMO World Opportunities Equity Allocation Fund morphs (slightly) into GMO Global Developed Equity Allocation Fund, all on February 12, 2014. Most of the funds tweaked their investment strategy statements to comply with the SEC’s naming rules which say that if you have a distinct asset class in your name (large/midcap equity), you need to have at least 80% of your portfolio in that class.
Effective February 28, MainStay Intermediate Term Bond Fund (MTMAX) becomes MainStay Total Return Bond Fund.
Nuveen NWQ Flexible Income Fund (NWQIX), formerly Nuveen NWQ Equity Income Fund has been rechristened as Nuveen NWQ Global Equity Income Fund, with James Stephenson serving as its sole manager. If you’d like to get a sense of what “survivorship bias” looks like, you might check out Nuveen’s SEC distributions filing and count the number of funds with lines through their names.
Old Westbury Global Small & Mid Cap Fund (OWSMX) has been rechristened as Old Westbury Small & Mid Cap Fund. It’s no longer required to have a global portfolio, but might. It’s been very solid, with about 20% of its portfolio in ETFs and the rest in individual securities.
At the meeting on December 3, 2013, the Board approved a change in Old Westbury Global Opportunities Fund’s (OWGOX) name to Old Westbury Strategic Opportunities Fund. Let’s see: 13 managers, $6 billion in assets, and a long-term record that trails 70% of its peers. Yep, a name change is just what’s needed!
OFF TO THE DUSTBIN OF HISTORY
Jeez, The Shadow is just a wild man here.
On December 6, 2013, the Board of the Conestoga Funds decided to close and liquidate the Conestoga Mid Cap Fund (CCMGX), effective February 28, 2014. At the same time, they’re launched a SMid cap fund with the same management team. I wrote the advisor to ask why this isn’t just a scam to bury a bad track record and get a re-do; they could, more easily, just have amended Mid Cap’s principal investment strategy to encompass small caps and called it SMid Cap. They volunteered to talk then reconsidered, suggesting that they’d be freer to walk me through their decision once the new fund is up and running. I’m looking forward to the opportunity.
Dynamic Energy Income Fund (DWEIS), one of the suite of former DundeeWealth funds, was liquidated on December 31, 2013.
Fidelity has finalized plans for the merger of Fidelity Europe Capital Appreciation Fund (FECAX) into Fidelity Europe Fund (FIEUX), which occurs on March 21.
The institutional firm Grantham, Mayo, van Otterloo (GMO) is not known for precipitous action, so their December announcement of a dozen fund closures is striking. One set of funds is simply slated to disappear:
|
Liquidating Fund
|
Liquidation Date
|
|
GMO Real Estate Fund
|
January 17, 2014
|
|
GMO U.S. Growth Fund
|
January 17, 2014
|
|
GMO U.S. Intrinsic Value Fund
|
January 17, 2014
|
|
GMO U.S. Small/Mid Cap Fund
|
January 17, 2014
|
|
GMO U.S. Equity Allocation Fund
|
January 28, 2014
|
|
GMO International Growth Equity Fund
|
February 3, 2014
|
|
GMO Short-Duration Collateral Share Fund
|
February 10, 2014
|
|
GMO Domestic Bond Fund
|
February 10, 2014
|
In addition, the Board has approved the termination of GMO Asset Allocation International Small Companies Fund and GMO International Large/Mid Cap Value Fund, neither of which had commenced operations.
They then added two sets of fund mergers: GMO Debt Opportunities Fund into GMO Short-Duration Collateral Fund (with the freakish coda that “GMO Short-Duration Collateral Fund is not pursuing an active investment program and is gradually liquidating its portfolio” but absorbing Debt Opportunities gives it reason to live) and GMO U.S. Flexible Equities Fund into GMO U.S. Core Equity Fund, which is expected to occur on or about January 24, 2014.
Not to be outdone, The Hartford Mutual Funds announced ten fund mergers and closures themselves. Hartford Growth Fund (HGWAX) is merging with Hartford Growth Opportunities Fund (HGOAX), Hartford Global Growth (HALAX) merges with Hartford Capital Appreciation II (HCTAX) and Hartford Value (HVFAX) goes into Hartford Value Opportunities (HV)AX), all effective April 7, 2014. None of which, they note, requires shareholder approval. I have real trouble seeing any upside for the funds’ investors, since most going from one sub-par fund into another and will see expenses drop by just a few basis points. The exceptions are the value funds, both of which are solid and economically viable on their own. In addition, Hartford is pulling the plug on its entire target-date retirement line-up. The funds slated for liquidation are Hartford Target Retirement 2010 through 2050. That dirty deed will be done on June 30, 2014.
Highbridge Dynamic Commodities Strategy Fund (HDSAX) is slated to be liquidated and dissolved (an interesting visual image) on February 7, 2014. In the interim, it’s going to cash.
John Hancock Sovereign Investors Fund (SOVIX) will merge into John Hancock Large Cap Equity Fund (TAGRX), on or about April 30, 2014.
Principal SmallCap Growth Fund II (PPMIX) will be absorbed by SmallCap Growth Fund I (PGRTX) on or about April 25, 2014.
It’s with some sadness that we bid adieu to Tom Kerr and his Rocky Peak Small Cap Value Fund (RPCSX), which liquidated on December 30. The fund sagged from “tiny” to “microscopic” by the end of its run, with under a million in assets. Its performance in 2013 was pretty much calamitous, which was both curious and fatal. Tom was an experienced manager and sensible guy who will, we hope, find a satisfying path forward.
In a sort of three-for-one swap, Pax World International Fund (PXIRX) and Pax MSCI EAFE ESG Index ETF (EAPS) are merging to form the Pax World International ESG Index Fund.
On October 21, 2013, the Board of Directors of the T. Rowe Price Summit GNMA Fund (PRSUX) approved a proposed merger with, and into, T. Rowe Price GNMA Fund (PRGMX).
The Vanguard Managed Payout Growth Focus Fund (VPGFX) and Vanguard Managed Payout Distribution Focus Fund (VPDFX) are each to be reorganized into the Vanguard Managed Payout Growth and Distribution Fund (VPGDX) on or about January 17, 2014.
W.P. Stewart & Co. Growth Fund (WPSGX) is merging into the AllianceBernstein Concentrated Growth Fund (WPCSX), which has the same manager, investment discipline and expenses of the WPS fund. Alliance acquired WPS in December, so the merger was a sort of foregone conclusion.
Wegener Adaptive Growth Fund (WAGFX) decided, on about three days’ notice, to close and liquidate at the end of December, 2013. It had a couple very solid years (2008 and 2009) then went into the dumper, ending with a portfolio smaller than my retirement account.
A small change
 Our navigation menu is growing. If you look along the top of our page, you’ll likely notice that “Featured Funds” is no longer a top-level menu item. Instead the “Featured Funds” category can now be found under the “Fund” or “The Best” menus. Replacing it as a new top-level menu is “Search Tools”, which is the easiest way to directly access new search functionality that Accipiter, Charles, and Chip have been working on for the past few months.
Our navigation menu is growing. If you look along the top of our page, you’ll likely notice that “Featured Funds” is no longer a top-level menu item. Instead the “Featured Funds” category can now be found under the “Fund” or “The Best” menus. Replacing it as a new top-level menu is “Search Tools”, which is the easiest way to directly access new search functionality that Accipiter, Charles, and Chip have been working on for the past few months.
Under Search Tools, you’ll find:
- Risk Profile – designed to help you understand the different measures of a fund’s risk profile. No one measure of risk captures the full picture and most measures of risk are not self-explanatory. Our Risk Profile reporter allows you to enter a single ticker symbol for any fund and it will generate a short, clear report, in simple, conversational English, that walks you through the various means of risk and returns and will provide you with the profiles for a whole range of possible benchmarks. Alternatively, entering multiple ticker symbols will return a tabular results page, making side-by-side comparisons more convenient.
- Great Owls – allows you to screen our Great Owl Funds – those which have top tier performance in every trailing period of three years or more – by category or profile. We know that past performance should never be the primary driver of your decision-making, but working from a pool of consistently superior performers and learning more about their risk-return profile strikes us as a sensible place to start.
- Fund Dashboard – a snapshot of all of the funds we’ve profiled, is updated monthly and is available both as a .pdf and as a searchable and sortable search.
- Miraculous Multi-Search – Accipiter’s newest screening tool helps us search Charles’ database of risk elements. Searches are available by fund name, category, risk group and age group. There’s even an option to restrict the results to GreatOwl funds. Better yet, you can search on multiple criteria and further refine your results list by choosing to hide certain results.
In Closing . . .
Thank you, dear friends. It’s been a remarkable year. In December of 2012, we served 9000 readers. A year later, 24,500 readers made 57,000 visits to the Observer in December – a gain of 150%. The amount of time readers spend on site is up, too, by about 50% over last year. The percentage of new visitors is up 57%. But almost 70% of visits are by returning readers.
It’s all the more striking because we’re the antithesis of a modern news site: our pieces tend to be long, appear once a month and try to be reflective and intelligent. NPR had a nice piece that lamented the pressure to be “first, loud and sensational” (This is (not) the most important story of the year, 12/29/2013). The “reflective and intelligent” part sort of reflects our mental image of who you are.
We’ve often reminded folks of their ability to help the Observer financially, either through our partnership with Amazon (they rebate us about 7% of the value of items purchased through our link) or direct contributions. Those are both essential and we’re deeply grateful to the dozens of folks who’ve acted on our behalf. This month we’d like to ask for a different sort of support, one which might help us make the Observer better in the months ahead.
Would you tell us a bit about who you are and why you’re here? We do not collect any information about you when you visit. The cosmically-talented Chip found a way to embed an anonymous survey directly in this essay, so that you could answer a few questions without ever leaving the comfort of your chair. What follows are six quick questions. We’re setting aside questions about our discussion board for now, since it’s been pretty easy to keep in touch with the folks there. Complete as many as you’re comfortable with.
Create your free online surveys with SurveyMonkey , the world’s leading questionnaire tool.
We’ll share as soon as we hear back from you.
Thanks to Deb (the first person ever to set up an automatic monthly contribution to the site, which was really startling when we found out), to David and the other contributors scattered (mostly) in warm states (and Indianapolis), and to friends who’ve shared books, cookies, well-wishes and holiday cheer.
Finally, thanks to the folks whose constant presence makes the Observer happen: the folks who’ve spent this entire century supporting the discussion board (BobC, glampig, rono, Slick, the indefatigable Ted, and Whakamole among them) and the hundred or so folks regularly on the board; The Shadow, who can sense the presence of interesting SEC filings from a mile away; Accipiter, whose programming skills – generally self-taught – lie behind our fund searches; Ed, who puzzles and grumbles; Charles, who makes data sing; and the irreplaceable Chip, friend, partner and magician. I’m grateful to you all and look forward to the adventures of the year ahead.
As ever,

 Oakseed Opportunity Fund (SEEDX)
Oakseed Opportunity Fund (SEEDX)
 How Good Is Your Fund Family? An Update…
How Good Is Your Fund Family? An Update…
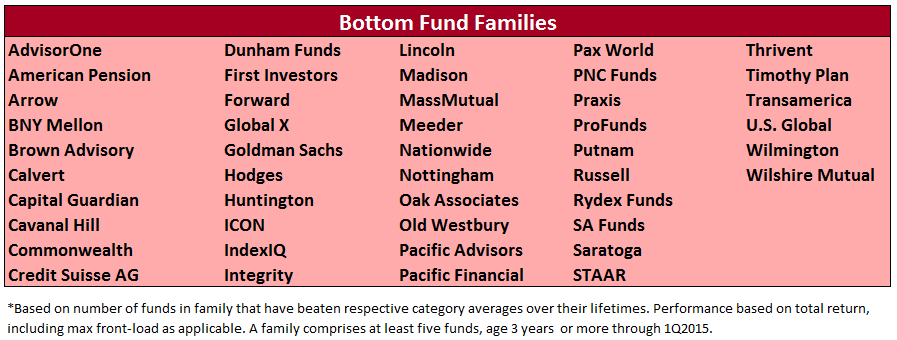
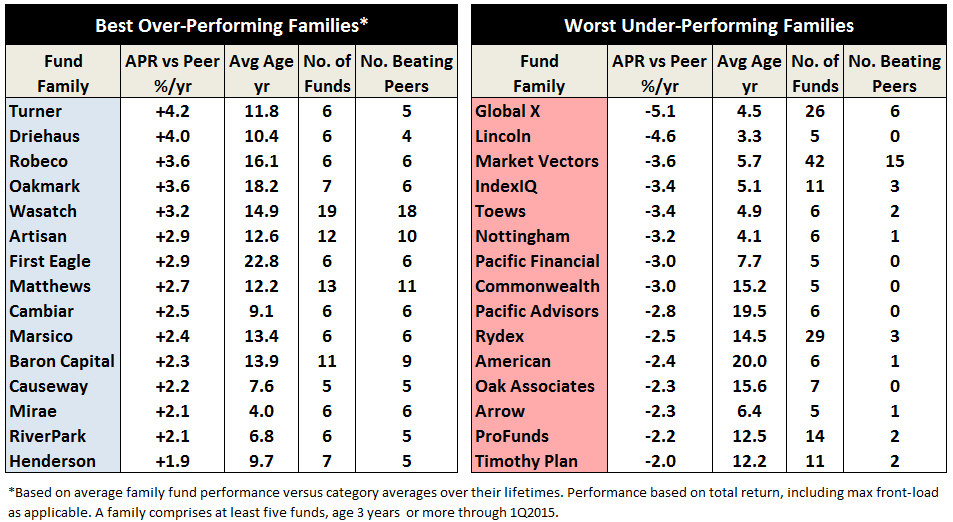
 Ed is one of a growing number of investors who are fearful that we might be approaching a roach motel; that is, a situation where it’s easy to get into a particular security but where it might be impossible to get back out of it when you urgently want to.
Ed is one of a growing number of investors who are fearful that we might be approaching a roach motel; that is, a situation where it’s easy to get into a particular security but where it might be impossible to get back out of it when you urgently want to.
 The spring has brought new life into the liquid alternatives market with both March and April seeing robust activity in terms of new fund launches and registrations, as well as fund flows. Touching on new fund flows first, March saw more than $2 billion of new asset flow into alternative mutual funds and ETFs, while US equity mutual funds and ETFs had combined outflows of nearly $6 billion.
The spring has brought new life into the liquid alternatives market with both March and April seeing robust activity in terms of new fund launches and registrations, as well as fund flows. Touching on new fund flows first, March saw more than $2 billion of new asset flow into alternative mutual funds and ETFs, while US equity mutual funds and ETFs had combined outflows of nearly $6 billion. Here are some quick highlights from our April 16th conversation with Andrew Foster of Seafarer.
Here are some quick highlights from our April 16th conversation with Andrew Foster of Seafarer.

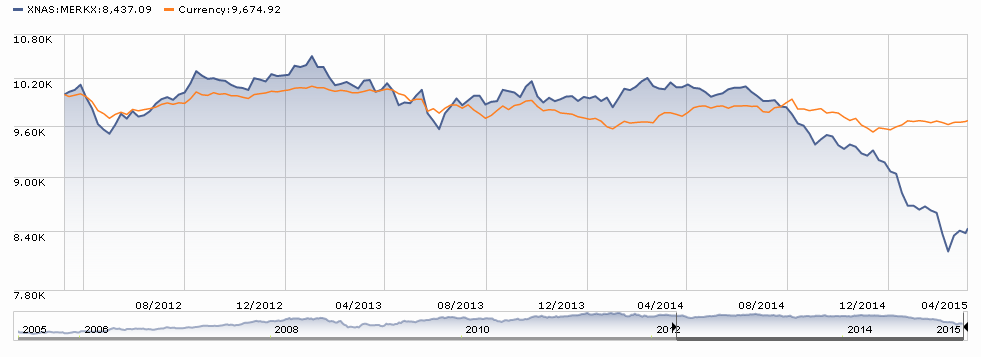

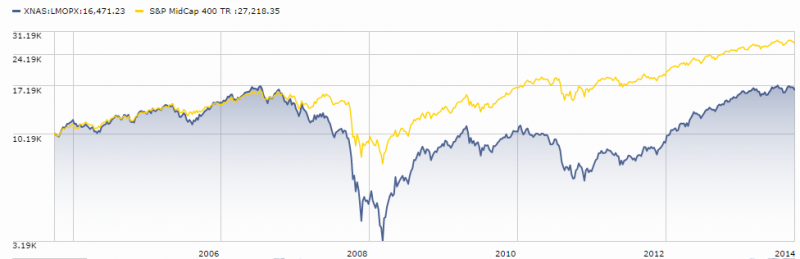
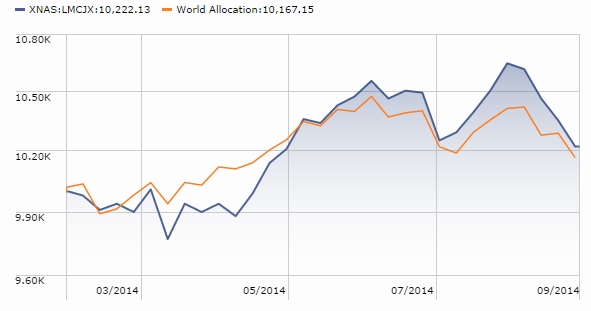

 One of the joys of having entered the investment business in the 1980’s is that you came in at a time when the profession was still populated by some really nice and thoughtful people, well-read and curious about the world around them. They were and are generally willing to share their thoughts and ideas without hesitation. They were the kind of people that you hoped you could keep as friends for life. One such person is my friend, Bruce, who had a thirty-year career on the “buy side” as both an analyst and a director of research at several well-known money management firms. He retired in 2008 and divides his time between homes in western Connecticut and Costa Rica.
One of the joys of having entered the investment business in the 1980’s is that you came in at a time when the profession was still populated by some really nice and thoughtful people, well-read and curious about the world around them. They were and are generally willing to share their thoughts and ideas without hesitation. They were the kind of people that you hoped you could keep as friends for life. One such person is my friend, Bruce, who had a thirty-year career on the “buy side” as both an analyst and a director of research at several well-known money management firms. He retired in 2008 and divides his time between homes in western Connecticut and Costa Rica.
 From Bruce’s perspective, too much money is chasing too few good ideas. This has resulted in what we call “style drift”. Firms that had made their mark as small cap or mid cap investors didn’t want to kill the goose laying the golden eggs by shutting off new money, so they evolved to become large cap investors. But ultimately that is self-defeating, for as the assets come in, you either have to shut down the flows or change your style by adding more and larger positions, which ultimately leads to under-performance.
From Bruce’s perspective, too much money is chasing too few good ideas. This has resulted in what we call “style drift”. Firms that had made their mark as small cap or mid cap investors didn’t want to kill the goose laying the golden eggs by shutting off new money, so they evolved to become large cap investors. But ultimately that is self-defeating, for as the assets come in, you either have to shut down the flows or change your style by adding more and larger positions, which ultimately leads to under-performance.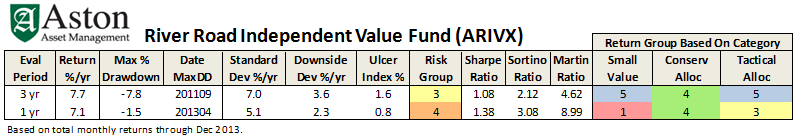
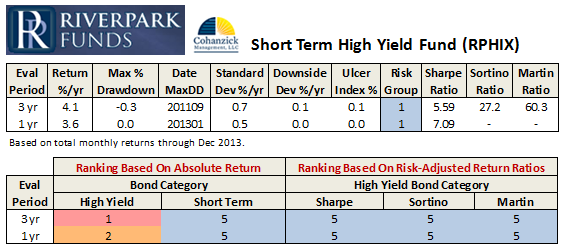
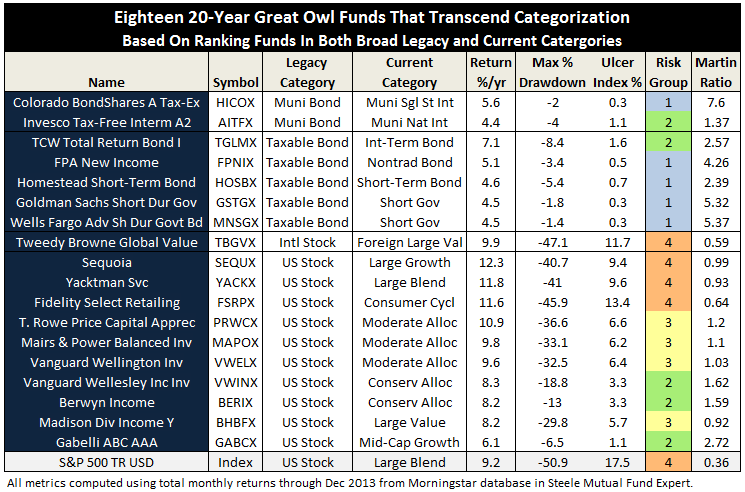 Roy Weitz grouped funds into only five equity and six specialty “benchmark categories” when he established the legacy
Roy Weitz grouped funds into only five equity and six specialty “benchmark categories” when he established the legacy 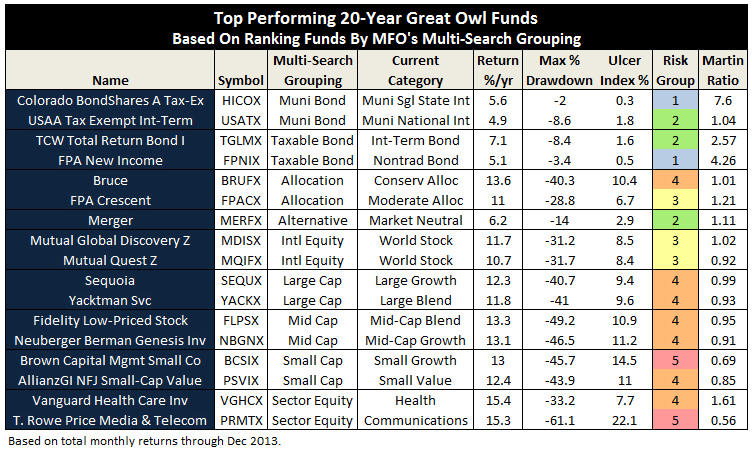
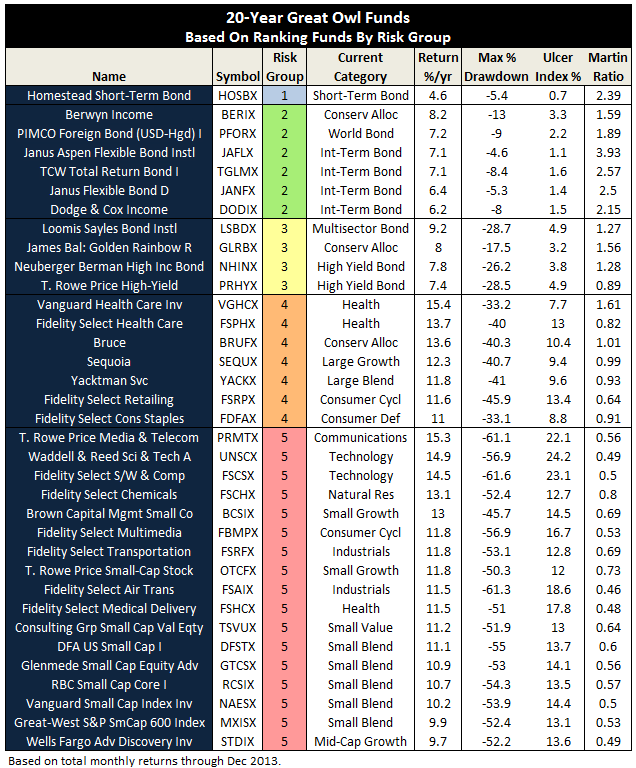


 I go out of the darkness
I go out of the darkness When I mention to institutional investors that I think the change in Japan is real, the most common response I get is a concern about “Abenomics.” This is usually expressed as “They are printing an awful lot of money.” Give me a break. Ben Bernanke and his little band of merry Fed governors have effectively been printing money with their various QE efforts. Who thinks that money will be repaid or the devaluation of the U.S. dollar will be reversed? The same can be said of the EU central bankers. If anything, the U.S. has been pursuing a policy of beggar thy creditor, since much of our debt is owed to others. At least in Japan, they owe the money to themselves. They have also gone through years of deflation without the social order and fabric of society breaking down. One wonders how the U.S. would fare in a similar long-term deflationary environment.
When I mention to institutional investors that I think the change in Japan is real, the most common response I get is a concern about “Abenomics.” This is usually expressed as “They are printing an awful lot of money.” Give me a break. Ben Bernanke and his little band of merry Fed governors have effectively been printing money with their various QE efforts. Who thinks that money will be repaid or the devaluation of the U.S. dollar will be reversed? The same can be said of the EU central bankers. If anything, the U.S. has been pursuing a policy of beggar thy creditor, since much of our debt is owed to others. At least in Japan, they owe the money to themselves. They have also gone through years of deflation without the social order and fabric of society breaking down. One wonders how the U.S. would fare in a similar long-term deflationary environment. 






 Since the number of funds we can cover in-depth is smaller than the number of funds worthy of in-depth coverage, we’ve decided to offer one or two managers each month the opportunity to make a 200 word pitch to you. That’s about the number of words a slightly-manic elevator companion could share in a minute and a half. In each case, I’ve promised to offer a quick capsule of the fund and a link back to the fund’s site. Other than that, they’ve got 200 words and precisely as much of your time and attention as you’re willing to share. These aren’t endorsements; they’re opportunities to learn more.
Since the number of funds we can cover in-depth is smaller than the number of funds worthy of in-depth coverage, we’ve decided to offer one or two managers each month the opportunity to make a 200 word pitch to you. That’s about the number of words a slightly-manic elevator companion could share in a minute and a half. In each case, I’ve promised to offer a quick capsule of the fund and a link back to the fund’s site. Other than that, they’ve got 200 words and precisely as much of your time and attention as you’re willing to share. These aren’t endorsements; they’re opportunities to learn more.  The traditional approach to buffering the stock market’s volatility without entirely surrendering the prospect of adequate returns was to divide the portfolio between (domestic, large cap) stocks and (domestic, investment grade) bonds, at a ratio of roughly 60/40. That strategy worked passably well as long as stocks could be counted on to produce robust returns and bonds could be counted on to post solid though smaller gains without fail. As the wheels began falling off that strategy, advisors began casting about for alternative strategies.
The traditional approach to buffering the stock market’s volatility without entirely surrendering the prospect of adequate returns was to divide the portfolio between (domestic, large cap) stocks and (domestic, investment grade) bonds, at a ratio of roughly 60/40. That strategy worked passably well as long as stocks could be counted on to produce robust returns and bonds could be counted on to post solid though smaller gains without fail. As the wheels began falling off that strategy, advisors began casting about for alternative strategies. 



 Vanguard Global Minimum Volatility Fund (VMVFX) launched on December 12, 2013. It’s Vanguard’s answer to the craze for “smart beta,” a strategy that seemingly promises both higher returns and lower risk over time. Vanguard dismisses the possibility with terms like “new-age investment alchemy,” and promise instead to provide reasonable returns with lower risk than an equity investor would otherwise be subject to. They are, they say, “trying to deliver broadly diversified exposure to the equity asset class, with lower average volatility over time than the market. We will use quantitative models to assess the expected volatility of stocks and correlation to one another.” They also intend to hedge currency risk in order to further dampen volatility.
Vanguard Global Minimum Volatility Fund (VMVFX) launched on December 12, 2013. It’s Vanguard’s answer to the craze for “smart beta,” a strategy that seemingly promises both higher returns and lower risk over time. Vanguard dismisses the possibility with terms like “new-age investment alchemy,” and promise instead to provide reasonable returns with lower risk than an equity investor would otherwise be subject to. They are, they say, “trying to deliver broadly diversified exposure to the equity asset class, with lower average volatility over time than the market. We will use quantitative models to assess the expected volatility of stocks and correlation to one another.” They also intend to hedge currency risk in order to further dampen volatility.  Meridian Small Cap Growth Fund launched on December 16th. The prospectus says very little about what the managers will be doing: “The portfolio managers apply a ‘bottom up’ fundamental research process in selecting investments. In other words, the portfolio managers analyze individual companies to determine if a company presents an attractive investment opportunity and if it is consistent with the Fund’s investment strategies and policies.”
Meridian Small Cap Growth Fund launched on December 16th. The prospectus says very little about what the managers will be doing: “The portfolio managers apply a ‘bottom up’ fundamental research process in selecting investments. In other words, the portfolio managers analyze individual companies to determine if a company presents an attractive investment opportunity and if it is consistent with the Fund’s investment strategies and policies.” Grandeur Peak Emerging Opportunities (GPEOX) launched two weeks ago, hasn’t released a word about its portfolio, has earned one half of one percent for its investors . . . and has drawn nearly $100 million in assets. Mr. Gardiner and company have a long-established plan to close the fund at $200 million. I’d encourage interested parties to (quickly!) read our review of
Grandeur Peak Emerging Opportunities (GPEOX) launched two weeks ago, hasn’t released a word about its portfolio, has earned one half of one percent for its investors . . . and has drawn nearly $100 million in assets. Mr. Gardiner and company have a long-established plan to close the fund at $200 million. I’d encourage interested parties to (quickly!) read our review of  Seafarer Overseas Growth & Income (SFGIX and SIGIX) is beginning to draw well-earned attention. Seafarer offers a particularly risk-conscious approach to emerging markets investing. It offers a compact (40 names), all-cap portfolio (20% in small- and microcap names and 28% in mid-caps, both vastly higher than its peers) that includes both firms domiciled in the emerging markets (about 70%) and those headquartered in the developing world but profiting from the emerging one (30%). It finished 2013 up 5.5%, which puts it in the top tier of all emerging markets funds.
Seafarer Overseas Growth & Income (SFGIX and SIGIX) is beginning to draw well-earned attention. Seafarer offers a particularly risk-conscious approach to emerging markets investing. It offers a compact (40 names), all-cap portfolio (20% in small- and microcap names and 28% in mid-caps, both vastly higher than its peers) that includes both firms domiciled in the emerging markets (about 70%) and those headquartered in the developing world but profiting from the emerging one (30%). It finished 2013 up 5.5%, which puts it in the top tier of all emerging markets funds. 
 And so they did what any sensible group would do. They partied. One day’s worth of oil became eight nights’ worth of light; Jewish friends gathered, ate and gifted. Bacchus reigned from our Thanksgiving to the Winter Solstice, and the Romans drank straight through it. The Kalash people of Pakistan sang, danced, lit bonfires and feasted on goat tripe “and other delicacies” (oh, yum!). Chinese and Korean families gathered and celebrated with balls of glutinous rice (more yum!). Welsh friends dressed up like wrens (yuh), and marched from home to home, singing and snacking. Romans in the third century CE celebrated Dies Natalis Solis Invicti (festival of the birth of the Unconquered Sun) on December 25th, a date later borrowed by Christians for their own mid-winter celebration. Some enterprising soul, having consumed most of the brandy, inexplicably mashed together figs, stale bread and the rest of the brandy. Figgy pudding was born and revelers refused to go until they got some (along with a glass of good cheer).
And so they did what any sensible group would do. They partied. One day’s worth of oil became eight nights’ worth of light; Jewish friends gathered, ate and gifted. Bacchus reigned from our Thanksgiving to the Winter Solstice, and the Romans drank straight through it. The Kalash people of Pakistan sang, danced, lit bonfires and feasted on goat tripe “and other delicacies” (oh, yum!). Chinese and Korean families gathered and celebrated with balls of glutinous rice (more yum!). Welsh friends dressed up like wrens (yuh), and marched from home to home, singing and snacking. Romans in the third century CE celebrated Dies Natalis Solis Invicti (festival of the birth of the Unconquered Sun) on December 25th, a date later borrowed by Christians for their own mid-winter celebration. Some enterprising soul, having consumed most of the brandy, inexplicably mashed together figs, stale bread and the rest of the brandy. Figgy pudding was born and revelers refused to go until they got some (along with a glass of good cheer).

 Roy Weitz first published the legacy Three Alarm fund list in 1996. He wanted to help investors decide when to sell mutual funds. Being on the list was not an automatic sell, but a warning signal to look further and see why.
Roy Weitz first published the legacy Three Alarm fund list in 1996. He wanted to help investors decide when to sell mutual funds. Being on the list was not an automatic sell, but a warning signal to look further and see why.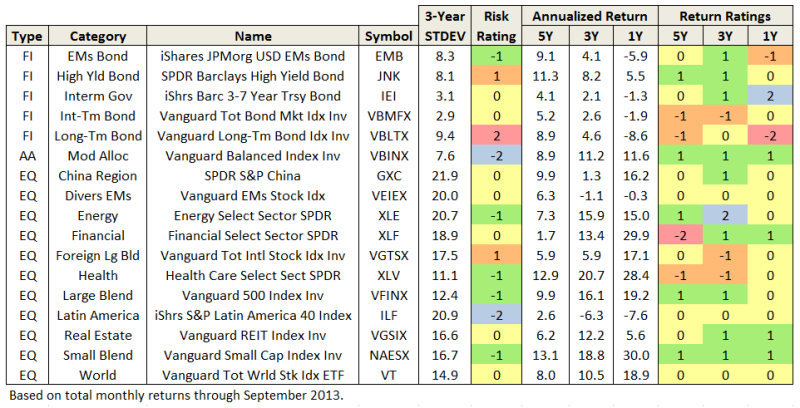
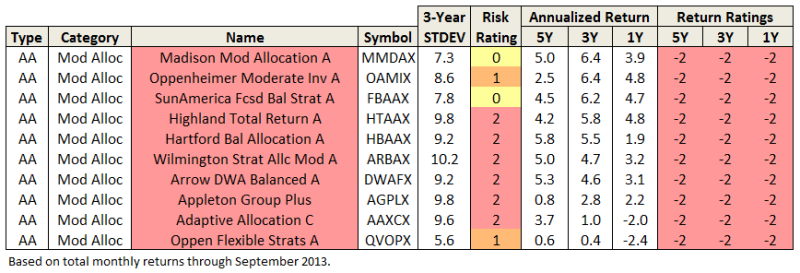

 On November 13, Morningstar published an essay entitled “
On November 13, Morningstar published an essay entitled “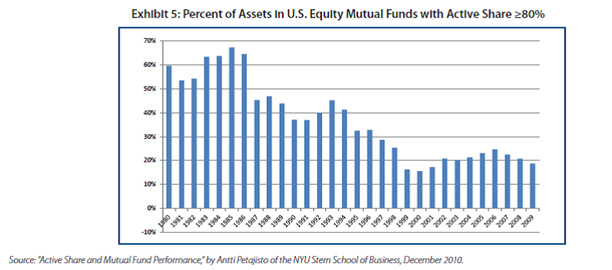
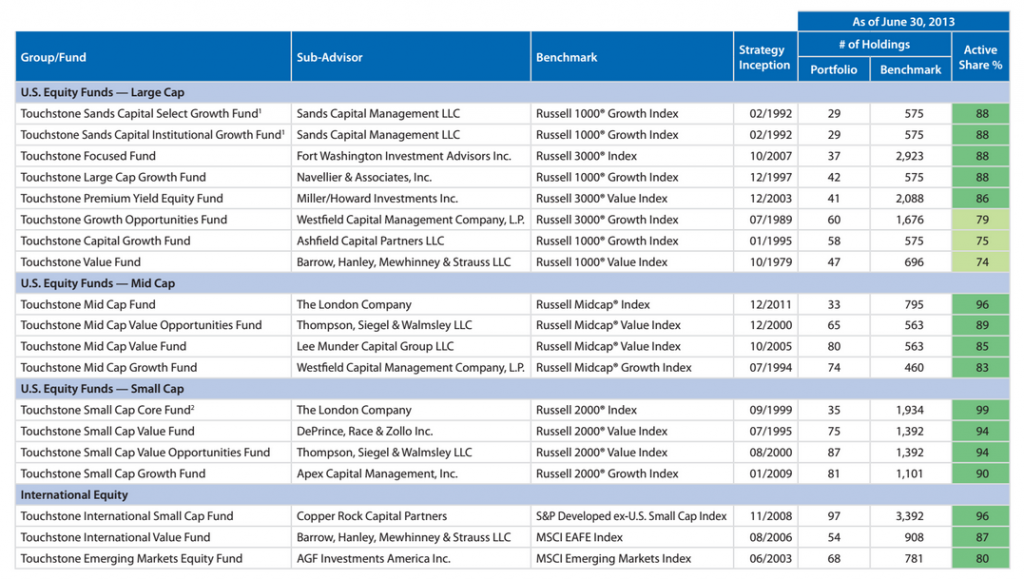

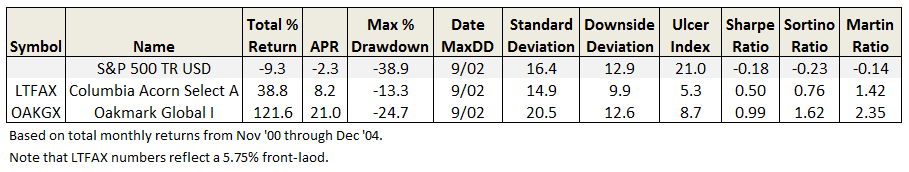

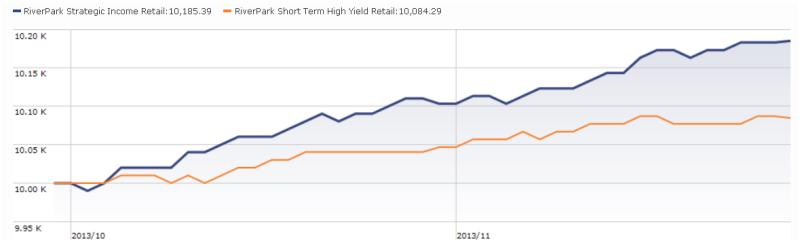
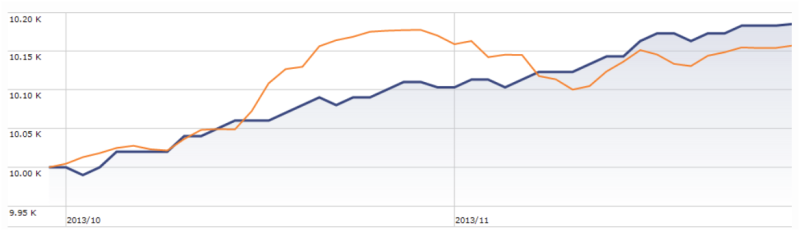
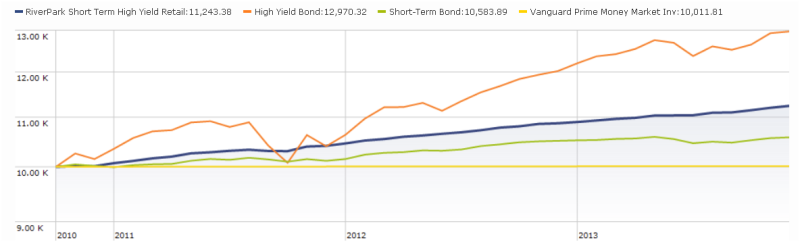
 Last month we noted, with unwarranted snarkiness, the reorganization of Aegis Value Fund (AVALX). We have now had a chance to further review
Last month we noted, with unwarranted snarkiness, the reorganization of Aegis Value Fund (AVALX). We have now had a chance to further review  In a surprising announcement, Forward Funds removed a four-person team from Cedar Ridge Partners as the sub-advisers responsible for Forward Credit Analysis Long/Short Fund (FLSLX). The fund was built around Cedar Ridge’s expertise in muni bond investing and the team had managed the fund from inception. Considered as a “non-traditional bond” fund by Morningstar, FLSLX absolutely clubbed their peers in 2009, 2011, and 2012 while trailing a bit in 2010. Then this in 2013:
In a surprising announcement, Forward Funds removed a four-person team from Cedar Ridge Partners as the sub-advisers responsible for Forward Credit Analysis Long/Short Fund (FLSLX). The fund was built around Cedar Ridge’s expertise in muni bond investing and the team had managed the fund from inception. Considered as a “non-traditional bond” fund by Morningstar, FLSLX absolutely clubbed their peers in 2009, 2011, and 2012 while trailing a bit in 2010. Then this in 2013:


 Some guys wear ties rarely enough that they need to keep that little “how to tie a tie” diagram taped to their bathroom mirrors. Other guys really wish that they had a job where they wore ties rarely enough that they needed to keep that little “how to tie a tie” diagram taped up.
Some guys wear ties rarely enough that they need to keep that little “how to tie a tie” diagram taped to their bathroom mirrors. Other guys really wish that they had a job where they wore ties rarely enough that they needed to keep that little “how to tie a tie” diagram taped up.




 Here’s today’s “know your Morningstar!” quiz.
Here’s today’s “know your Morningstar!” quiz. 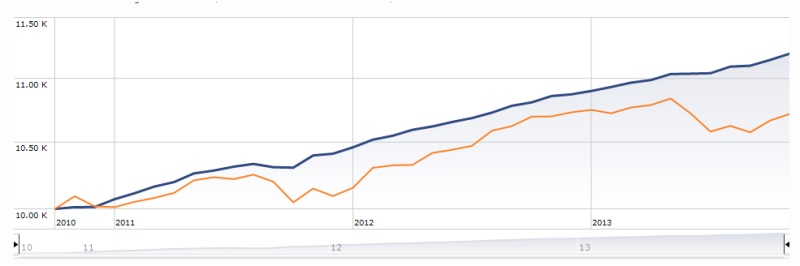

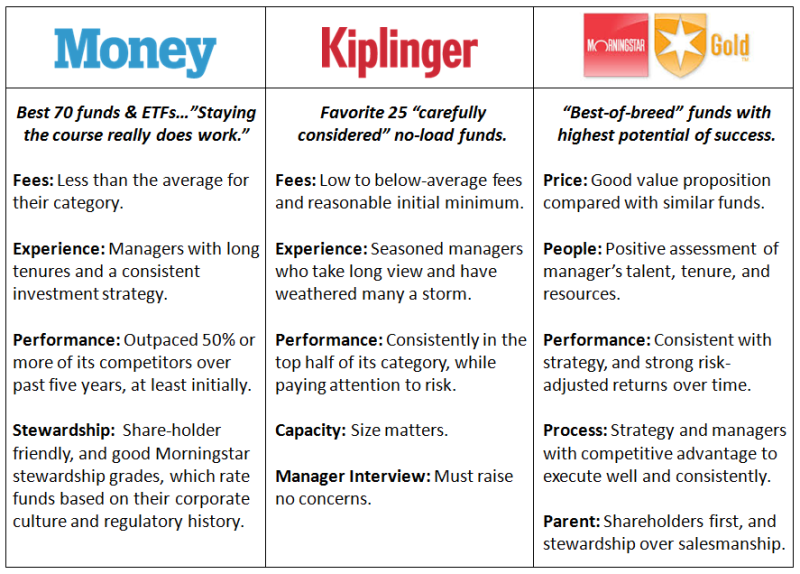
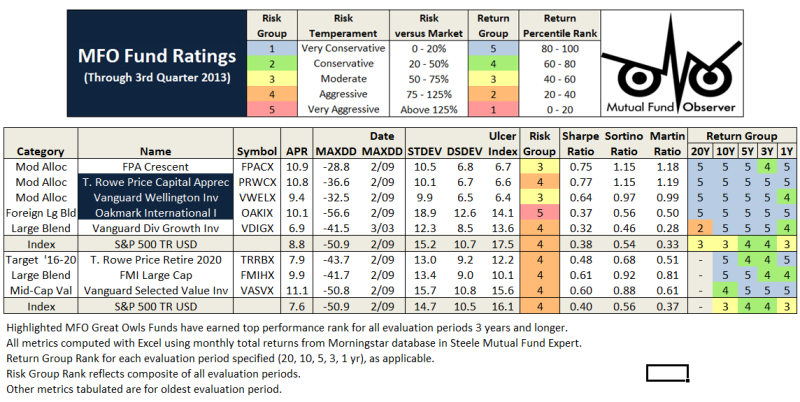
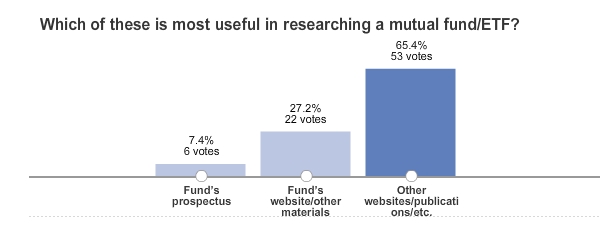
 In a fundamentally hostile environment, investors need to have a flexible approach to income investing. Some funds express that flexibility by investing in emerging market bonds, financial derivatives such as options, or illiquid securities (think: “lease payments from the apartment complex we just bought”).
In a fundamentally hostile environment, investors need to have a flexible approach to income investing. Some funds express that flexibility by investing in emerging market bonds, financial derivatives such as options, or illiquid securities (think: “lease payments from the apartment complex we just bought”).
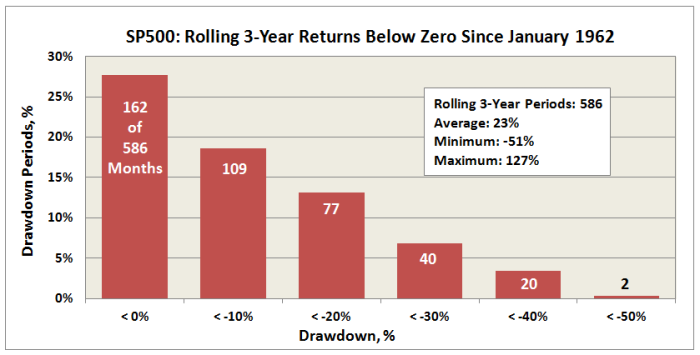
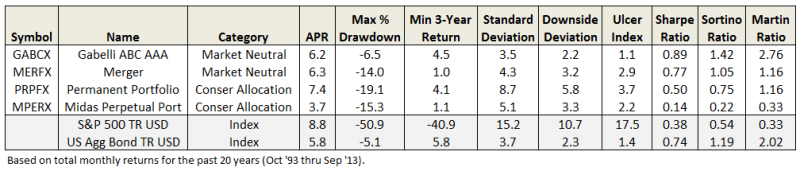
 On November 18, Observer readers will have the opportunity to hear from, and speak to John Park and Greg Jackson, co-managers of
On November 18, Observer readers will have the opportunity to hear from, and speak to John Park and Greg Jackson, co-managers of  A Centaur arises! The Tilson funds used to be a two-fund family: the one that Mr. Tilson ran and the one that was really good. After years of returns that never quite matched the hype, Mr. Tilson liquidated his Tilson Focus (TILFX) fund in June 2013. That left behind the Tilson-less
A Centaur arises! The Tilson funds used to be a two-fund family: the one that Mr. Tilson ran and the one that was really good. After years of returns that never quite matched the hype, Mr. Tilson liquidated his Tilson Focus (TILFX) fund in June 2013. That left behind the Tilson-less  On-going thanks to The Shadow for help in tracking the consequences of “the perennial gale of creative destruction” blowing through the industry. Shadow, a member of the Observer’s discussion community, has an uncanny talent for identifying and posting fund liquidations (and occasionally) launches to our discussion board about, oh, 30 seconds after the SEC first learns of the change. Rather more than three dozen of the changes noted here and elsewhere in Briefly Noted were flagged by The Shadow. While my daily reading of SEC 497 filings identified most of the them, his work really does contribute a lot.
On-going thanks to The Shadow for help in tracking the consequences of “the perennial gale of creative destruction” blowing through the industry. Shadow, a member of the Observer’s discussion community, has an uncanny talent for identifying and posting fund liquidations (and occasionally) launches to our discussion board about, oh, 30 seconds after the SEC first learns of the change. Rather more than three dozen of the changes noted here and elsewhere in Briefly Noted were flagged by The Shadow. While my daily reading of SEC 497 filings identified most of the them, his work really does contribute a lot. 
 October’s a month of surprises, from the first morning that you see frost on the grass to the appearance of ghosts and ghouls at month’s end. It’s a month famous of market crashes – 1929, 1987, 2008 – and for being the least hospitable to stocks. And now it promises to be a month famous for government showdowns and shutdowns, when the sales of scary Halloween masks (Barackula, anyone?) take off.
October’s a month of surprises, from the first morning that you see frost on the grass to the appearance of ghosts and ghouls at month’s end. It’s a month famous of market crashes – 1929, 1987, 2008 – and for being the least hospitable to stocks. And now it promises to be a month famous for government showdowns and shutdowns, when the sales of scary Halloween masks (Barackula, anyone?) take off.
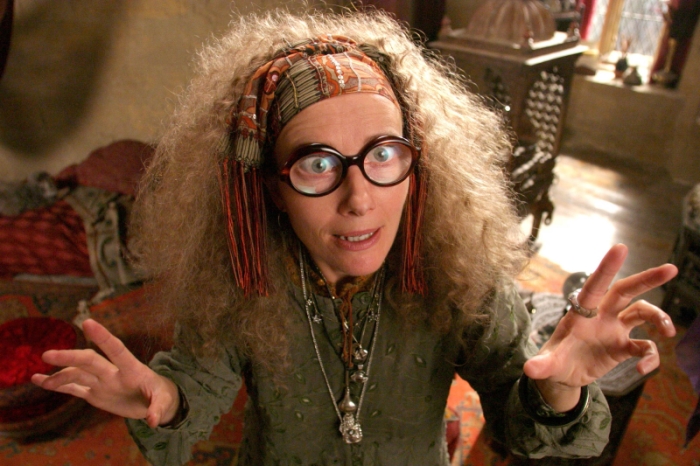



 Wise Capital (WISEX) provides investors with an opportunity for diversification in a fund category (short term bonds) mostly distinguished by bland uniformity: 10% cash, one equity security thrown in for its thrill-value, about 90% of the bond portfolio would be US with a dribble of Canadian and British issues, 90% A-AAA rated and little distance between the fund and its peers.
Wise Capital (WISEX) provides investors with an opportunity for diversification in a fund category (short term bonds) mostly distinguished by bland uniformity: 10% cash, one equity security thrown in for its thrill-value, about 90% of the bond portfolio would be US with a dribble of Canadian and British issues, 90% A-AAA rated and little distance between the fund and its peers. 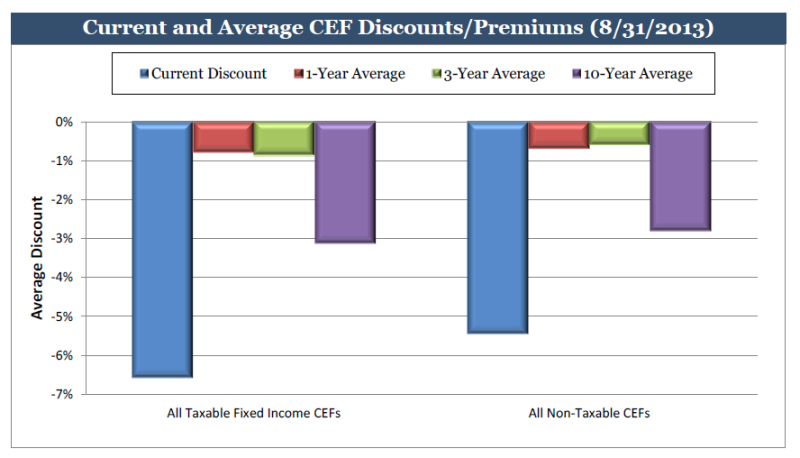
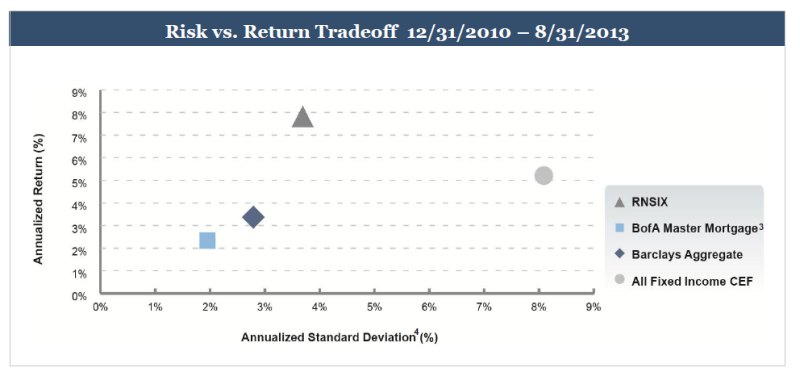

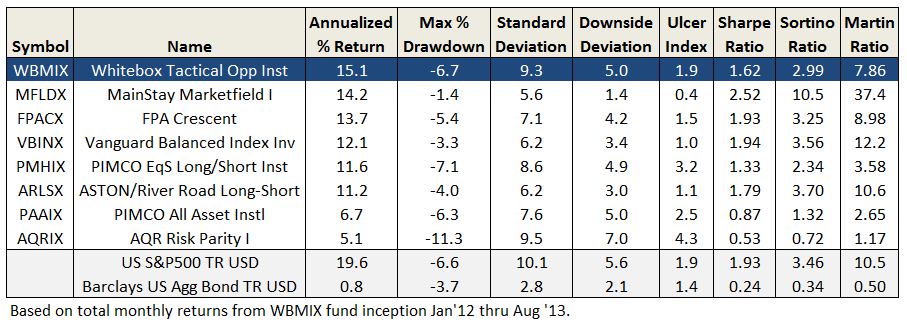
 Morningstar declared
Morningstar declared  I really like Manning & Napier. They are killing off three funds that were never a good match for the firm’s core strengths. Manning & Napier Small Cap (MNSMX), Life Sciences (EXLSX), and Technology (EXTCX) will all cease to exist on or about January 24, 2014. My affection for them comes to mind because these funds, unlike the vast majority that end up in the trash heap, were all economically viable. Between them they have over $600 million in assets and were producing $7 million/year in revenue for M&N. The firm’s great strength is risk-conscious, low-cost, team-managed diversified funds. Other than a real estate fund, they offer almost no niche products really. Heck, the tech fund even had a great 10-year record and was no worse than mediocre in shorter time periods. But, it seems, they didn’t make sense given M&N’s focus.
I really like Manning & Napier. They are killing off three funds that were never a good match for the firm’s core strengths. Manning & Napier Small Cap (MNSMX), Life Sciences (EXLSX), and Technology (EXTCX) will all cease to exist on or about January 24, 2014. My affection for them comes to mind because these funds, unlike the vast majority that end up in the trash heap, were all economically viable. Between them they have over $600 million in assets and were producing $7 million/year in revenue for M&N. The firm’s great strength is risk-conscious, low-cost, team-managed diversified funds. Other than a real estate fund, they offer almost no niche products really. Heck, the tech fund even had a great 10-year record and was no worse than mediocre in shorter time periods. But, it seems, they didn’t make sense given M&N’s focus. 
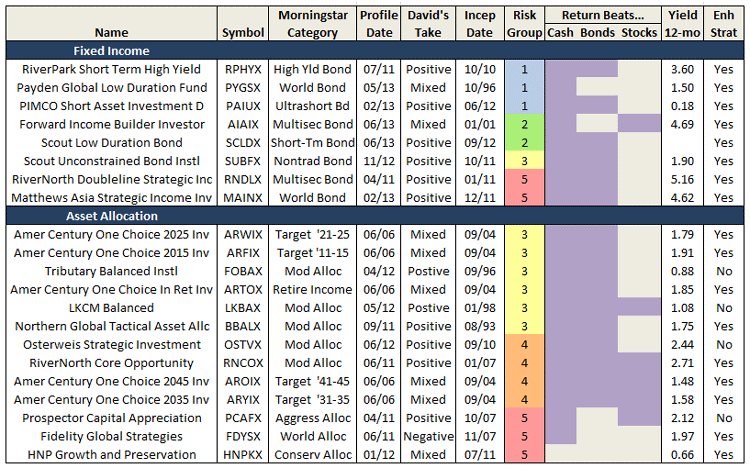
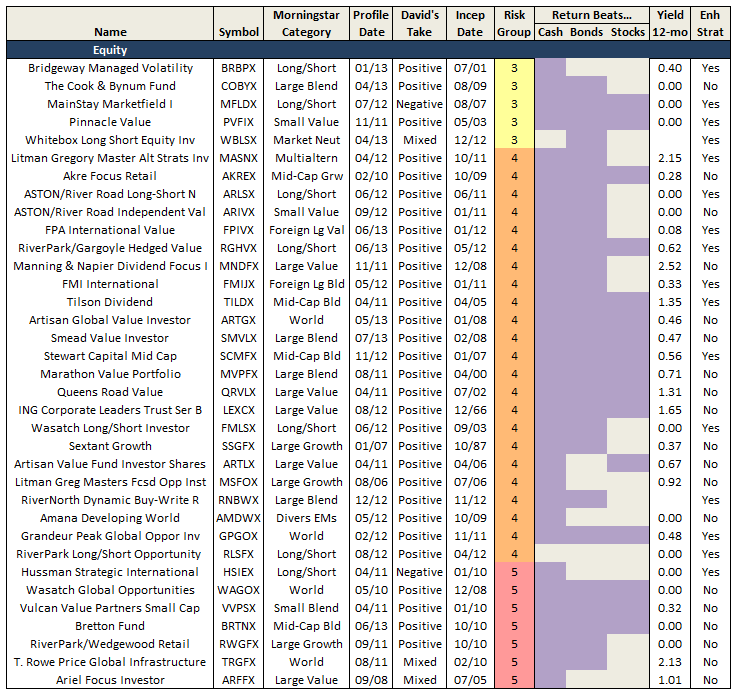
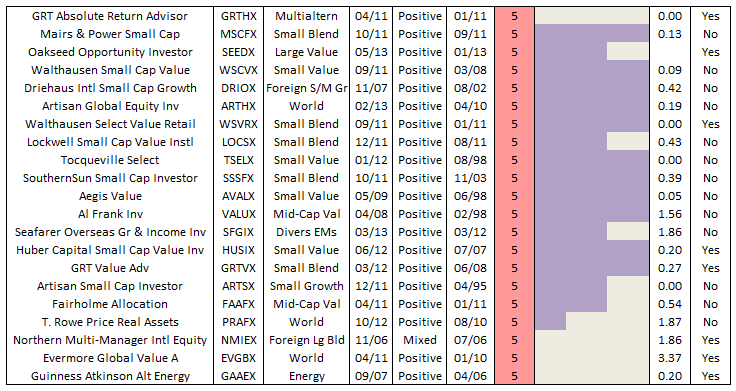
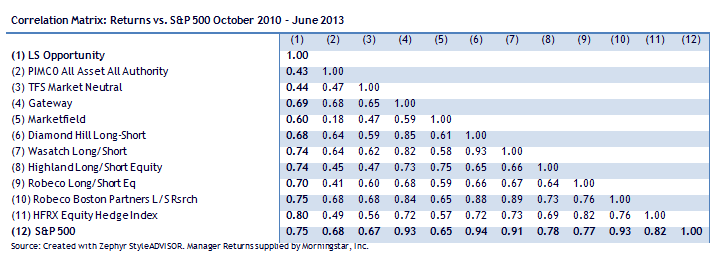 This does not automatically justify inclusion of a second or third long-short fund in your portfolio, but it does demonstrate two things. First, that long-short funds really are vastly different from one another, which is why their correlations are so low. Second, a single long-short fund offers considerable diversification in a long-only portfolio and a carefully selected second fund might add a further layer of independence.
This does not automatically justify inclusion of a second or third long-short fund in your portfolio, but it does demonstrate two things. First, that long-short funds really are vastly different from one another, which is why their correlations are so low. Second, a single long-short fund offers considerable diversification in a long-only portfolio and a carefully selected second fund might add a further layer of independence.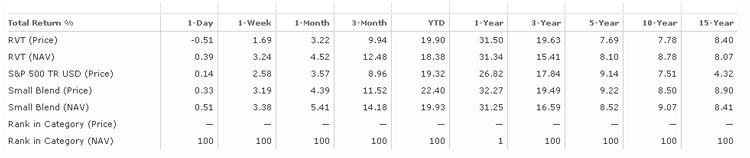





 This comes up only because I was moved to sudden and profound pity over the cruel ways in which the poor, innocent rich folks are being ruthlessly exploited. Two new articles highlight their plight.
This comes up only because I was moved to sudden and profound pity over the cruel ways in which the poor, innocent rich folks are being ruthlessly exploited. Two new articles highlight their plight. “it’s somewhere between highly probable and certain that you will underperform [a stock portfolio] if you are being sold commodities, hedge funds and private equity right now.”
“it’s somewhere between highly probable and certain that you will underperform [a stock portfolio] if you are being sold commodities, hedge funds and private equity right now.”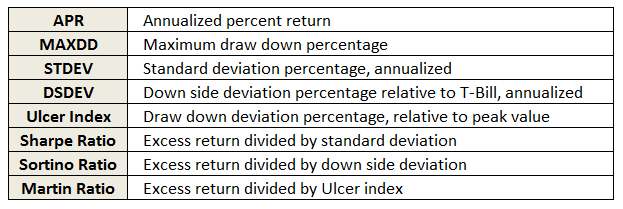
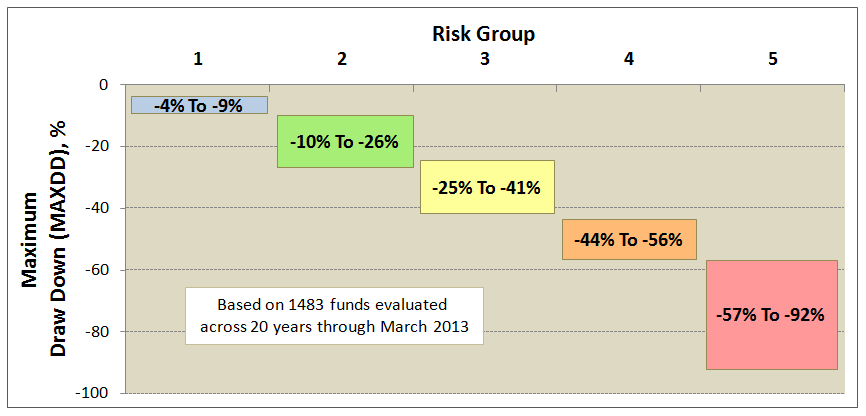
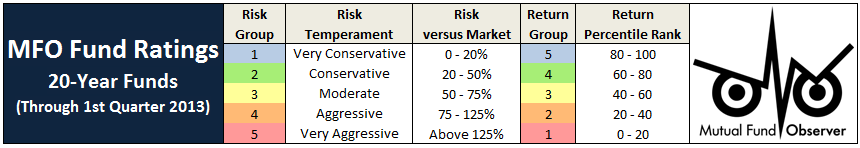
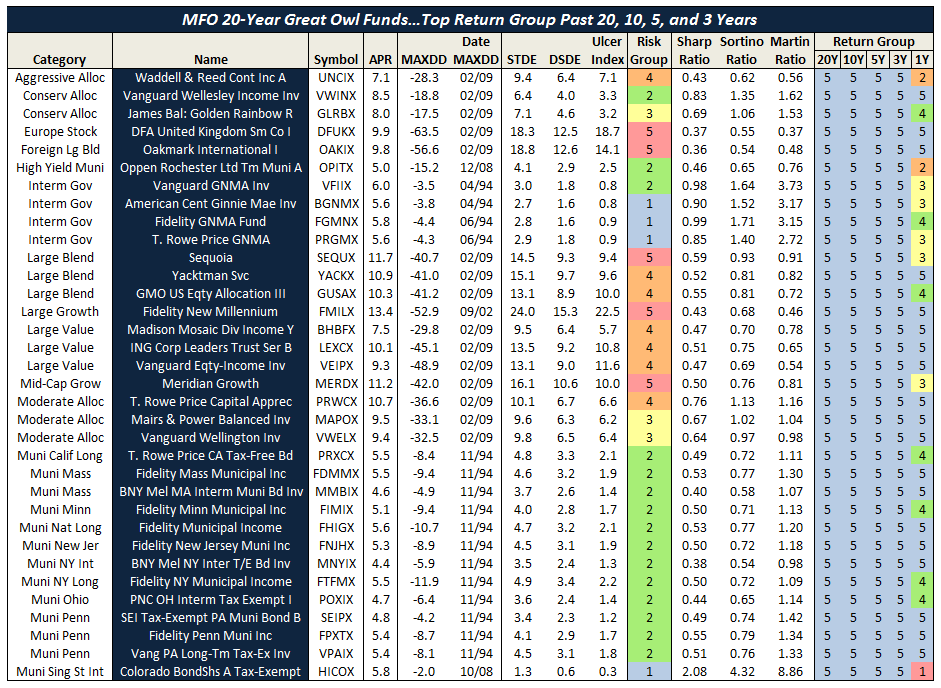
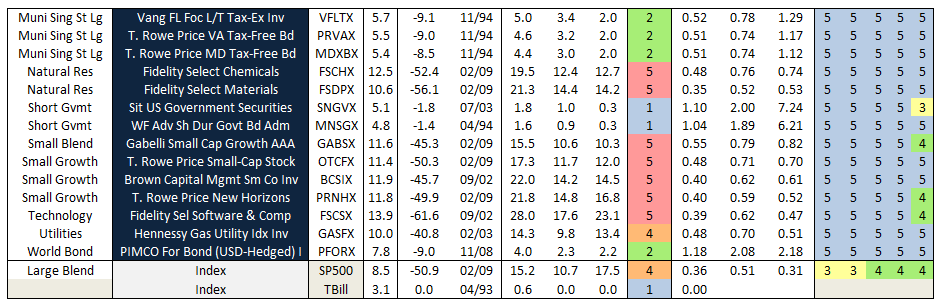
 Does it make sense to you that you could profit from following the real-life choices of the professionals in your life? What hospital does your doctor use when her family needs one? Where does the area’s best chef eat when he wants to go out for a weeknight dinner? Which tablet computer gets Chip and her IT guys all shiny-eyed?
Does it make sense to you that you could profit from following the real-life choices of the professionals in your life? What hospital does your doctor use when her family needs one? Where does the area’s best chef eat when he wants to go out for a weeknight dinner? Which tablet computer gets Chip and her IT guys all shiny-eyed?
 Valley Forge Fund (VAFGX) closes the gap, a bit. We reported in May that Valley Forge’s manager died on November 3, but that the Board of Directors didn’t seem to have, well, hired a new one. We stand corrected. First, according to an April proxy statement, the Board had terminated the manager three days before his actual, well, you know, termination.
Valley Forge Fund (VAFGX) closes the gap, a bit. We reported in May that Valley Forge’s manager died on November 3, but that the Board of Directors didn’t seem to have, well, hired a new one. We stand corrected. First, according to an April proxy statement, the Board had terminated the manager three days before his actual, well, you know, termination. MFO has periodically been the object of as many at 400 break-in attempts an hour. Either manually or through our security software we’ve “blacklisted” nearly a thousand IP addresses, including a vast number from China.
MFO has periodically been the object of as many at 400 break-in attempts an hour. Either manually or through our security software we’ve “blacklisted” nearly a thousand IP addresses, including a vast number from China. Alan Abelson (October 12, 1925 – May 9, 2013), Barron’s columnist and former editor, passed away at age 87. He joined Barron’s the year I was born, began his “Up & Down Wall Street” column during the Johnson Administration and continued it for 47 years. His crankiness made him, for a long while, one of the folks I actively sought out each week. In recent years he seemed to have become a sort of parody of his former self, cranky on principle rather than for any particular cause. I’ll remember him fondly and with respect. Randall Forsyth will continue the column.
Alan Abelson (October 12, 1925 – May 9, 2013), Barron’s columnist and former editor, passed away at age 87. He joined Barron’s the year I was born, began his “Up & Down Wall Street” column during the Johnson Administration and continued it for 47 years. His crankiness made him, for a long while, one of the folks I actively sought out each week. In recent years he seemed to have become a sort of parody of his former self, cranky on principle rather than for any particular cause. I’ll remember him fondly and with respect. Randall Forsyth will continue the column. Speaking of cranks, John Rekenthaler has resumed his
Speaking of cranks, John Rekenthaler has resumed his 

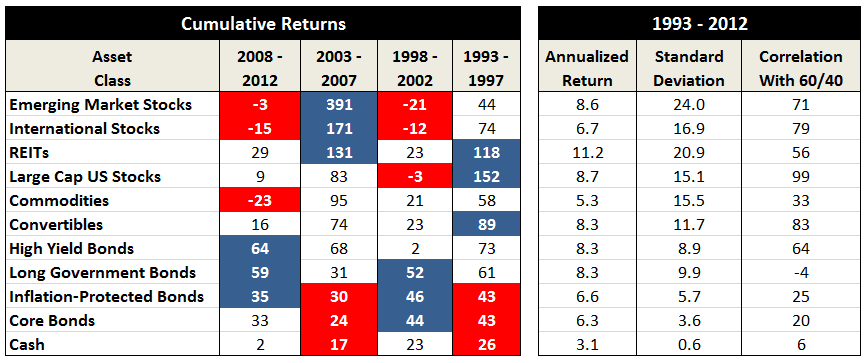

 We started by thinking about the Observer’s mission and ethos, and how best to capture that visually. The apparent dignity, quiet watchfulness and unexpected ferocity of the Great Horned Owl – they’re sometimes called “tigers with wings” and are quite willing to strike prey three times their own size – was immediately appealing. Barb’s genius is in identifying the essence of an image, and stripping away everything else. She admits, “I don’t know what to say about the wise old owl, except he lends himself soooo well to minimalist geometric treatment just naturally, doesn’t he? I wanted to trim off everything not essential, and he still looks like an owl.”
We started by thinking about the Observer’s mission and ethos, and how best to capture that visually. The apparent dignity, quiet watchfulness and unexpected ferocity of the Great Horned Owl – they’re sometimes called “tigers with wings” and are quite willing to strike prey three times their own size – was immediately appealing. Barb’s genius is in identifying the essence of an image, and stripping away everything else. She admits, “I don’t know what to say about the wise old owl, except he lends himself soooo well to minimalist geometric treatment just naturally, doesn’t he? I wanted to trim off everything not essential, and he still looks like an owl.”
 r. Hillary manages Independence Capital Asset Partners (ICAP), a long/short equity hedge fund he launched on November 1, 2004 that serves as the sub-advisor to the LS Opportunity Fund (LSOFX), which in turn launched on September 29, 2010. Prior to embarking on a hedge fund career, Mr. Hillary was a co-founder and director of research for Marsico Capital Management where he managed the Marsico 21st Century Fund (MXXIX) until February 2003 and co-managed all large cap products with Tom Marsico. In addition to his US hedge fund and LSOFX in the mutual fund space, ICAP runs a UCITS for European investors. Jim offers these 200 words on why his mutual fund could be right for you:
r. Hillary manages Independence Capital Asset Partners (ICAP), a long/short equity hedge fund he launched on November 1, 2004 that serves as the sub-advisor to the LS Opportunity Fund (LSOFX), which in turn launched on September 29, 2010. Prior to embarking on a hedge fund career, Mr. Hillary was a co-founder and director of research for Marsico Capital Management where he managed the Marsico 21st Century Fund (MXXIX) until February 2003 and co-managed all large cap products with Tom Marsico. In addition to his US hedge fund and LSOFX in the mutual fund space, ICAP runs a UCITS for European investors. Jim offers these 200 words on why his mutual fund could be right for you: I had a chance to speak with David Rolfe of Wedgewood Partners and Morty Schaja, president of RiverPark Funds. A couple dozen listeners joined us, though most remained shy and quiet. Morty opened the call by noting the distinctiveness of RWGFX’s performance profile: even given a couple quarters of low relative returns, it substantially leads its peers since inception. Most folks would expect a very concentrated fund to lead in up markets. It does, beating peers by about 10%. Few would expect it to lead in down markets, but it does: it’s about 15% better in down markets than are its peers. Mr. Schaja is invested in the fund and planned on adding to his holdings in the week following the call.
I had a chance to speak with David Rolfe of Wedgewood Partners and Morty Schaja, president of RiverPark Funds. A couple dozen listeners joined us, though most remained shy and quiet. Morty opened the call by noting the distinctiveness of RWGFX’s performance profile: even given a couple quarters of low relative returns, it substantially leads its peers since inception. Most folks would expect a very concentrated fund to lead in up markets. It does, beating peers by about 10%. Few would expect it to lead in down markets, but it does: it’s about 15% better in down markets than are its peers. Mr. Schaja is invested in the fund and planned on adding to his holdings in the week following the call. Manager Steve Dodson, former president of the Parnassus Funds, is an experienced investment professional, pursuing a simple discipline. He wants to buy deeply discounted stocks, but not a lot of them. Where some funds tout a “best ideas” focus and then own dozens of the same large cap stocks, Mr. Dodson seems to mean it when he says “just my best.”
Manager Steve Dodson, former president of the Parnassus Funds, is an experienced investment professional, pursuing a simple discipline. He wants to buy deeply discounted stocks, but not a lot of them. Where some funds tout a “best ideas” focus and then own dozens of the same large cap stocks, Mr. Dodson seems to mean it when he says “just my best.”