Update: This fund has been liquidated.
Objective and Strategy
The fund seeks to provide investors with a positive return regardless of the direction and fluctuations of the U.S. equity markets by creating a market neutral portfolio designed to exploit inefficiencies in the markets. While they can invest in stocks of any size, they anticipate a small- to mid-cap bias. The managers advertising three reasons to consider the fund:
Downside Management: they seek to limit exposure to downside risk by running a beta neutral portfolio (one with a target beta of 0.2 to minus 0.2 which implies a net equity exposure of 20% to minus 20%) designed to capitalize on arbitrage opportunities in the equity markets.
Portfolio Diversification: they seek to generate total return that is not correlated to traditional asset classes and offers portfolio diversification benefits.
Experienced, Talented Investment Team: The team possess[es] decades of experience investing in long short equity strategies for institutional investors.
Morningstar analysis of their portfolio bears no resemblance to the team’s description of it (one short position or 198? 65% cash or 5%?), so you’ll need to proceed with care and vigilance. Unlike many of its competitors, this is not a quant fund.
Adviser
Whitebox Advisors LLC, a multi-billion dollar alternative asset manager founded in 2000. Whitebox manages private investment funds (including Credit Arbitrage, Small Cap L/S Equity, Liquid L/S Equity, Special Opportunities and Asymmetric Opportunities), separately managed accounts and the two (soon to be three) Whitebox funds. As of January 2012, they had $2.3 billion in assets under management (though some advisor-search sites have undated $5.5 billion figures).
Manager
Andrew Redleaf, Jason E. Cross, Paul Karos and Kurt Winters. Mr. Redleaf founded the advisor, has deep hedge fund experience and also manages Whitebox Tactical Opportunities. Dr. Cross has a Ph.D. in Statistics, had a Nobel Laureate as an academic adviser and published his dissertation in the Journal of Mathematical Finance. Together they also manage a piece of Collins Alternative Solutions (CLLIX). Messrs. Karos and Winters are relative newcomers, but both have substantial portfolio management experience.
Management’s Stake in the Fund
Not yet reported but, as of 12/31/12, Whitebox and the managers owned 42% of fund shares and the Redleaf Family Foundation owned 6.5% Mr. Redleaf also owns 85% of the advisor.
Opening date
November 01, 2012 but The Fund is the successor to Whitebox Long Short Equity Partners, L.P., a private investment company managed by the Adviser from June, 2004 through October, 2012.
Minimum investment
$5000, reduced to $1000 for IRAs.
Expense ratio
1.95% after waivers on assets of $17 million (as of March, 2013). The “Investor” shares carry a 4.5% front-end sales load, the “Advisor” shares do not.
Comments
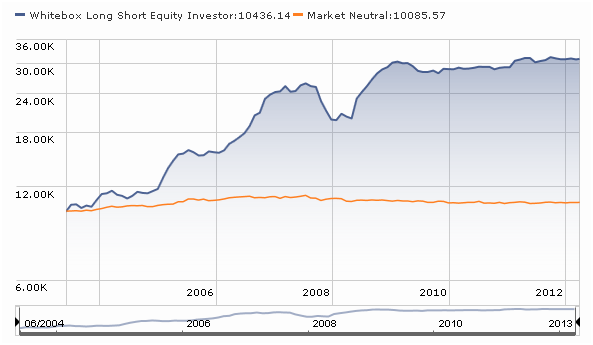
Here’s the story of the Whitebox Long Short Equity fund, in two pictures.
Picture One, what you see if you include the fund’s performance when it was a hedge fund:
Picture Two, what you see if you look only at its performance as a mutual fund:
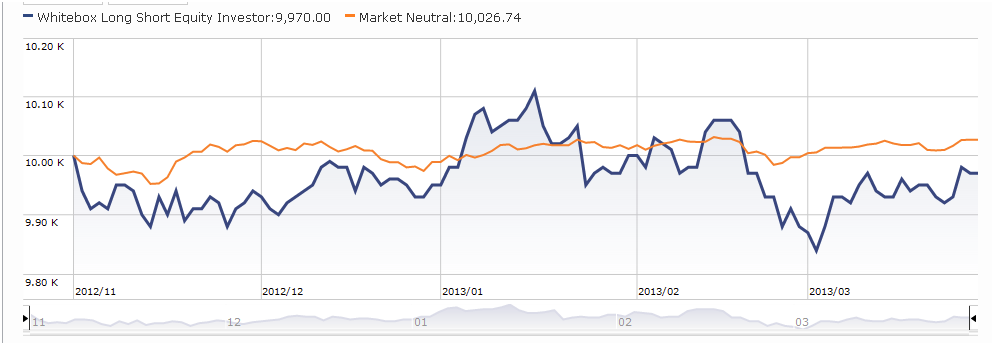
The divergence between those two graphs is striking and common. There are lots of hedge funds – the progenitors of Nakoma Absolute Return, Baron Partners, RiverPark Long Short Opportunities – which offered mountainous chart performance as hedge funds but whose performance as a mutual fund was somewhere between “okay” and “time to turn out the lights and go home.” The same has been true of some funds – for example, Auer Growth and Utopia Core – whose credentials derive from the performance of privately-managed accounts. Similarly, as the Whitebox managers note, there are lots of markets in which their strategy will be undistinguished.
So, what do they do? They operate with an extremely high level of quantitative expertise, but they are not a quant fund (that’s the Whitebox versus “black box” distinction). We know that there are predictable patterns of investor irrationality (that’s the basis of behavioral finance) and that those investor preferences can shift substantially (for example, between obsessions with greed and fear). Whitebox believes that those irrationalities continually generate exploitable mispricings (some healthy firms or sound sectors priced as if bankruptcy is imminent, others priced as if consumers are locked into an insane spending binge). Whitebox’s models attempt to identify which factors are currently driving prices and they assign a factor score to stocks and sectors.
Whitebox does not, however, immediately act on those scores. Instead, they subject the stocks to extensive, fundamental analysis. They’re especially sensitive to the fact that quant outputs become unreliable in suddenly unstable markets, and so they’re especially vigilant in such markets are cast a skeptical eye on seemingly objective, once-reliable outputs.
They believe that the strengths of each approach (quant and fundamental, machine and human) can be complementary: they discount the models in times of instability but use it to force their attention on overlooked possibilities otherwise.
They tend assemble a “beta neutral” portfolio, one that acts as if it has no exposure to the stock market’s volatility. They argue that “risk management … is inseparable from position selection.” They believe that many investors mistakenly seek out risky assets, expecting that higher risk correlates with higher returns. They disagree, arguing that they generate alpha by limiting beta; that is, by not losing your money in the first place. They’re looking for investments with asymmetric risks: downside that’s “relatively contained” but “a potentially fat tailed” upside. Part of that risk management comes from limits on position size, sector exposure and leverage. Part from daily liquidity and performance monitoring.
Whitebox will, the managers believe, excel in two sorts of markets. Their discipline works well in “calm, stable markets” and in the recovery phase after “pronounced market turmoil,” where prices have gotten seriously out-of-whack. The experience of their hedge fund suggests that they have the ability to add serious alpha: from inception, the fund returned about 14% per year while the stock market managed 2.5%.
Are there reasons to be cautious? Yep. Two come to mind:
- The fund is expensive. After waivers, retail investors are still paying nearly 2% plus a front load of 4.5%. While that was more than offset by the fund’s past returns, current investors can’t buy past returns.
- Some hedge funds manage the transition well, others don’t. As I noted above, success as a hedge fund – even sustained success as a hedge fund – has not proven to be a fool-proof predictor of mutual fund success. The fund’s slightly older sibling, Whitebox Tactical Opportunities (WBMAX) has provided perfectly ordinary returns since inception (12/2011) and weak ones over the past 12 months. That’s not a criticism, it’s a caution.
Bottom Line
There’s no question that the managers are smart, successful and experienced hedge fund investors. Their writing is thoughtful and their arguments are well-made. They’ve been entrusted with billions of other people’s money and they’ve got a huge personal stake – financial and otherwise – in this strategy. Lacking a more sophisticated understanding of what they’re about and a bit concerned about expenses, I’m at best cautiously optimistic about the fund’s prospects.
Fund website
Whitebox Market Neutral Equity Fund. (The Whitebox homepage is just a bit grandiose, so it seems better to go straight to the fund’s page.)
© Mutual Fund Observer, 2013. All rights reserved. The information here reflects publicly available information current at the time of publication. For reprint/e-rights contact us.