Dear friends,
 What a difference a month makes. When I wrote to you last month, it was 18 degrees below zero. Right now it’s
What a difference a month makes. When I wrote to you last month, it was 18 degrees below zero. Right now it’s 90 … 100 degrees warmer … and my students have noticed. Not only is there spring finery on display, but attendance at late afternoon classes seems to be just a bit iffy. All for good reason, of course: horrible contagious hacking coughs, migraines, spontaneously-combusting roommates, all the usual signs of spring.
I admit to a profound ambivalence about the weather. I visited Lake Mead, the reservoir behind Boulder Dam, a couple weeks ago. The water level is 100’ below capacity and neither the recorded audio nor the tour guides really wanted to talk about why or what it might mean. As I flew home, I noticed mountains with virtually no snow pack. California today imposed the first statewide water restrictions in the state’s history as they faced the prospect of absolute rather than just relative shortage. Geologists have discovered rivers flowing under Antarctica’s “grounded ice” and oceanographers note that the Atlantic oceans currents are slowing.
I worry that all too many of us think something like, “the worst-case is too awful to imagine, so I’m not going to think about this stuff.” Meanwhile, members of the U.S. Congress excuse their refusal to take it seriously with the carefully-rehearsed excuse, “I’m not a scientist,” as if that had some meaning greater than “I don’t want to offend either donors or primary voters, so I think I’ve found a slick way to dodge my responsibilities.”
I worry, too, that my efforts (a garden that needs little by way of watering or chemicals, a carefully insulated house that sips electric, carbon offsets for my travel, a small car matched with a tendency to walk where I need to go) and the Observer’s (we’ve got a very small carbon footprint, in part because we use a “green” hosting service) are trivial. All of which puts me in a state to cry:
The End is coming! The End is coming!
Soon … er.
Or later. That is, the stock market is going to crash.
I don’t really know when. Okay, fine: I haven’t got an earthly clue. Then again, neither does anyone else. I looked back at the financial media in the months before the market crash in 2007. The Lexis-Nexis database contains around 800 stock market stories for the three months immediately before the worst collapse in three-quarters of a century. By limiting the search to U.S. sources, I got it down to a nearly-manageable 400 or so which I proceeded to scan.
Here’s what I discovered: almost without exception, the public statements of major financial media outlets, mutual fund managers and hedge fund managers were stunningly clueless. Almost without exception, the story was that other than for one or two little puffy clouds in the distance, the skies were clear, you should have a song in your heart and a buy order in your hands.
Kiplinger’s led that parade with “Why Stocks Will Keep Going Up” (July). BusinessWeek urged us, “Don’t Be Afraid of the Dark” (August 13). Money asked “Is This Bull Ready to Leave” (July) and concluded that the market was undervalued and that large cap growth stocks had “a strong outlook.” Fortune did some fortune-telling and found “A Sunny Second Half” (July 9); relying on “a hedge fund superstar,” they promised “This Bull Has Legs” (August 20). John Rogers of the Ariel Funds declared “Subprime Risks: Overblown … [it’s] time to buy” (September 17). Standard & Poor’s thought “equities could register nice gains by the end of the year” (September 20) as the result of a Fed-fueled breakout.
Only GMO’s Jeremy Grantham stood out:
Even if the credit crunch passes without a major catastrophe, the prices of stocks, bonds, and real estate have a long way to fall
Credit crises have always been painful and unpredictable. The current one is particularly hair-raising because it’s occurring amid the first truly global bubble in asset pricing. It is also accompanied by a plethora of new and ingenious financial instruments. These are designed overtly to spread risk around and to sell fee-bearing products that are in great demand. Inadvertently (to be generous), they have been constructed to hide risk and confuse buyers. How this credit crisis works out and what price we end up paying has to be largely unknowable, depending as it does on hundreds of interlocking and often novel factors and how they in turn affect animal spirits. In the end it is, of course, the management of animal spirits that makes and breaks credit crises. “Danger: Steep Drop Ahead” (Fortune, September 17).
My scan excludes results for The Wall Street Journal, since neither the Journal’s own archive search nor the Lexis database cover the Journal’s articles for the period so it’s possible that the clear-eyed Jason Zweig was standing on the parapet crying “beware!”
|
This just in! Jason wrote and allowed that he was actually more between “Pollyanna-ish” and “probably not dour enough”. Huh…he can be forgiven his youthful optimism. If only he understood the wisdom of the aging brain. |
We do know that, in general, markets are more apt to fall when valuations get out of hand and the market encounters an exogenous shock. That is, some cataclysmic event outside of the market; for example, in 2013 Fed chair Ben Bernanke allowed that “we could take a step down in our pace of purchase” of Treasury securities. The subsequent “taper tantrum” saw US bond markets drop 3% in three months. Ummm … that would be a trillion dollar setback.
If we can’t know when the crash will come, can we at least figure out whether the market is overvalued?
Ummm … no, though heaven knows we’ve tried. Here’s a sampling:
- Morningstar suggests that the market is overvalued by 4% (as of 3/23), which seems modest until you notice that the market seems to correct when it hits 5% overvalued. It hit 5% in May 2011 and the market dropped about 19% by the beginning of August. The market reached 10-14% overvalued in late 2004 and 2005, during which time it surged 17%. Other than for that stretch, market overvaluation hasn’t exceeded 5-7% before correcting. Matt Coffina, StockInvestor editor, agrees that “we see little margin of safety and few opportunities in current stock prices… Investors in common stocks must have a long time horizon and the patience and discipline to ride out volatility.” He identified industrials, technology, health care, consumer defensive, and utilities as the most overvalued sectors.
- Mark Hulbert argues that, “based on six well-known and time-tested indicators, equities are more overvalued today than they’ve been between 69% and 89% of the past century’s bull-market tops.”
- Doug Short, one of the guys behind Advisor Perspectives, worries that, “Based on the latest S&P 500 monthly data, the market is overvalued somewhere in the range of 64% to 98%, depending on the indicator, up from the previous month’s 60% to 94%.” He does allow that markets can remain overvalued for years, though today’s high valuations translate to tomorrow’s tepid returns.
- Jim Paulsen, chief investment strategist at Wells Capital Management, finds that the median stock in the NYSE trades, based on its price/earnings and price/cash flow ratios, at post WW2 highs. Why look at the median? Because most stock indices are cap-weighted, the valuations of the few largest stocks can materially change the entire index’s weight; he admits the S&P500 appears “slightly above average but not excessive.” By looking at the median stock, he’s trying to gauge whether the market is broadly overvalued.
- Doug Ramsey, chief investment officer for the Leuthold Group and co-manager of the outstanding Leuthold Core Investment Fund (LCORX), in an email exchange, notes that “We have a composite Intrinsic Value reading for the stock market based on 25 different measures, with weightings based on the long-term correlation of each measure with subsequent 3-, 5- and 10-yr. total returns … The composite of our 25 measures finds U.S. stocks moderately overvalued, but the situation is different than peaks like 2000 and 2007 because we find the overvaluation to be very broad-based. In other words, valuation measures on the median or ‘typical’ U.S. stock are even higher than seen at 2000 or 2007. This phenomenon isn’t fully captured by valuation measures on the cap-weighted indexes.”
Even when high valuations aren’t followed by crashes, they tend to predict weak future returns. GMO’s forward-looking asset class forecast is among the glummest I’ve seen: they anticipate negative real returns over the next 5-7 years in nine of the 12 asset classes they track:
(3.5%) Int’l bonds (currency hedged)
(3.4%) US small cap
(2.4%) US large cap
(1.0%) US bonds
(0.5%) TIPs
(0.3%) Cash
(0.2%) Int’l small cap
(0.1%) US high quality
0.0% Int’l large cap
2.6% EM bonds
2.9% EM equity
5.4% Managed timber
AQR, a global investment management firm “built at the intersection of financial theory and practical application” advises the AQR funds and manages about $120 billion. Their projections for the next five to ten years, courtesy of our friends at DailyAlts.com, are more optimistic than Leuthold’s, but nothing it celebrate:
AQR’s current estimate of U.S. stocks’ long-term real (above inflation) returns is just 3.8%. European, Australian, Canadian, and emerging market stocks are all projected to outperform the U.S., with respective long-term real returns of 5.5%, 6.1%, 4.6%, and 6.6%. U.K. stocks are expected to generate long-term real returns of 6.2%, also besting the U.S.; while only Japanese stocks are expected to underperform American equities, with returns of 3.5% above inflation.
So, 3.8 – 6.6% real returns. That’s not far from Leuthold’s estimate: “For investors who’ve missed the entire bull market to this point, we’d advise strongly against jumping into stocks with both feet; long-term (5- to 10-yr.) total returns are almost assured to be depressed (on the order of 3 to 5%, we would estimate).”
At the other end, several recent analyses by serious investors have reached the opposite conclusion: that the market is no more than modestly pricey, if that. After warning folks not to base their conclusions on a single valuation measure, the estimable Barry Ritholtz identifies a single valuation measure (enterprise value to EBITDA) as the most probative and concludes from it that the market is modestly valued.
… what has been considered the best-performing measure of markets suggests that U.S. stocks are not expensive — are indeed priced fairly. This strongly suggests that the expected future returns for U.S. equities will be about their historic average.
Ritholtz’s faith in EV:EBITDA derives, in part, from research by Wesley Gray. We contacted Mr. Gray who was busily crunching numbers in response to Mr. Ritzholtz’s piece. In a mid-March essay, he too concluded that there was no cause for concern:
The metrics aren’t screaming “overvalued:” P/E, P/B, TEV/EBITDA, and TEV/GP are all in the 50-75 percentile; TEV/FCF is actually in the 2 to 25 percentile. In fact, adjusted for the current interest rate environment (much lower than it was in the past), the argument that the market is extremely overvalued is far-fetched.
Here’s where that leaves us: the stock market has recorded double-digit gains in five of the past six years, the Vanguard Total Stock Market Index Fund (VTSMX) is up 230% in six years (though, Charles hastens to remind us, only 4.6% annualized over the past 15 years dating back to the last days of the 1990s bubble), but we have no idea of whether a correction (or worse) is imminent nor even whether conditions are right for a major correction.
So what’s an investor to do? Your two most common reactions are:
- Do nothing until the storm hits, utterly confident in your ability to diagnose and smoothly adjust to the storm when it comes (the technical term here is “delusional thinking”) or
- Panic, needlessly churning your portfolio in hopes of finding The One Safe Spot.
As it turns out, we endorse neither. For almost every investor, success is the product of patience. And patience is the product of a carefully considered plan and a thorough understanding of the managers and funds that you’re entrusting to execute that plan.
To be plain: if you have only half a clue about what you’re invested in, and why, you have much less than half a chance of succeeding. That’s graphically illustrated in data on 20-year asset class and investor returns:
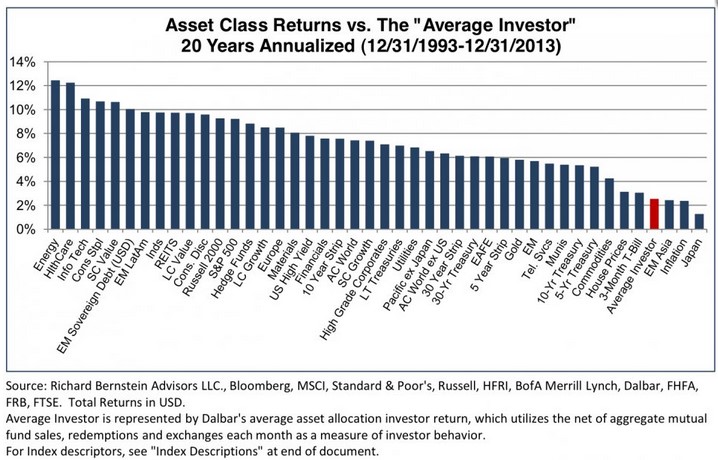
Some pundits, fearful that we don’t quite understand the significance of life on the far right of the chart clarify it for us:
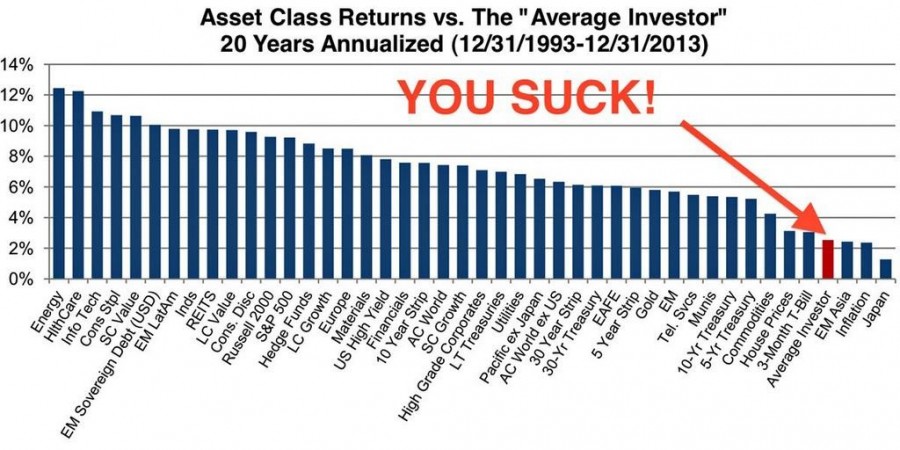
The Observer tries to help. We’re one of the few places that treat risk-conscious managers with respect, even when sticking with their principles costs them dearly in relative performance and investor assets. We know that some of the funds we’ve profiled recently have not been at the top of the recent charts; in many cases, we view that as a very good thing. We explain how you might think about investing and give you the chance to speak directly with really good managers on our conference calls. Within the next few months we’ll make our fund screener more widely available; it’s distinguished by the fact that it focuses on risk as much as returns and on meaningful time periods (entire market cycles, as well as up- and down-market phases) rather than random periods (uhhh, “last week”? Why on earth would you care?).
We’re grateful for your support and we’d really like to encourage you to take more advantage of the rich archive and tools here. There’s a lot that can help, crash or no.
 Identifying Bear-Market Resistant Funds During Good Times
Identifying Bear-Market Resistant Funds During Good Times
It’s easy enough to look back at the last bear market to see which funds avoided massive drawdown. Unfortunately, portfolio construction of those same funds may not defend against the next bear, which may be driven by different instabilities.
Dodge & Cox Balanced Fund (DODBX) comes to mind. In the difficult period between August 2000 and September 2002, it only drew down 11.6% versus the S&P 500’s -44.7% and Vanguard’s Balanced Index VBINX -22.4%. Better yet, it actually delivered a healthy positive return versus a loss for most balanced funds.
Owners of that fund (like I was and remain) were disappointed then when during the next bear market from November 2007 to February 2009, DODBX performed miserably. Max drawdown of -45.8%, which took 41 months to recover, and underperformance of -6.9% per year versus peers. A value-oriented fund house, D&C avoided growth tech stocks during the 2000 bubble, but ran head-on into the financial bubble of 2008. Indeed, as the saying goes, not all bear markets are the same.
Similarly, funds may have avoided or tamed the last bear by being heavy cash, diversifying into uncorrelated assets, hedging or perhaps even going net short, only to underperform in the subsequent bull market. Many esteemed fund managers are in good company here, including Robert Arnott, John Hussman, Andrew Redleaf, Eric Cinnamond to name a few.
Morningstar actually defines a so-called “bear-market ranking,” although honestly this metric must be one of least maintained and least acknowledged on its website. “Bear-market rankings compare how funds have held up during market downturns over the past five years.” The metric looks at how funds have performed over the past five years relative to peers during down months. Applying the methodology over the past 50 years reveals just how many “bear-market months” investors have endured, as depicted in the following chart:
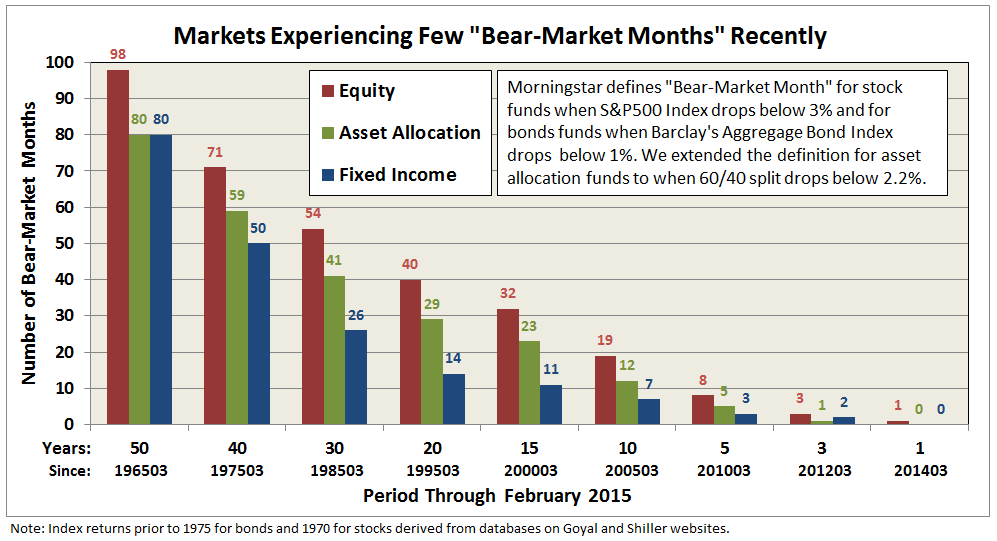
The long term average shows that equity funds experience a monthly drop below 3% about twice a year and fixed income funds experience a drop below 1% about three times every two years. There have been virtually no such drops this past year, which helps explain the five-year screening window.
The key question is whether a fund’s performance during these relatively scarce down months is a precursor to its performance during a genuine bear market, which is marked by a 20% drawdown from previous peak for equity funds.
Taking a cue from Morningstar’s methodology (but tailoring it somewhat), let’s define “bear market deviation (BMDEV)” as the downside deviation during bear-market months. Basically, BMDEV indicates the typical percentage decline based only on a fund’s performance during bear-market months. (See Ratings System Definitions and A Look at Risk Adjusted Returns.)
The bull market period preceding 2008 was just over five years, October 2002 through October 2007, setting up a good test case. Calculating BMDEV for the 3500 or so existing funds during that period, ranking them by decile within peer group, and then assessing subsequent bear market performance provides an encouraging result … funds with the lowest bear market deviation (BMDEV) well out-performed funds with the highest bear market deviation, as depicted below.
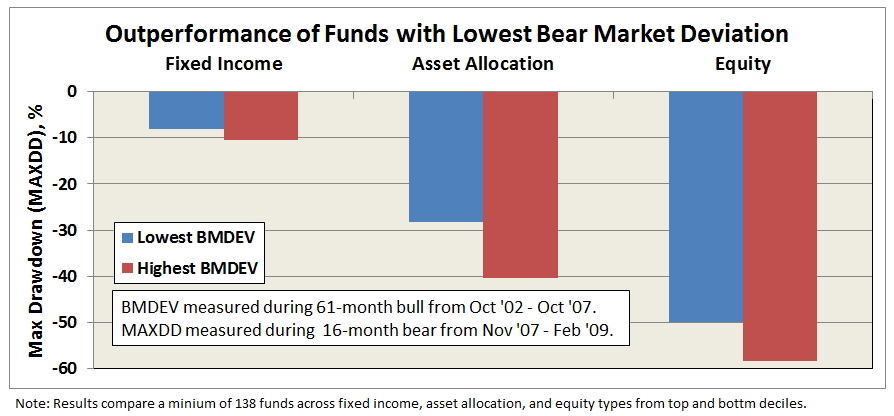
Comparing the same funds across the full cycle reveals comparable if not superior absolute return performance of funds with the lowest bear market deviation. A look at the individual funds includes some top performers:
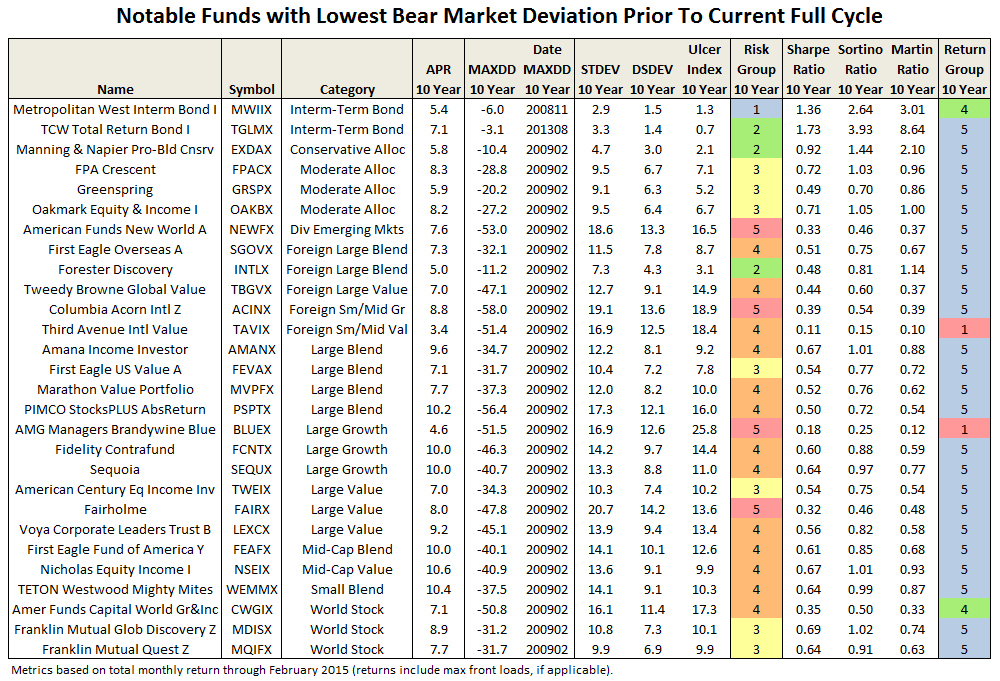
The correlation did not hold up in all cases, of course, but it is a reminder that the superior return often goes hand-in-hand with protecting the downside.
Posturing then for the future, which funds have the lowest bear-market deviation over the current bull market? Evaluating the 5500 or so existing funds since March 2009 produces a list of about 450 funds. Some notables are listed below and the full list can be downloaded here. (Note: The full list includes all funds with lowest decile BMDEV, regardless of load, manager change, expense ratio, availability, min purchase, etc., so please consider accordingly.)
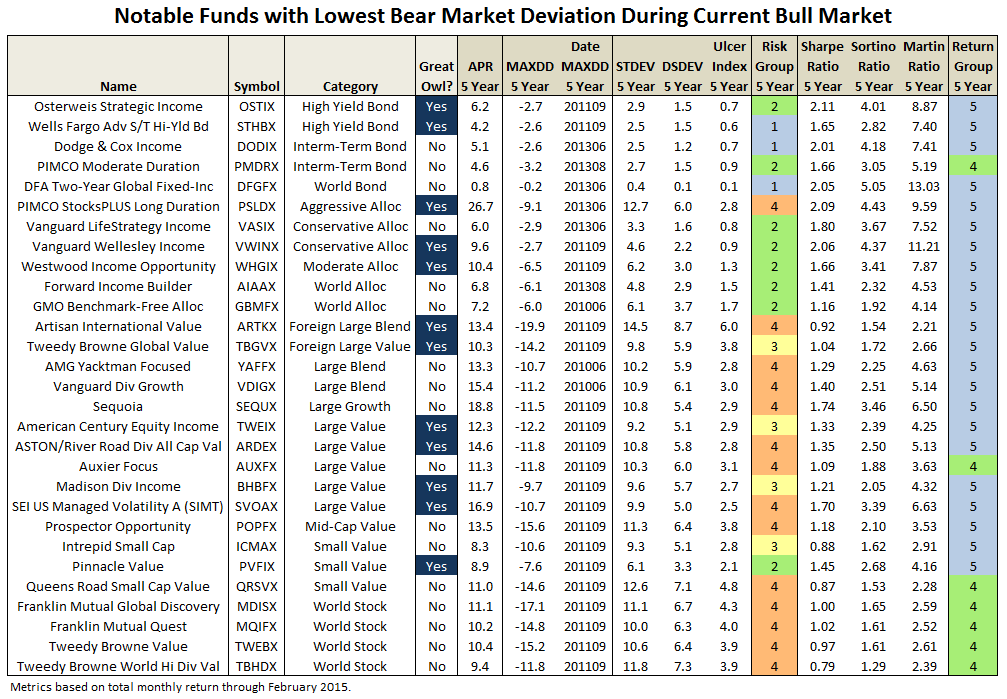
All of the funds on the above list seem to make a habit of mitigating drawdown, experiencing a fraction of the market’s bear-market months. In fact, a backward look of the current group reveals similar over-performance during the financial crisis when compared to those funds with the highest BMDEV.
Also, scanning through the categories above, it appears quite possible to have some protection against downside without necessarily resorting to long/short, market neutral, tactical allocation, and other so-called alternative investments. Although granted, the time frame for many of the alternatives categories is rather limited.
In any case, perhaps there is something to be said for “bear-market rankings” after all. Certainly, it seems a worthy enough risk metric to be part of an investor’s due diligence. We will work to make available updates of bear-market rankings for all funds to MFO readers in the future.
 There’s Got to be a Pony In This Room …….
There’s Got to be a Pony In This Room …….
By Edward Studzinski
“Life is an unbroken succession of false situations.”
Thornton Wilder
Given my predilection to make reference to scenes from various movies, some of you may conclude I am a frustrated film critic. Since much that is being produced these days appears to be of questionable artistic merit, all I would say is that there would be lifetime employment (or the standards that exist for commercial success have declined). That said, an unusual Clint Eastwood movie came out in 1970. One of the more notable characters in the movie was Sergeant “Oddball” the tanker, played by Canadian actor Donald Sutherland. And one of the more memorable scenes and lines from that movie has the “Oddball” character saying “Always with the negative waves Moriarty, always with the negative waves.”
Over the last several months, my comments could probably be viewed as taking a pessimistic view of the world and markets. Those who are familiar with my writings and thoughts over the years would not have been surprised by this, as I have always tended to be a “glass half-empty” person. As my former colleague Clyde McGregor once said of me, the glass was not only half-empty but broken and on the floor in little pieces. Some of this is a reflection of innate conservatism. Some of it is driven by having seen too many things “behind the curtain” over the years. In the world of the Mutual Fund Observer, there is a different set of rules by which we have to play, when comments are made “off the record” or a story cannot be verified from more than one source. So what may be seen as negativism or an excess of caution is driven by a journalistic inability to allow those of you would so desire, to paraphrase the New Testament, to “put your hands into the wounds.” Underlying it all of course, as someone who finds himself firmly rooted in the camp of “value investor” is the need for a “margin of safety” in investments and adherence to Warren Buffett’s Rules Numbers One and Two for Investing. Rule Number One of course is “Don’t lose money.” Rule Number Two is “Don’t forget Rule Number One.”
So where does this leave us now? It is safe to say that it is not easy to find investments with a margin of safety currently, at least in the U.S. domestic markets. Stocks on various metrics do not seem especially undervalued. A number of commentators would argue that as a whole the U.S. market ranges from fully valued to over-valued. The domestic bond market, on historic measures does not look cheap either. Only when one looks at fixed income on a global basis does U.S. fixed income stand out when one has negative yields throughout much of Europe and parts of Asia starting to move in that direction. All of course is driven by central banks’ increasing fear of deflation.
Thus, global capital is flowing into U.S. fixed income markets as they seem relatively attractive, assuming the strengthening U.S. currency is not an issue. Overhanging that is the fear that later this year the Federal Reserve will begin raising rates, causing bond prices to tumble. Unfortunately, the message from the Fed seems to be clearly mixed. Will it be a while before rates really are increased in the U.S. , or, will they start to raise rates in the second half of this year? No one knows, nor should they.
As one who built portfolios on a stock by stock basis, rather than paying attention to index weightings, does this mean I could not put together a portfolio of undervalued stocks today? I probably could but it would be a portfolio that would have a lot of energy-related and commodity-like issues in it. And I would be looking for long-term investors who really meant it (were willing to lock up their money) for at least a five-year time horizon. Since mutual funds can’t do that, it explains why many of the value-oriented investors are carrying a far greater amount of cash than they would like or is usual. As an aside, let me say that in the last month, I have had more than one investment manager tell me that for the first time in their investing careers, they really were unsure as to how to deal with the current environment.
What I will leave you with are questions to ponder. Over the years, Mr. Buffett and Mr. Munger have indicated that they would prefer to buy very good businesses at fair prices. And those businesses have traditionally been tilted towards those that did not require a lot of capital expenditures but rather threw off lots of cash with minimal capital investment requirements, and provided very high returns on invested capital. Or they had a built-in margin of safety, such as property and casualty insurance businesses where you were in effect buying a bond portfolio at a discount to book, had the benefit of investing the premium float, had a necessary product (automobile insurance) and again did not need a lot of capital investment. But now we see, with the Burlington Northern and utility company investments a different kettle of fish. These are businesses that will require continued capital investment going forward, albeit in oligopoly-like businesses with returns that may be fairly certain (in an uncertain world). Those investments will however not leave as much excess capital to be diverted into new portfolio investments as has historically been the case. There will be in effect required capital calls to sustain the returns from the current portfolio of businesses. And, we see investments being made as joint ventures (Kraft, Heinz) with private equity managers (3G) with a very different mindset than U.S. private equity or investment banking firms. That is, 3G acquires companies to fix, improve, and run for the long term. This is not like your typical private equity firm here, which buys a company to put into a limited life fund which they will sell or take public again later.
So here are your questions to ponder? Does this mean that the expectation for equity returns in the U.S. for the foreseeable future is at best in the low single digit range? Are the days of the high single digit domestic long-term equity returns a thing of the past? And, given how Buffett and Munger have positioned Berkshire now, what does this say about the investing environment? And in a world of increased volatility (which value investors like as it presents opportunities) what does it say about the mutual fund model, with the requirement for daily pricing and liquidity?
Morningstar: one hit and one miss
Morningstar, like many effective monopolies, provides an essential service. The quality of that service varies rather more than you might suspect. Last month I suggested that the continued presence of their “buy the unloved” strategy has increasingly become a travesty. Likewise, the folks on our discussion board, for example, have been maddened by the prevalence of “stale data” in the site’s daily NAV reports. To their enduring credit, one of the folks from Morningstar actually waded into the discussion, albeit briefly and ankle-deep.
On the other hand, the Morningstar folks really do some very solid, actionable research. As a recent case in point, Russel Kinnel, directory of fund analysis, offered up Why You Should Invest With Managers Who Eat Their Own Cooking (3/31/15). While the metrics (Success Rate and Success Rate MRAR) could use a bit of clarification, his research continues to substantiate an important point: when your manager is deeply invested, your prospects for success – both in raw and risk-adjusted returns – climbs substantially. It’s one of the reasons why we report so consistently on manager ownership in our fund profiles. The data point that almost no one discusses but which turns out to be equally important, ownership of fund shares by the board’s trustees, is something we’ll pursue in the next couple months.
 Now if only I could understand the logic of Morningstar’s grumbling about my portfolio. U.S. equities accounted for 36% of the total market capitalization of all equities markets worldwide on 10/21/14. In my portfolio, US equities account for 40% of all equity exposure. On face, that’s a slight underweight. Morningstar’s x-ray interpreter, however, insists on fretting that I have “a very large stake in foreign stocks” (no, I’m underweight), with special notes of my “extremely large” stake in Asia (“this is very risky”) and extremely small stake in Western Europe (which “probably isn’t a big deal”). I understand that most American investors have a substantial “home bias,” but I’m not sure that the bias should be reinforced in Morningstar’s portfolio analyzer.
Now if only I could understand the logic of Morningstar’s grumbling about my portfolio. U.S. equities accounted for 36% of the total market capitalization of all equities markets worldwide on 10/21/14. In my portfolio, US equities account for 40% of all equity exposure. On face, that’s a slight underweight. Morningstar’s x-ray interpreter, however, insists on fretting that I have “a very large stake in foreign stocks” (no, I’m underweight), with special notes of my “extremely large” stake in Asia (“this is very risky”) and extremely small stake in Western Europe (which “probably isn’t a big deal”). I understand that most American investors have a substantial “home bias,” but I’m not sure that the bias should be reinforced in Morningstar’s portfolio analyzer.
Top developments in fund industry litigation
 Fundfox, launched in 2012, is the mutual fund industry’s only litigation intelligence service, delivering exclusive litigation information and real-time case documents neatly organized and filtered as never before. For a complete list of developments last month, and for information and court documents in any case, log in at www.fundfox.com and navigate to Fundfox Insider.
Fundfox, launched in 2012, is the mutual fund industry’s only litigation intelligence service, delivering exclusive litigation information and real-time case documents neatly organized and filtered as never before. For a complete list of developments last month, and for information and court documents in any case, log in at www.fundfox.com and navigate to Fundfox Insider.
Orders
- The U.S. Supreme Court denied a certiorari petition in the section 36(b) lawsuit regarding BlackRock‘s securities lending practices with respect to iShares ETFs. The district court, affirmed on appeal, held that an SEC exemptive order (approving the challenged securities lending arrangements) constituted an exception to potential liability under section 36(b). Defendants included independent directors. (Laborers’ Local 265 Pension Fund v. iShares Trust.)
- The court denied BlackRock‘s motion to dismiss fee litigation regarding its Global Allocation and Equity Dividend Funds, stating that plaintiffs’ fee comparison (between the challenged fees and fees charged by BlackRock as sub-advisor to unaffiliated funds) “is appropriate.” (In re BlackRock Mut. Funds Advisory Fee Litig.)
- The court granted Fidelity‘s motion to dismiss an ERISA class action regarding Fidelity’s practices with respect to the “float income” generated from retirement plan redemptions, holding that “plaintiffs have not plausibly alleged that float income is a plan asset” and that “Fidelity is not an ERISA fiduciary as to float.” (In re Fid. ERISA Float Litig.)
- The court denied J.P. Morgan‘s motion to dismiss fee litigation regarding three bond funds. The court cited allegations of “a notable disparity” between the fees obtained by J.P. Morgan for servicing those three funds and the fees obtained by J.P. Morgan for subadvising unaffiliated funds, notwithstanding that its services in each instance were allegedly “substantially the same.” (Goodman v. J.P. Morgan Inv. Mgmt., Inc.)
- The court preliminarily approved settlements totaling $60 million in a pair of class actions regarding Northern Trust‘s securities lending program. (Diebold v. N. Trust Invs., N.A.; La. Firefighters’ Ret. Sys. v. N. Trust Invs., N.A.)
- The court granted plaintiffs’ motion for class certification in consolidated litigation alleging bad prospectus disclosure for Oppenheimer‘s California Municipal Bond Fund. Plaintiffs’ claims are premised on a theory that the fund’s stated investment objectives and implied price volatility assurances were rendered materially misleading by the fund’s heavy investment in derivative instruments known as inverse floaters. Defendants include independent directors. (In re Cal. Mun. Fund.)
- The court granted Oppenheimer‘s motion to dismiss a breach-of-contract suit filed by assignees of claims purportedly held by the New Mexico boards that administered the state’s 529 college savings plans. (Lu v. OppenheimerFunds, Inc.)
- The court consolidated fee lawsuits regarding ten Russell funds. (In re Russell Inv. Co. Shareholder Litig.)
- In the long-running securities class action alleging that the Schwab Total Bond Market Fund deviated from two fundamental investment objectives adopted by a shareholder vote, a divided panel of the Ninth Circuit allowed multiple state-law claims to proceed but declined to reach the question of whether any of those claims are barred by the Securities Litigation Uniform Standards Act (leaving that issue to the district court on remand). Schwab has filed a petition for rehearing en banc. Defendants include independent directors. (Northstar Fin. Advisors Inc. v. Schwab Invs.)
- In the class action alleging that TIAA-CREF failed to honor customer requests to pay out funds in a timely fashion, the court dismissed the state-law claims, holding that they were preempted by ERISA. (Cummings v. TIAA-CREF.)
The Alt Perspective: Commentary and news from DailyAlts.
 Before we dive into the details of liquid alternatives, there are two important publications that were released this past month that have implications for nearly all investors.
Before we dive into the details of liquid alternatives, there are two important publications that were released this past month that have implications for nearly all investors.
The first is a paper from AQR that provides forward looking return projections for stocks, bonds and smart beta. This is the first return projection I have seen that includes smart beta (given that AQR offers smart beta products, they do have an incentive to include the strategy in their assumptions). The projections for stocks and bonds don’t look so rosy: 3.8% real return for US stocks and 0.60% for US 10-year government bonds. Multi-factor smart beta looks a bit better at 5.7% over inflation. Download a copy, have a look and re-calibrate your expectations: AQR Q1 2015 Alternative Thinking.
The second paper is from Howard Marks, founder and co-chairman of Oaktree Capital who released his quarterly memo that discussed, among other things, liquid alternatives. But more importantly, Marks made two important points that we, as investors, shouldn’t forget – especially in this era of liquidity and rising markets:
- “Liquidity is ephemeral: it can come and go.”
- “No investment vehicle should promise greater liquidity than is afforded by its underlying assets.”
In regard to point one, Marks reminds us that when we most want liquidity is when it is hard to find. The second point is a warning to investors – don’t expect something for nothing. The liquidity of an investment vehicle is only as good as its underlying investments in times of crisis. I would recommend you read the entire paper.
Now, jumping to a few highlights of flows and assets for liquid alternatives:
- February flows totaled $1.5 billion, which were interestingly split but active funds ($767 million) and passive funds $768 million)
- 1 year flows of $13.5 billion ($9.5 billion to active funds and $4.1 billion to passive funds)
- Total category assets of $204 billion
- 1 year organic growth rate of 6.9% based on Morningstar’s Alternative category classification
February Asset Flow Details
In February, multi-alternative and managed futures funds dominated the inflows, while investors soured on non-traditional bonds, market neutral and long/short equity funds.
Flows out of the long/short equity category continue to be dominated by outflows from the MainStay Marketfield Fund, which saw $941 million of outflows in January, bringing the 12-month total to $11.6 billion. Excluding Marketfield, the long/short equity category had $564 million of inflows in February.
With increased levels of volatility, a rising dollar and a potential bottoming of commodity prices, investors jumped into each of those categories in February, driving up assets in each by $$527 million (volatility), $389 million (currencies) and $657 million (commodities), respectively. In fact, have gathered almost $5 billion in assets in the first two months of 2015.
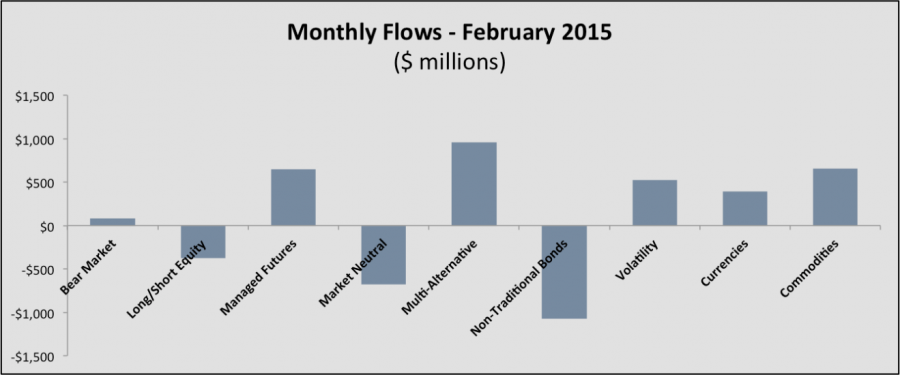
On a 1-year basis, non-traditional bonds and multi-alternative funds have dominated the inflows to alternative funds, gathering $11.2 billion and $9.4 billion, respectively. Non-traditional bond funds have filled the need for investors and advisors who have a concern about the potential negative impact of rising interest rates, as well as the need for higher levels of income.
At the same time, most investors looking to gain exposure to alternative investment strategies are looking to diversified alternative funds for that first time exposure. This is done with pre-packaged alternative funds that deliver exposure to a range of alternative strategies in a single fund. As the market matures, and investors become more comfortable with individual strategies, this trend may shift as it did in the institutional market.
New Funds
I will keep it short, but there were several new funds of interest that launched this month, most notably a long/short equity fund from Longboard, which we wrote about in a story titled Longboard Launches Second Alternative Mutual Fund and two new hedge fund replication ETFs from IndexIQ, both of which are detailed in New ETFs Allow Investors to Build their Own Hedge Fund Strategies.
Until next month, feel free to stop by DailyAlts.com for regular news and analysis of the liquid alts market.
Observer Fund Profiles
Each month the Observer provides in-depth profiles of between two and four funds. Our “Most Intriguing New Funds” are funds launched within the past couple years that most frequently feature experienced managers leading innovative newer funds. “Stars in the Shadows” are older funds that have attracted far less attention than they deserve.
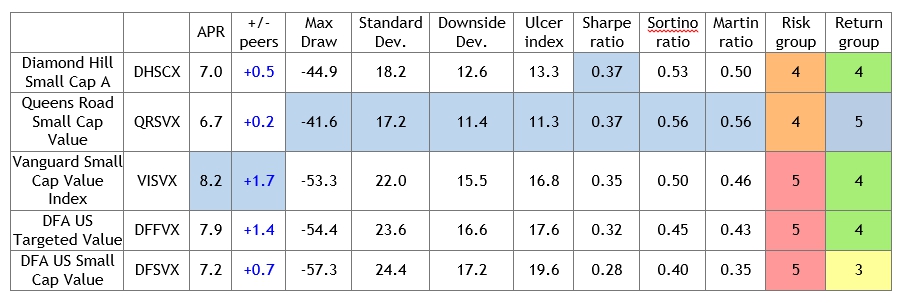
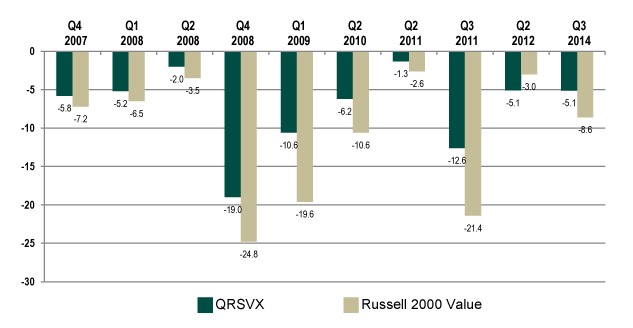
Queens Road Small Cap Value (QRSVX): in writing last month’s profile of Pinnacle Value, we used our risk-sensitive screener to screen for a bunch of measures over a bunch of time periods. We kept coming up with a very short, very consistent list of the best small cap value funds. That list might be described as “closed, closed, loaded, institutional, Pinnacle and Queens Road.”
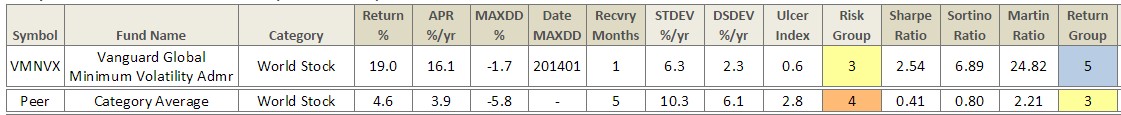
Vanguard Global Minimum Volatility (VMVFX): at our colleague Ed’s behest, I spent a bit of time reading about VMVFX, reviewing Charles’s data and a lot of academic research on the “low volatility anomaly.” The combination of inquiries points to VMVFX as a potentially quite compelling core holding which quietly and economically exploits a durable anomaly.
Elevator Talk: Lee Kronzon, Gator Opportunities (GTOAX/GTOIX)
 Since the number of funds we can cover in-depth is smaller than the number of funds worthy of in-depth coverage, we’ve decided to offer one or two managers each month the opportunity to make a 200 word pitch to you. That’s about the number of words a slightly-manic elevator companion could share in a minute and a half. In each case, I’ve promised to offer a quick capsule of the fund and a link back to the fund’s site. Other than that, they’ve got 200 words and precisely as much of your time and attention as you’re willing to share. These aren’t endorsements; they’re opportunities to learn more.
Since the number of funds we can cover in-depth is smaller than the number of funds worthy of in-depth coverage, we’ve decided to offer one or two managers each month the opportunity to make a 200 word pitch to you. That’s about the number of words a slightly-manic elevator companion could share in a minute and a half. In each case, I’ve promised to offer a quick capsule of the fund and a link back to the fund’s site. Other than that, they’ve got 200 words and precisely as much of your time and attention as you’re willing to share. These aren’t endorsements; they’re opportunities to learn more.
Gator Opportunities Fund describes itself as “a concentrated, quality-driven, valuation-sensitive, small/midcap-focused mutual fund.” They’re a very Graham-and-Dodd kind of bunch, invoking maxims like
- Buy for the long-term
- Invest in high-quality growth businesses
- Purchase businesses we understand
- Invest with a margin of safety
- Concentrate!
They hold 36 stocks, more or less equally split between small caps and midcaps, at least as of March 2015. The fund has substantially more exposure to international markets, both developed and developing, than does its peers.
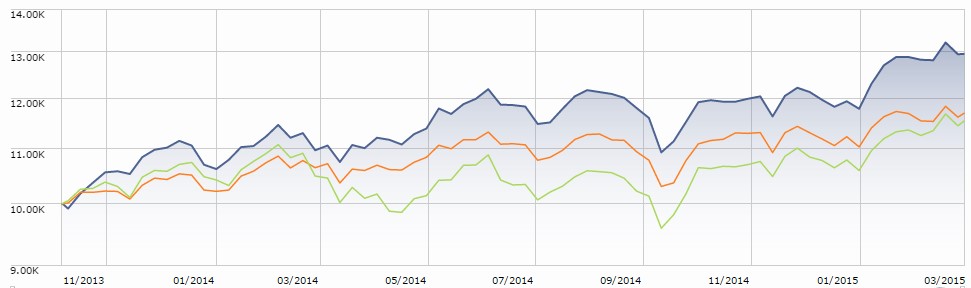
On face, it’s a pretty mainstream fund. What’s striking is that it’s produced distinctly non-mainstream returns. While Morningstar characterizes it as a mid-cap blend fund, its current portfolio leans a bit more toward smaller and growthier stocks. Regardless of which peer group you use, the results are striking. The fund (in blue) has substantially outperformed both midcap (orange) and small growth (green) Morningstar peer groups since launch.
 Lee Kronzon manages the Gator Opportunities Fund (GTOAX/GTOIX), which launched in early November 2013. While this is his first stint managing a mutual fund, he’s had a interesting and varied career, and it appears that lots of serious people have reason to respect him. He came to Gator after more than a decade as an equity analyst and strategist with the Fundamental Equities Group at Goldman Sachs Asset Management (GSAM). Earlier he cofounded Tower Hill Securities, a merchant bank that funded global emerging growth companies. Earlier still he taught at Princeton as a Faculty Lecturer at the Woodrow Wilson School. In that role he co-taught several courses in applied quantitative and economic analysis with Professors Ben Bernanke (subsequently chairman of the Federal Reserve) and Alan Krueger (chair of Obama’s Council of Economic Advisors). Fortunately, he predated a rating at RateMyProfessors.com where Princeton professor and talking head Paul Krugman gets a pretty durn mediocre rating.
Lee Kronzon manages the Gator Opportunities Fund (GTOAX/GTOIX), which launched in early November 2013. While this is his first stint managing a mutual fund, he’s had a interesting and varied career, and it appears that lots of serious people have reason to respect him. He came to Gator after more than a decade as an equity analyst and strategist with the Fundamental Equities Group at Goldman Sachs Asset Management (GSAM). Earlier he cofounded Tower Hill Securities, a merchant bank that funded global emerging growth companies. Earlier still he taught at Princeton as a Faculty Lecturer at the Woodrow Wilson School. In that role he co-taught several courses in applied quantitative and economic analysis with Professors Ben Bernanke (subsequently chairman of the Federal Reserve) and Alan Krueger (chair of Obama’s Council of Economic Advisors). Fortunately, he predated a rating at RateMyProfessors.com where Princeton professor and talking head Paul Krugman gets a pretty durn mediocre rating.
 His celebration of the alligator gives you a sense of how he’s thinking: “The gator is a survivor, one of the planet’s oldest species and a remnant of the dinosaur era. He’s made it through all sorts of different climates and challenges. And his strategy just works: be still, wait patiently for an opportunity to present itself and then strike. Really, it’s a creature with no weaknesses!”
His celebration of the alligator gives you a sense of how he’s thinking: “The gator is a survivor, one of the planet’s oldest species and a remnant of the dinosaur era. He’s made it through all sorts of different climates and challenges. And his strategy just works: be still, wait patiently for an opportunity to present itself and then strike. Really, it’s a creature with no weaknesses!”
Here’s a lightly-edited version of Mr. Kronzon’s 200 words on why you should add GTOAX to your due-diligence list:
As a Warren Buffett disciple, I believe that growth and value investment disciplines are joined at the hip, and I try to provide investors the best of both worlds. Quality is the key indicator of business success, and that it ultimately separates investment winners from losers. The Fund focuses on quality by investing in firms with sizable and sustainable competitive advantages, best-in-class business models that generate attractive and predictable returns, and successful, shareholder-friendly management teams. My goal is to invest in such superior businesses when they are undiscovered, out of favor, or misunderstood; curiously, I often find them in dynamic sectors like Industrials and Technology.
Our strategy is to achieve the intersection of quality with growth and value by investing long-term in a concentrated set of public equities issued primarily by domestically-listed, small/mid-cap firms that I believe are high quality and have solid growth prospects yet are undervalued based on fundamental analysis with catalysts to close this valuation gap. We have a flexible mandate to invest across all sectors and regions, and a high active share since it is built bottom-up and not managed to track any benchmark. And I’m proud of the fact that the Fund has delivered robust returns since its launch in November 2013 to date.
Gator Opportunities (GTOAX) has a $5000 minimum initial investment which is reduced to $1000 for IRAs and other types of tax-advantaged accounts. Expenses are capped at 1.49% on the investor shares, at least through 2017. The fund has about gathered about $1 million in assets since its November 2013 launch. More information can be found at the fund’s homepage. Here’s a nice interview with Mr. Kronzon that Chuck Jaffe did in late March, 2015.
Conference Call Highlights: David Berkowitz, RiverPark Focused Value
 David Berkowitz, manager of the newly-launched RiverPark Focused Value Fund, and Morty Schaja, RiverPark’s cofounder and CEO, chatted with me (and about 30 of you) for an hour in mid-March. It struck me as a pretty remarkable call, largely because of the clarity of Mr. Berkowitz’s answers. Here are what I take to be the highlights.
David Berkowitz, manager of the newly-launched RiverPark Focused Value Fund, and Morty Schaja, RiverPark’s cofounder and CEO, chatted with me (and about 30 of you) for an hour in mid-March. It struck me as a pretty remarkable call, largely because of the clarity of Mr. Berkowitz’s answers. Here are what I take to be the highlights.
The snapshot: 20-25 stocks, likely all US-domiciled because he likes GAAP reporting standard (even where they’re weak, he knows where the weaknesses are and compensate for them), mostly north of$10 billion in market cap though some in the $5-9 billion range. Long only with individual positions capped at 10%. They have price targets for every stock they buy, so turnover is largely determined by how quickly a stock moves to its target. In general, higher turnover periods are likely to correspond with higher returns.
His background (and why it matters): Mr. Berkowitz was actually interested in becoming a chemist, but his dad pushed him into chemical engineering because “chemists don’t get jobs, engineers do.” He earned a B.A. and M.A. in chemical engineering at MIT and went to work first for Union Carbide, then for Amoco (Standard Oil of Indiana). While there he noticed how many of the people he worked with had MBAs and decided to get one, with the expectation of returning to run a chemical company. While working on his MBA at Harvard, he discovered invested and a new friend, Bill Ackman. Together they launched the Gotham Partners LP fund. Initially Gotham Partners used the same discipline in play at the RiverPark funds and he described their returns in the mid-90s as “spectacular.” They made what, in hindsight, was a strategic error in the late 1990s that led to Gotham’s closure: they decided to add illiquid securities to the portfolio. That was not a good mix; by 2002, they decided that the strategy was untenable and closed the hedge fund.
Takeaways: (1) the ways engineers are trained to think and act are directly relevant to his success as an investor. Engineers are charged with addressing complex problems while possessing only incomplete information. Their challenge is to build a resilient system with a substantial margin of safety; that is, a system which will have the largest possible chance of success with the smallest possible degree of system failure. As an investor, he thinks about portfolios in the same way. (2) He will never again get involved in illiquid investments, most especially not at the new mutual fund.
His process: as befits an engineer, he starts with hard data screens to sort through a 1000 stock universe. He’s looking for firms that have three characteristics:
- Durable predictable businesses, with many firms in highly-dynamic industries (think “fast fashion” or “chic restaurants,” as well as firms which will derive 80% of their profits five years hence from devices they haven’t even invented yet) as too hard to find reliable values for. Such firms get excluded.
- Shareholder oriented management, where the proof of shareholder orientation is what the managers do with their free cash flows.
- Valuations which provide the opportunity for annual returns in the mid-teens over the next 3-5 years. This is where the question of “value” comes in. His arguments are that overpaying for a share of a business will certainly depress your future returns but that there’s no simple mechanical metric that lets you know when you’re overpaying. That is, he doesn’t look at exclusively p/e or p/b ratios, nor at a firm’s historic valuations, in order to determine whether it’s cheap. Each firm’s prospects are driven by a unique constellation of factors (for example, whether the industry is capital-intensive or not, whether its earnings are interest rate sensitive, what the barriers to entry are) and so you have to go through a painstaking process of disassembling and studying each as if it were a machine, with an eye to identifying its likely future performance and possible failure points.
Takeaways: (1) The fund will focus on larger cap names both because they offer substantial liquidity and they have the lowest degree of “existential risk.” At base, GE is far more likely to be here in a generation than is even a very fine small cap like John Wiley & Sons. (2) You should not expect the portfolio to embrace “the same tired old names” common in other LCV funds. It aims to identify value in spots that others overlook. Those spots are rare since the market is generally efficient and they can best be exploited by a relatively small, nimble fund.
Current ideas: He and his team have spent the past four months searching for compelling ideas, many of which might end up in the opening portfolio. Without committing to any of them, he gave examples of the best opportunities he’s come across: Helmerich & Payne (HP), the largest owner-operator of land rigs in the oil business, described as “fantastic operators, terrific capital allocators with the industry’s highest-quality equipment for which clients willingly pay a premium.” McDonald’s (MCD), which is coming out of “the seven lean years” with a new, exceedingly talented management team and a lot of capital; if they get the trends right “they can explode.” AutoZone (AZO), “guys buying brake pads” isn’t sexy but is extremely predictable and isn’t going anywhere. Western Digital (WDG), making PCs isn’t a good business because there’s so little opportunity to add value and build a moat, but supplying components like hard drives – where the industry has contracted and capital needs impose relatively high barriers to entry – is much more attractive.
Even so, he describes this is “the most challenging period” he’s seen in a long while. If the fund were to open today, rather than at the end of April, he expects it would be only 80% invested. He won’t hesitate to hold cash in the absence of compelling opportunities (“we won’t buy just for the sake of buying”) but “we work really hard, turn over a lot of rocks and generally find a substantial number of names” that are worth close attention.
His track record: There is no public record of Mr. Berkowitz alone managing a long-only strategy. In lieu of that, he offers three thoughts. First, he’s sinking a lot of his own money – $10 million initially – into the fund, so his fortunes will be directly tied to his investors’. Second, “a substantial number of people who have direct and extensive knowledge of my work will invest a substantial amount of money in the fund.” Third, he believes he can earn investors’ trust in part by providing “a transparent, quantitative, rigorous, rational framework for everything we own. Investors will know what we’re doing and exactly why we’re doing it. If our process makes sense, then so will investing in the fund.”
Finally, Mr. Schaja announced an interesting opportunity. For its first month of operation, RiverPark will waive the normal minimum investment on its institutional share class for investors who purchase directly from them. The institutional share class doesn’t carry a 12(b)1 fee, so those shares are 0.25% (25 bps) cheaper than retail: 1.00 rather than 1.25%. (Of course it’s a marketing ploy, but it’s a marketing ploy that might well benefit you in you’re interested in the fund.)
The fund will also be immediately available NTF at Fidelity, Schwab, TDAmeritrade, Vanguard and maybe Pershing. It will eventually be available on most of the commercial platforms. Institutional shares will be available at the same brokerages but will carry transaction fees.
Bottom Line
Mr. Berkowitz comes across as a smart guy and RiverPark’s offer to waive the institutional minimum is really attractive. At the same time, most investors will be proceeding mostly on faith since we can’t document Mr. B’s track record. We don’t know the overall picture, much less what has blown up (things always blow up) and how he’s recovered. A lot of smart, knowledgeable people seem excited at the opportunity. In general, if I were you I’d proceed with caution and after a fair number of additional inquiries (Morty, in particular, is famously available to RiverPark’s investors).
Here’s the link to the mp3 of the call.
Conference Call Upcoming
We’d like to invite you to join us for a conversation with Andrew Foster, manager of Seafarer Overseas Growth & Income (SFGIX/SIGIX) on Thursday, April 16, from 7:00 – 8:00 Eastern. Click, well “register” to register:
Our contention has always been that Seafarer represents one of the best possible options for investors interested in approaching the emerging markets. There are two reasons for that conclusion.
- He’s a superb investor. While Andrew is a very modest and unassuming guy, and I know that fortune is fleeting, it’s hard to ignore the pattern reflected in Morningstar’s report of where Seafarer stands in its peer group over a variety of trailing periods:

- He’s a superb steward. Mr. Foster has produced consistently first-rate shareholder communications that are equally clear and honest about the fund’s successes and occasional lapses. And he’s been near-evangelical about reducing the fund’s expenses, often posting voluntary mid-year fee reductions as assets permit.
The first part of that judgment was substantiated in early March when Seafarer received its inaugural five-star rating from Morningstar. It is also a Great Owl fund, a designation which recognizes funds whose risk-adjusted returns have finished in the top 20% of their peers for all trailing periods. Our greater sensitivity to risk, based on the evidence that investors are far less risk-tolerant than they imagine, leads to some divergence between our results and Morningstar’s: five of their five-star EM funds are not Great Owls, for instance, while some one-star funds are.
Of 219 diversified EM funds currently tracked by Morningstar, 18 have a five-star rating (as of mid-March, 2015). 13 are Great Owls. Seafarer and nine others (representing 5% of the peer group) are both five-star and Great Owls.
As Andrew and I have talked about the call, he reflected on some of the topics that he thought folks should be thinking about:
- a brief (re) introduction to Seafarer’s strategy
- a discussion of why the strategy searches for growth, and why we make sure to marry that growth with some current income (dividends, bond coupons). Andrew’s made some interesting observations lately on whether “value investing” might finally be coming into play in the emerging markets.
- other key elements of Seafarer’s philosophy including his considerable skepticism about the construction of the various EM indexes, which leads to some confidence about his ability to add considerable value over what might be offered by passive products
- why the emerging markets (EM) have been so weak over the past few years and the implications of anemic growth in the EM, both in terms of economic output and corporate profits
- maybe some stuff on currency weakness and the decision of EM central banks to cut their rates while we raise ours
- Where do things go from here?
- And, of course, your questions.
By way of fair disclosure, I should note that I’ve owned shares of Seafarer in my personal account, pretty much since its inception, and also own shares of Matthews Asian Growth & Income (MACSX), which he managed (brilliantly) before leaving to found Seafarer.
HOW CAN YOU JOIN IN?
 If you’d like to join in the RiverPark call, just click on register and you’ll be taken to the Chorus Call site. In exchange for your name and email, you’ll receive a toll-free number, a PIN and instructions on joining the call. If you register, I’ll send you a reminder email on the morning of the call.
If you’d like to join in the RiverPark call, just click on register and you’ll be taken to the Chorus Call site. In exchange for your name and email, you’ll receive a toll-free number, a PIN and instructions on joining the call. If you register, I’ll send you a reminder email on the morning of the call.
Remember: registering for one call does not automatically register you for another. You need to click each separately. Likewise, registering for the conference call mailing list doesn’t register you for a call; it just lets you know when an opportunity comes up.
WOULD AN ADDITIONAL HEADS UP HELP?
Over four hundred readers have signed up for a conference call mailing list. About a week ahead of each call, I write to everyone on the list to remind them of what might make the call special and how to register. If you’d like to be added to the conference call list, just drop me a line.
Emerging markets funds that might be worth your attention
We mentioned, above, that only ten funds have earned both our designation as Great Owls (meaning that they have top-tier risk-adjusted returns in every trailing time period longer than one year) and Morningstar’s five-star rating. Knowing that you were being eaten alive with curiosity, here’s the quick run-down.
Baron Emerging Markets (BEXFX) – $1.5 billion in AUM, 1.5% e.r., not quite five years old, large-growth with an Asian bias. The manager also runs Baron International Growth (BIGFX). “Big F”? Really? BIG F actually earns a BIG C-.
City National Rochdale Emerging Markets (RIMIX) – 90% invested in Asia, City National Bank, headquartered in Hollywood, bought the Rochdale Funds and agreed t in January 2015 to be bought by the Royal Bank of Canada. Interesting funds. No minimum investment but a 1.61% e.r. The EM fund acquires exposure to Indian stocks by investing in a wholly owned subsidiary domiciled in Mauritius. Hmmm.
Driehaus EM Small Cap Growth (DRESX) – a $600 million hedged fund (and former hedge fund) for which we have a profile and some fair enthusiasm. Expenses are 1.71%.
Federated EM Equity (FGLEX) – a $13 million institutional fund with a $1 million minimum, not quite five years old and a mostly mega cap portfolio. It seems to have had two really good years followed by two really soft ones.
HSBC Frontier Markets (HSFAX) – 5% front load, 2.2% e.r., $200 million in AUM, midcap bias and a huge overweight in Africa & the Middle East at the expense of Asia. Curious.
Harding Loevner Frontier EM (HLMOX) – modest overweight in Asia, huge overweight in Africa & the Middle East, far lower-than-average market cap, half a billion in assets, 2.2% e.r.
Seafarer Overseas Growth & Income (SFGIX) – $136 million in AUM, 1.4% e.r., small- to mid-cap bias, top 4% returns over its first three years of operation.
Thornburg Developing World (THDAX) – oopsie: lead manager Lewis Kaufman just jumped from the $3 billion ship to launch Artisan Developing World Fund this summer.
Wasatch Frontier Emerging Small Countries (WAFMX) – $1.3 billion in AUM, 2.24% e.r. and closed to new investors
William Blair EM Small Cap Growth (WESNX) – $300 million in AUM, 1.65% e.r. and closed to new investors.
On face, the pattern seems to be that small works. The top tier of funds have lots of exposure to smaller firms and/or those located in smaller markets, even by EM standards.
The other big is big works. Big funds charging big fees. If you’re looking for no-load funds that are open to retail investors and charge under 2%, your due-diligence list is reduced to four funds: Baron, City Rochdale, Driehaus and Seafarer.
SFGIX is the second-smallest fund in the whole five star/Great Owl group, which makes it all the more striking that it’s the least expensive of all. And it’s among the least risky of this elite group.
Funds in Registration
Funds in Registration focuses on no-load, retail funds. There are three funds outside of that range are currently in registration and are worth noting.
Fidelity has jumped on two bandwagons at once, passive management and low volatility, with the impending launch of Fidelity SAI U.S. Minimum Volatility Index Fund and Fidelity SAI International Minimum Volatility Index Fund. The key is that the funds are not available for purchase by the public, they’re only available to folks running Fido funds-of-funds and similar products. That said, they seem to support the attractiveness of the minimum volatility strategy, which we discuss in this month’s Vanguard profile.
Speaking of Vanguard, it’s making its second foray in the world of liquid alts (after Vanguard Market Neutral) with Vanguard Alternative Strategies Fund seeks to generate returns that have low correlation with the returns of the stock and bond markets, and that are less volatile than the overall U.S. stock market. Michael Roach, who also helps manage Vanguard Global Minimum Volatility (VMVFX) and Vanguard Market Neutral (VMNFX), will manage the fund. Expenses of 1.10% and a $250,000 minimum, which manages the Market Neutral Minimum.
Of the retail funds in registration, by far the most intriguing is Artisan Developing World. The fund will be managed by Lewis Kaufman who had been managing the five-star, $2.8 billion Thornburg Developing World Fund (THDAX). By most accounts, Mr. Kaufman is one of the field’s legitimate stars.
All eight funds in the pipeline are sketched out on our Funds in Registration page.
Manager Changes
Chip reports that it felt like there were a million of them this month but the actual count is just 38 manager changes, none of them earth-shaking.
Briefly Noted . . .
GlobalX ups the rhetorical stake: not satisfied to hang with the mere “smart beta” crowd, GlobalX has filed to launch a series of “scientific beta” ETFS. Cranking Thomas Dolby’s cautionary tale, “She Blinded Me with Science,” in the background, I ventured into the prospectus, hoping to discover what sort of science I might be privy to.
As long as you think of “scientific” as a synonym for “impenetrable morass,” I found science. The US ETF will replicate the returns of the Scientific Beta United States Multi-Beta Multi-Strategy Equal Risk Contribution Index (scientific! It says so!), authored by EDHEC Risk Institute Asia Ltd. According to their website, EDHEC’s research is “Asia-focused work” which is being extended globally. Here’s the word on index composition:
The Index is composed of four sub-indices, each of which represents a specific beta exposure (or factor tilt): (i) high valuation, (ii) high momentum, (iii) low volatility, and (iv) size (each, a “Beta Sub-Index”). Each Beta Sub-Index comprises the top 50% of companies from the pre-screening universe that best represent that Beta Sub-Index’s specific beta exposure, except that the “size” sub-index is comprised of the bottom 50% of companies in the pre-screening universe according to free-float market capitalization. Once these companies are selected for the Beta Sub-Index, five different weighting schemes are applied to the constituents: (i) maximum deconcentration, (ii) diversified risk-weighting, (iii) maximum decorrelation, (iv) efficient minimum volatility and (v) efficient maximum Sharpe Ratio.
If you can understand all that, you might consider investing in the fund. If you have no earthly idea of what they’re saying, you might be better off moving quietly on.
Janus Diversified Alternatives Fund (JDDAX) has changed its statement of investing strategies to reflect the fact that they now have a higher volatility target and a higher “notional investment exposure.” They anticipate a standard deviation of about 6% and a notional exposure (a way of valuing the impact of their derivatives) of 300-400%.
Linde Hansen Contrarian Value Fund (LHVAX/LHVIX) has officially embraced diversification. It’s advertised itself as “non-diversified” since launch but it’s been “managed as a diversified fund since its inception.” The fund holds 20% cash and 22 stocks, which implies that their notion of “diversified” is “more than 20 stocks.”
SMALL WINS FOR INVESTORS
Effective February 28, 2015, the ASTON/TAMRO Small Cap Fund (ATASX) and the ASTON/River Road Independent Value Fund (ARIVX) are open to all investors.
Fairholme Focused Income (FOCIX) has reopened after a two year closure. Mr. Berkowitz closed all three of his funds simultaneously, and mostly in reaction to the flight of fickle investors. Well, “fickle,” “shell-shocked,” what’s in a name?
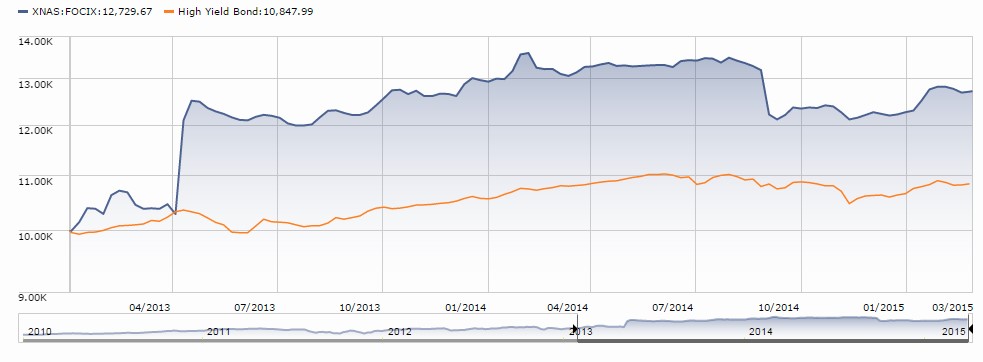
The key to this mostly high-yield bond fund is that it focuses more than anybody: it owns two stocks, two bonds (which seem to account for over 50% of the portfolio) and a handful of preferred shares. In any case, assets at FOCIX have declined from $240 to $210 million and the advisor is pretty sure that he’s got places to profitably invest new cash.
Effective immediately, all 15 of the Frost Funds have eliminated their sales loads and have redesignated their “A” shares as “Investor” shares. A couple of their shorter-term bond funds are worth a check and their Total Return Bond Fund (FIJEX) qualifies as a Great Owl. Of it, Charles notes: “Among highest return in short bond category across current full cycle (since Sept 2007 through Jan 2015…still going) and over its 14 year life. Low expenses. Low volatility. High dividend. 10 Year Great Owl.”
Lebenthal Asset Management purchased a minority stake in AH Lisanti Capital Growth LLC, adviser to Adams Harkness Small Cap Growth Fund, now called Lebenthal Lisanti Small Cap Growth (ASCGX). Mary Lisanti has been managing the fund since 2004 and has compiled a fine record without the benefit of, well, many shareholders in the fund. The fund is a small part (say 8%) of the assets of a small adviser, Adam Harkness & Hill. In theory, the partnership with Lebenthal will help raise the fund’s visibility. I wish them well, since Ms. Lisanti and her fund are both solid and under-appreciated.
Effective March 4, 2015, the management fee of Schwab International Small-Cap Equity ETF was reduced by one basis point! Woo hoo! The happy perspective is “by about 5%.”
Vanguard Convertible Securities Fund (VCVSX) is now open to new accounts for institutional clients who invest directly with Vanguard.
CLOSINGS (and related inconveniences)
On March 13, The Giralda Fund (GDMAX – really? The G-dam fund?) closed to new investors. It’s a five star fund with $200 million in assets, which makes the closing seem really disciplined and principled.
Vanguard Wellington Fund (VWELX) has closed to “all prospective financial advisory, institutional, and intermediary clients (other than clients who invest through a Vanguard brokerage account).” At base they’re trying to close the tap a bit by restricting investment through third-parties like Schwab though, at $90 billion, the question might be whether they’re a bit late. The fund is still performing staunchly, but the track record of funds at $100 billion is not promising.
Wasatch Emerging Markets Small Cap Fund, Frontier Emerging Small Countries Fund, International Growth Fund and Small Cap Growth Fund have all closed to new third-party accounts.
OLD WINE, NEW BOTTLES
In theory AllianzGI Behavioral Advantage Large Cap Fund (AZFAX) is going to be reorganized “with and into” Fuller & Thaler Behavioral Core Equity Fund, which sounds like the original fund is disappearing. Nay, nay. Fuller & Thayer manage the fund now. The Allianz fund simply becomes the Fuller & Thaler one, likely some time in the third quarter though the reorganization may be delayed. Nice fund, low expenses, good longer-term performance.
Effective May 1, 2015, the name of Eaton Vance Investment Grade Income Fund (EAGIX) changes to Eaton Vance Core Bond Fund.
Emerald Advisers has agreed to acquire the tiny Elessar Small Cap Value Fund (LSRIX). It appears that Emerald will manage the fund on a interim basis until June, when shareholders are asked to make it permanent. Not clear when or if the name will change.
Effective March 31, 2015, Henderson Emerging Markets Opportunities Fund (HEMAX) was renamed Henderson Emerging Markets Fund. The current five-person management team has been replaced by Glen Finegan. Finegan had been responsible for about $13 billion as an EM portfolio manager for First State Stewart, an Edinburgh-domiciled investment manager.
Henderson Global Investors (North America) Inc. is the investment adviser of the Fund. Henderson Investment Management Limited is the subadviser of the Fund. Glen Finegan, Head of Global Emerging Markets Equities, Portfolio Manager, has managed the Fund since March 2015.
Effective April 15, 2015, PIMCO Worldwide Long/Short Fundamental Strategy Fund (PWLAX) became PIMCO RAE Worldwide Long/Short PLUS Fund. The fund launched in December 2014 and I’m guessing that “RAE” is linked to its sub-advisor, Research Affiliates, Inc., Rob Arnott’s firm.
Effective March 1, Manning & Napier Dividend Focus Series (MDFSX) changed to the Disciplined Value Series.
Effective on or about May 1, 2015, the following “enhancements” are expected to be made to the Manning & Napier Core Plus Bond Series (EXCPX) – M&N doesn’t admit to having “funds,” they have “series.”
- It’s rechristened the Unconstrained Bond Series
- Its mandate shifts from “long-term total return by investing primarily in fixed income securities” to “long-term total return, and its secondary objective is to provide preservation of capital.”
- It stops buying just bonds and adds purchases of preferred stocks, ETFs and derivatives as well
- It stops focusing on US investment-grade debt and gains the freedom to own up to 50% high yield and up to 50% international, including emerging markets debt. Not clear whether those circles will overlap into EM HY debt.
Other than for those few tweaks, which were certainly not “fundamental,” it remains the same fund that investors have known and tolerated for the past decade.
Ryan Labs has agreed to be purchased by SunLife, whereupon SL acquired Ryan Labs Core Bond Fund (RLCBX). Given that the fund is tiny and launched four months ago, I’d guess that’s not what drove the purchase. In any case, the acquisition might change the fund’s name but apparently not its advisory contract.
Value Line Larger Companies Fund has changed its name to Value Line Larger Companies Focused Fund (VALLX). The plan is to shrink the portfolio from its current 45 stocks down to 30-50. You can see the new focusedness there.
OFF TO THE DUSTBIN OF HISTORY
This feature usually highlights funds slated to disappear in the next month or two. (Thanks to the indefatigable Shadow and the shy ‘n’ retiring Ted for their leads here.) We’re reporting this month on a slightly different phenomenon. A lot of these funds have already liquidated because their boards shortened the period between decision and death from months down to weeks, often three weeks or less. That really doesn’t give investors much time to adjust though I suppose the boards might be following Macbeth’s advice: “If [murder] were done when ’tis done, then ’twere well It were done quickly.”
But what to make of the rest of Macbeth’s insight?
… we but teach
Bloody instructions, which, being taught, return
To plague the inventor: this even-handed justice
Commends the ingredients of our poison’d chalic
To our own lips.
Perhaps that our impulse to sell, to liquidate, to dispatch might come back to bite us in the … uhh, we mean, “to haunt us”? During our conference call, David Berkowitz recounted the findings of a Fidelity study. Fidelity reviewed thousands of the portfolios they manage, trying to discover the shared characteristics of their most successful investors.
Their findings? The best performance came in accounts where the investors were dead or had forgotten that the account even existed.
ALPS Real Asset Income Fund became, on March 31st, an EX fund.
‘E’s not pinin’! ‘E’s passed on! This parrot is no more! He has ceased to be! ‘E’s expired and gone to meet ‘is maker!
‘E’s a stiff! Bereft of life, ‘e rests in peace! If you hadn’t nailed ‘im to the perch ‘e’d be pushing up the daisies!
‘Is metabolic processes are now ‘istory! ‘E’s off the twig!
(Monty Python)
BTS Hedged Income Fund (BDIAX), a fund of funds, will disappear on April 27, 2015. Apparently the combination of $300,000 in assets and poor performance weighed against its survival.
Dreyfus Greater China Fund (DPCAX) will be liquidated around May 21, 2015
Forward Equity Long/Short Fund (FENRX) goes backward, pretty much terminally backward, on April 24, 2015. It’s not a terrible fund, as long/short funds go; it’s just that nobody was interested in investing in it.
The Board of Trustees approved liquidation of the Fountain Short Duration High Income Fund, with the execution carried out March 27, 2015
Harbor Funds’ Board of Trustees has determined to liquidate and dissolve Harbor Emerging Markets Debt Fund (HAEDX) on April 29, 2015. The fund lost roughly 4% over its four-year life while its peers made roughly the same amount. It’s admirable that the fund was doggedly independent of its peers; it’s less admirable that it lost money in 17 calendar months, often while its peers were posting gains. It’s curious that the same team manages another EM debt fund with a dramatically different record of success:
|
|
Three-year total return |
Total return since inception of HAEDX* |
|
Stone Harbor EM Debt (SHMDX) |
5.0% |
14.0 |
|
Harbor EM Debt |
(7.3%) |
(4.1) |
|
Average EM debt fund |
0.9% |
4.8 |
* 05/02/2011
In mid-March, ISI Total Return U.S. Treasury Fund (TRUSX) and North American Government Bond Fund (NOAMX, which had 15% each in Canadian and Mexican bonds) reorganized into Centre Active U.S. Treasury Fund (DHTRX, which has no such exposure to explain its parlous performance); ISI Strategy Fund (STRTX, which holds a 10% bond stake) merged into Centre American Select Equity Fund (DHAMX, which doesn’t but which still manages to trail STRTX, its peers and the S&P 500); and, finally, Managed Municipal Fund (MUNIX, which was also a substantial laggard) was absorbed by Centre Active U.S. Tax Exempt Fund (DHBIX).
On March 13, the Board of Trustees decided to liquidate the tiny, sucky Loomis Sayles International Bond Fund (LSIAX), which will take place around May 15, 2015.
Morgan Stanley finalized in March a fund merger that we highlighted a couple months ago: the five-star, $350 million Morgan Stanley Global Infrastructure Fund (UTLAX) merged into Morgan Stanley Institutional Fund Select Global Infrastructure Portfolio (MTIPX) at the end of March. MTIPX is … uhh, dramatically smaller, more expensive and marginally less successful. No word on whether the five-fold rise in assets at MTIPX will be occasioned by a dramatic expense reduction, or at least a reduction to the level enjoyed by the former UTLAX shareholders.
Pathway Advisors Growth and Income Fund (PWGFX) was closed and liquidated on March 31, 2015. It strikes me as the sort of fund that an adviser might want to sell to someone getting into the business since those filings are a lot cheaper than the initial filings for a new fund. Generally buying a failed fund is undesirable because you’re buying (and hauling along) its failed record, but there are instances like this where the trailing record isn’t disastrous. Curiously, this decision leaves open the family’s other two (weaker, smaller) funds.
On March 12, 2015, the Board of Directors of The Glenmede Fund approved a plan of liquidation and termination for the Glenmede Philadelphia International Fund (GTIIX). On or about May 15, the fund will be liquidated
 The Royce Fund’s Board of Trustees recently approved a plan of liquidation for Royce Select Fund II (RSFDX), Royce Enterprise Select Fund (RMISX), Royce SMid-Cap Value Fund (RMVSX), Royce Partners Fund (RPTRX) and Royce Global Dividend Value Fund (RGVDX). In their delicately worded phrase, “the plan will be effective on April 23, 2015.” That puts the plan in contrast to the funds themselves, which were part of the seemingly mindless expansion of the Royce lineup. Between 1962 and 2001, Royce launched nine funds – all domestic small caps. They were acquired by Legg Mason in 2001. Between 2001 and the present, they launched 21 mutual funds and three closed-end funds in a striking array of flavors. Almost none of the newer funds found traction, with 10 of the 21 sitting under $10 million in assets. Shostakovich, one of our discussion board’s most experienced correspondents, pretty much cut to the chase: “Chuck sold his soul. He kept his cashmere sweaters and his bow ties, but he sold his soul. And the devil’s name is Legg Mason.”
The Royce Fund’s Board of Trustees recently approved a plan of liquidation for Royce Select Fund II (RSFDX), Royce Enterprise Select Fund (RMISX), Royce SMid-Cap Value Fund (RMVSX), Royce Partners Fund (RPTRX) and Royce Global Dividend Value Fund (RGVDX). In their delicately worded phrase, “the plan will be effective on April 23, 2015.” That puts the plan in contrast to the funds themselves, which were part of the seemingly mindless expansion of the Royce lineup. Between 1962 and 2001, Royce launched nine funds – all domestic small caps. They were acquired by Legg Mason in 2001. Between 2001 and the present, they launched 21 mutual funds and three closed-end funds in a striking array of flavors. Almost none of the newer funds found traction, with 10 of the 21 sitting under $10 million in assets. Shostakovich, one of our discussion board’s most experienced correspondents, pretty much cut to the chase: “Chuck sold his soul. He kept his cashmere sweaters and his bow ties, but he sold his soul. And the devil’s name is Legg Mason.”
Lutherans are a denomination renowned for the impulse toward merger, so it should be no real surprise that Lutheran funds (Thrivent Funds used to be the Aid Association for Lutherans Funds) would follow the same path. On August 28, eight Thrivent funds will become three:
|
Target Fund |
Acquiring Fund |
|
|
Thrivent Partner Small Cap Growth Fund |
into |
Thrivent Small Cap Stock Fund |
|
Thrivent Partner Small Cap Value Fund |
into |
Thrivent Small Cap Stock Fund |
|
Thrivent Mid Cap Growth Fund |
into |
Thrivent Mid Cap Stock Fund |
|
Thrivent Partner Mid Cap Value Fund |
into |
Thrivent Mid Cap Stock Fund |
|
Thrivent Natural Resources Fund |
into |
Thrivent Large Cap Stock Fund |
Pending shareholder approval, Touchstone Capital Growth Fund (TSCGX) merges into the Touchstone Large Cap Fund (TACLX) on or about June 26, 2015. Pending that move, Capital Growth is closed to new investors. Not to suggest that anyone is trying to bury a consistently bad record, but the decedent fund is 12 years old where the acquiring fund is barely 12 months old and the decedent is well more than twice the size of its acquirer.
Sometime during the third quarter, Transamerica Tactical Allocation (TTAAX) will merge into Transamerica Tactical Rotation (ATTRX). They were launched on the same day and are managed by the same team, but the Rotation fund has posted far stronger returns. That said, neither fund has attracted serious assets.
The Turner Titan Fund (TTLFX) is now scheduled to be liquidated on April 30, about six weeks later than originally announced. No word as to why. It wasn’t a bad fund as far as long/short funds go but that, sadly, isn’t saying much. It’s up about 22% total since inception in 2011 (right, about 4% a year) against a peer average of 15%. But no one was impressed and the fund never attracted enough assets to cover its cost of operation.
Van Eck Multi-Manager Alternatives Fund VMAAX) “is expected to be liquidated and dissolved on or about June 3, 2015.” $10 million in assets, 2.84% e.r., consistently bottom decile returns. Yeah, it’s about time to go.
On February 25, 2015, the Board of Trustees of the Virtus Opportunities Trust voted to liquidate the Virtus Global Commodities Stock Fund (VGCAX). On or about April 30, 2015, the Fund will be no more. The fund has turned $10,000 invested at inception into $7200, bad even by the standards of the funds in Morningstar’s natural resources category.
In Closing . . .
My friend Linda approaches some holidays, particularly those that lead to her receiving presents, with the mantra “it’s not a day, it’s a season!” We’re taking the same perspective on the Observer’s fourth anniversary. We launched in phases between early April and early May, 2011. April saw the “soft launch” as we got the discussion board and archival fund profiles moved over from our former home as FundAlarm. Since then, something like 550,000 readers have joined us with about 25,000 “unique” visitors each month now. May saw the debut of our first monthly commentary and our first four fund profiles (each of which, by the way, was brilliant).
In that same easy spirit, we rolled out a series of visual upgrades this month. The new design features our trademark owl peering at you from the top of the page, a brighter and more consistent color palette, better response times (pages are loading about 30% faster than before), new Amazon and Paypal badges (try them out! really) and a responsive design that should provide much better readability on smart phones, tablets and other mobile devices.
In May we’ll freshen up our homepage and will look back at the stories and funds that launched the Observer.
Your support, both intellectual and financial, makes that happen. Thanks most immediately go to the Messrs. Gardey & co. at Gardey Financial, to Dan at Callahan Capital, to Capt. Neel (hope retirement is treating you well, sir!), to Ed and Charles (no, not the Ed and Charles whose work appears above; rather, the Ed and Charles who seem to appreciate the yeoman work done by, well, Ed and Charles), to Joseph whom we haven’t met before and Eric E. who’s a sort of repeat offender when it comes to supporting the Observer and, as ever, to our two subscribers. (Deb and Greg have earned the designation by setting up automatic monthly contributions through PayPal. It was even their idea.)
As ever,

Egads! I’ve been unmasked.