At the time of publication, this fund was named Huber Equity Income. This fund was formerly named Huber Capital Equity Income.
Objective and strategy
The Fund is pursuing both current income and capital appreciation. They typically invest in 40 of the 1000 largest domestic large cap stocks. It normally invests in stocks with high cash dividends or payout yields relative to the market but can buy non-payers if they have growth potential unrecognized by the market or have undergone changes in business or management that indicate growth potential.
Adviser
Huber Capital Management, LLC, of Los Angeles. Huber has provided investment advisory services to individual and institutional accounts since 2007. The firm has about $4 billion in assets under management, including $450 million in its three mutual funds.
Manager
Joseph Huber. Mr. Huber was a portfolio manager in charge of security selection and Director of Research for Hotchkis and Wiley Capital Management from October 2001 through March 2007, where he helped oversee over $35 billion in U.S. value asset portfolios. He managed, or assisted with, a variety of successful funds across a range of market caps. He is assisted by seven other investment professionals.
Strategy capacity and closure
Approximately $10 billion. That’s based on their desire to allow each position to occupy about 2% of the fund’s portfolio while not owning a controlling position in any of their stocks. Currently they manage about $1.5 billion in their Select Large Value strategy.
Active share
Not calculated. “Active share” measures the degree to which a fund’s portfolio differs from the holdings of its benchmark portfolio. High active share indicates management which is providing a portfolio that is substantially different from, and independent of, the index. An active share of zero indicates perfect overlap with the index, 100 indicates perfect independence. Mr. Huber, independently enough, dismisses it as “This year’s new risk-control nomenclature. Next year it’ll be something else.”
Management’s stake in the fund
Mr. Huber has over $1 million invested in each of his three funds. His analysts are all on track to become partners and equity owners of the advisor.
Opening date
June 29, 2007
Minimum investment
$5,000 for regular accounts and $2,500 for retirement accounts.
Expense ratio
1.39% on $85 million in assets, as of July 2023.
Comments
There’s no question that it works.
None at all.
Morningstar thinks it works:
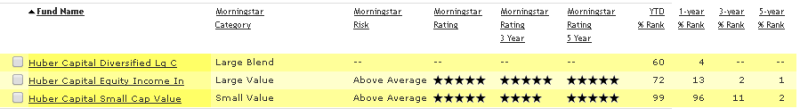
Lipper lavishly thinks so:
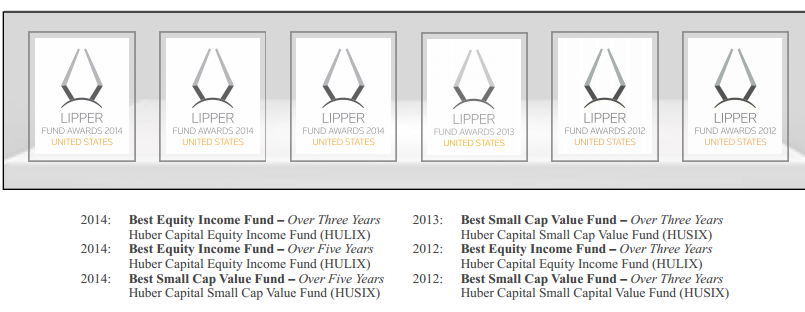
And the Observer mostly concurs, recognizing both of the established Huber funds as Great Owls based on their consistently excellent risk-adjusted performance:
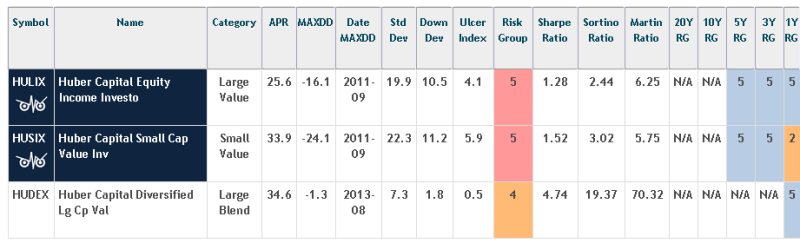
In addition to generating top-tier absolute and risk-adjusted returns, the Huber funds also generate very light tax burdens. By consciously managing when to sells securities (preferably when they qualify for lower long-term rates) and tax-loss harvesting, his investors have lost almost nothing to taxes over the past five years.
It works.
There’s only one question: does it work for you?
Mr. Huber pursues a rigorous, research-driven, value-oriented style. He’s been refining it for 20 years but the core has remained unchanged since his Hotchkis & Wiley days. He has done a lot of reading in behavioral finance and has identified a series of utterly predictable mistakes that investors – his team as much as other folks – are prone to make over and over. His strategy is two-fold:
Exploit other investors’ mistakes. Value investors tend to buy too early and sell too early; growth investors do the opposite. Both sides tend to extrapolate too much from the present, assuming that companies with miserable financials (for example, extremely low return on capital) will continue to flounder. His research demonstrates the inevitability of mean reversion, the currently poorest companies will tend to rise over time and the currently-strongest will fall. By targeting low ROC firms, which most investors dismiss as terminal losers, he harvests over time a sort of arbitrage gain as ROC rises toward the mean on top of market gains.
Guard against his own tendency to make mistakes. He’s created a red flags list, a sort of encyclopedia of all the errors that he or other investors have made, and then subjects each holding to a red flag review. They also have a “negative first to negative second derivative” tool that keeps them from doubling down on a firm whose rate of decline is accelerating and a positive version that might slow down their impulse to sell early.
Beyond that, they do rigorous and distinctive research. While many investors believe that large caps occupy the most efficient part of the market, Mr. Huber strongly disagrees. His argument is that large caps have an enormous number of moving parts, divisions within the firm that have their own management, culture, internal dynamics and financials. Pfizer, a top holding, has divisions specializing in Primary Care; Specialty Care and Oncology; Established Products and Emerging Markets; Animal Health; and Consumer Healthcare. Pfizer need not report the divisions’ financials separately, so many investors are stuck with investing backs on aggregate free cash flow firm-wide and a generic metric about what that flow should be. The Huber folks approach it differently: they start by looking at smaller monoline firms (for example, a firm that just specializes in animal care) which allows them to see that area’s internal dynamics. They then adjust the smaller firm’s financials to reflect what they know of Pfizer’s operations (Pfizer might, for example, have lower cost of capital than the smaller firm). By modeling each unit or division that way and then assembling the parts, they end up with a surrogate for Pfizer as a whole.
Huber’s success is illustrated when we compare HULIX to three similarly-vintaged large-value funds:
Artisan Value (ARTLX), mostly because Artisan represents consistent excellence and this four-star fund from the U.S. Value team is no exception.
LSV Conservative Core (LSVPX) because LSV’s namesake founders published some 200 papers on behavioral finance and incorporated their research into LSV’s genes.
Hotchkis and Wiley Diversified Value (HWCAX) because Mr. Huber was the guy who built, designed and implemented H&W’s state of the art research program.
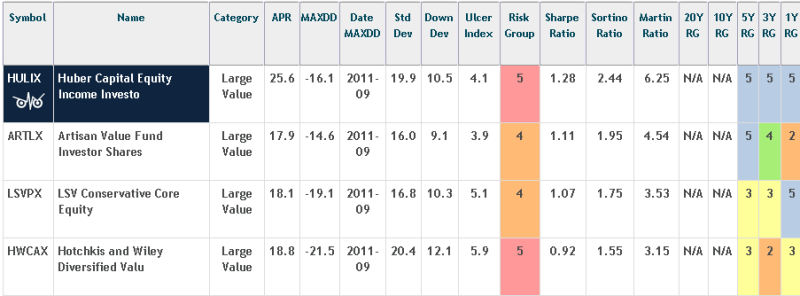
Higher returns, competitive downside, and higher risk-adjusted returns (those are all the ratios on the right where higher is better).
The problem is those returns are accompanied by levels of volatility that many investors are unprepared to accept. It’s a problem that haunted two other Morningstar Manager of the Decade award winners. Here are the markers to keep in mind:
-
- Morningstar risk: over the past five years is high.
- Beta: over the past five years is 1.18, or 18% greater than average.
- Standard deviation: over the past five years is 18% compared to 14.9 for its peers.
- Investor returns: by Morningstar’s calculation, the average investor in the fund over the past five years has earned 23.9% while the fund returned 32.1%. That pattern usually reflects bad investor behavior: buying in greed, selling in fear. This pattern is generally associated with funds that are more volatile investors can bear. (There’s an irony in the prospect that investors in the fund might be undone by the very sorts of behavioral flaws that the manager so profitably exploits.)
He also remains fully invested at all times, since he assumes that his clients have made their own asset allocation decisions. His job is to buy the best stocks possible for them, not to decide whether they should be getting conservative or aggressive.
Mr. Huber’s position on the matter is two-fold. First, short-term volatility should have no place in an investor’s decision-making. For the 45 year old with a 40 year investment horizon, nothing that happens over the next 40 months is actually consequential. Second, he and his team try to inform, guide, educate and calm their investors through both written materials and conference calls.
Bottom Line
Huber Equity Income has all the hallmarks of a classic fund: it has a disciplined, distinctive and repeatable process. There’s a great degree of intention and thought in its design. Its performance, like that of its small cap sibling, is outstanding. It is a discipline well-suited to Huber’s institutional and pension-plan accounts, which contribute 90% of the firm’s assets. Those institutions have long time horizons and, one hopes, the sort of professional detachment that allows them to understand what “investing for the long-term” really entails. The challenge is deciding whether, as a small investor or advisor, you will be able to maintain that same cool, unflustered demeanor. If so, this might be a very, very good move for you.
Fund website
Huber Capital Equity Income Fund
© Mutual Fund Observer, 2014. All rights reserved. The information here reflects publicly available information current at the time of publication. For reprint/e-rights contact us.