By David Snowball
Dear friends,
In the midst of the stock market’s recent generosity – 250 mutual funds booked returns of 20% or more in the first two months of 2012 – it’s easy to forget how bad 2011 was for the smart money crowd. The average equity hedge fund, represented by the HFRX Equity Hedge Index, lost 19% for the year. The value guys lost more than the growth guys. The Economist took some glee in reproducing a hypothetical letter from a hedge fund manager. It reads, in part,
It is also time to move on from the concept of delivering “alpha”, the skill you’ve paid us such fat fees for. Upon reflection, we have decided that we’re actually much better at giving you “smart beta”. This term is already being touted at industry conferences and we hope shortly to be able to explain what it means. Like our peers we have also started talking a lot about how we are “multi-strategy” and “capital-structure agnostic”, and boasting about the benefits of our “unconstrained” investment approach. This is better than saying we don’t really understand what’s going on.
As an unofficial representative of the dumb money crowd, I’ll peel my eyes away from the spectacle of the Republican Party deciding which vital organ to stab next, just long enough to offer a cheery “nyah-nyah-nyah.”
The Observer in The Journal
As many of you know, The Wall Street Journal profiled the Observer in a February 6 article entitled “Professor’s Advice: It’s Best to Be Bored.” I talked a bit about the danger of “exciting” opportunities, offered leads on a dozen cool funds, and speculated about two emerging bubbles. Neither should be a great surprise, but both carry potentially enormous consequences.
The bubbles in question are U.S. bonds and gold. And those bubbles are scary because those assets have proven to be the last refuge for tens of millions of older investors (who, by the way, vote in huge numbers) whose portfolios were slammed by the stock market’s ferocious, pointless decade. Tim Krochuk of GRT Capital Partners volunteers the same observation in a conversation this week. “If rates return to normal – 4 or 5% – holders of long bonds are going to lose 40 – 50%. If you thought that a 40% stock market fall led to blood in the streets, wait until you see what happens after a hit that big in retirees’ ‘safe’ portfolios.” Folks from Roger Ibbotson to Teresa Kong have, this week, shared similar concerns.
For visual learners, here are the two graphs that seem best to reflect the grounds for my concern.
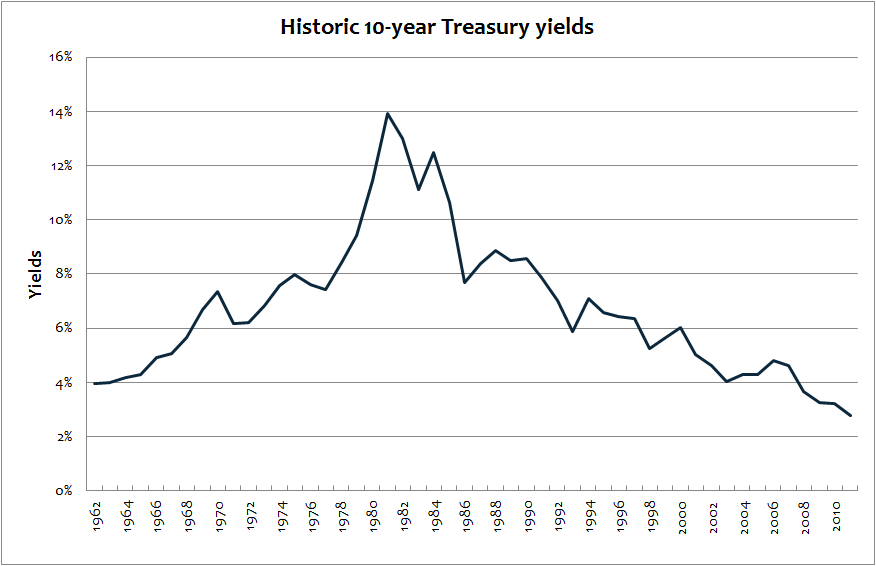
The first graph is the yield on benchmark 10-year Treasuries. When the line is going up, Treasuries are in a bear market. When the line is going down, they’re in a bull market. Three things stand out, even to someone like me who’s not a financial professional:
- A bear market in bonds can last decades.
- The current bull market in bonds has proceeded, almost without interruption for 30 years.
- With current yields at 2% and inflation at 3% (i.e., there’s a negative real yield already), there’s nowhere much for the bull to go from here.
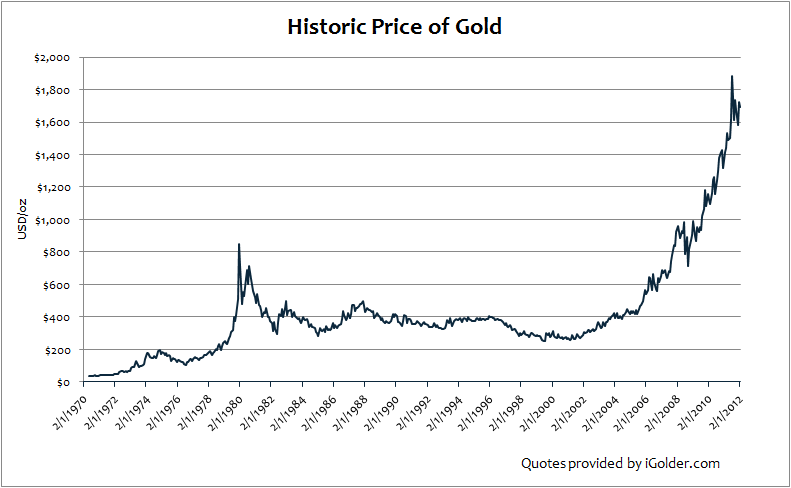
The second graph is the price of gold. Since investing in gold is a matter of theology rather than economics, there’s not much to say beyond “gee, do you suppose it’ll rise forever?”
It might. Thomas Sowell’s Basic Economics calculates that $1 investing in U.S. stocks in 1800 and held for about 200 years would be worth $500,000. $1 in gold would be worth $0.78. But this time’s different. It always is.
In celebration of boring investments
In investing terms, “income” was once dismissed as the province of the elderly whose other eccentricities included reflection on the state of their bowel movements and strong convictions about Franklin Roosevelt. Market strategies abjured dividend-paying firms, reasoning that dividends only arose when management was too timid or stupid to find useful things to do with their earnings. And equity managers who were trapped by the word “income” in their fund name tried various dodges to avoid it. In the mid-90s, for example, Fidelity Dividend Growth fund (FDGFX) invested in fast growing small caps, under the theory that those firms had “the potential to increase (or begin paying) dividends in the future.” Even today, it’s possible to find funds (Gabelli, Columbia, Huber, FAM) named “Equity Income” with yields below 0.6%.
The problem was compounded by organizational structures that isolated the equity and fixed-income teams from each other. Even most stock/bond hybrid funds maintained the division: 60% of the portfolio was controlled by the equity manager, 40% by the fixed income manager. Period. Only a handful of managers – chief among them, David Winters at Wintergreen (WGRNX) and his forebears at the Mutual Series, Marty Whitman at Third Avenue Value (TAVFX), Steve Romick at FPA Crescent (FPACX) and Andrew Foster and Paul Matthews at Matthews Asian Growth and Income (MACSX) – had the freedom, the confidence and the competence to roam widely over a firm’s capital structure.
Today, some of the best analysis and most innovative product design is being done on income-sensitive funds. That might reflect the simple fact that funds without income (alternately, gold exposure) have had a disastrous decade. Jeremy Grantham observes in his latest quarterly letter
The U.S. market was terrible for the last 10 years, gaining a pathetic 0.5% per year overall, after inflation adjustments and even including dividends. Without dividends, the [S&P 500] index itself has not gone up a penny in real terms from mid-1997 to end-2011, or 14½ years. This is getting to be a long time!
Now dividend-stocks are (unwisely) declared as an alternative to bonds (“stock dividends, as an alternative or supplement to bonds, are shaping up to have better yields and less risk” notes a 2012 article in Investment News) and investors poured money into them in 2011.
The search for income is increasingly global. Morningstar reports that “There now are 24 equity income funds that invest at least 25% of their assets outside of the U.S. and 30 funds that invest at least 75%, with the majority of those funds being launched in the last few years, according to Lipper.”
Among the cool options now available:
Calamos Evolving World Growth (CNWGX), which invests broadly in emerging market stocks, the stocks of developed market firms which derive at least 20% of sales in emerging markets, then adds convertibles or bonds to manage volatility. 4.75% front load, 1.68% e.r.
Global X Permanent ETF (PERM) which will pursue a Permanent Portfolio-like mix of 25% stocks, 25% gold and silver, 25% short-term bonds, and 25% long-term government bonds. Leaving aside the fact that with Global X nothing is permanent, this strategy for inflation-proofing your portfolio has some merits. We’ll look at PERM and its competitors in detail in our April issue.
Innovator Matrix Income Fund (IMIFX), which intends to rotate through a number of high-yielding surrogates for traditional asset classes. Those include master limited partnerships, royalty trusts, REITs, closed end funds and business development companies. In, for example, a low-inflation, low-growth environment, the manager would pursue debt REITs and closed-end bond funds to generate yield but might move to royalty trusts and equity REITs if both inflation and growth accelerated. Hmmm.
iShares Morningstar Multi-Asset High Income Index Fund, still in registration, which will invest 20% in stocks, 60% in bonds (including high-yield corporates, emerging markets and international) and 20% in “alternative assets” (which means REITs and preferred shares). Expenses not yet announced.
WisdomTree Emerging Markets Equity Income (DEM), which launched in 2007. It holds the highest-paying 30% of stocks (about 300) in the WisdomTree Emerging Markets Dividend Index. The fund has returned 28% annually over the past three years (through 1/31/12), beating the emerging markets average by 5% annually. By Morningstar’s calculation, the fund outperforms its peers in both rising and falling markets. Expenses of 0.63%.
In September of 2010, I lamented “the best fund that doesn’t exist,” an emerging markets balanced fund. Sophisticated readers searched and did find one closed-end fund that fit the bill, First Trust Aberdeen Emerging Opportunities (FEO), which I subsequently profiled as a “star in the shadows.” A pack of emerging markets balanced funds have since comes to market:
AllianceBernstein Emerging Markets Multi Asset (ABAEX) will hold 0-65% bonds (currently 40%), with the rest in stocks and cash. 4.25% front load, 1.65% e.r.
Dreyfus Total Emerging Markets (DTMAX), which has an unconstrained allocation between stocks and bonds. 5.75% load, 1.65% e.r.
Fidelity Total Emerging Markets (FTEMX), launched in November and already approaching $100 million in assets, the fund has a pretty static 60/40 allocation. No-load, 1.40% e.r.
First Trust/Aberdeen Emerging Opportunities (FEO), a closed-end fund and an Observer “Star in the Shadows” fund. About 60% bonds, 40% stocks. Exchange traded, 1.76% e.r.
Lazard Emerging Markets Multi-Strategy (EMMOX), which has a floating allocation between stocks, bonds (including convertibles) and currency contracts. No-load, 1.60% e.r.
PIMCO Emerging Multi-Asset (PEAAX), the most broadly constructed of the funds, is benchmarked against an index which invests 50/50 between stocks and bonds. The fund itself can combine stocks, bonds, currencies and commodities. 5.5% load for the “A” shares, 1.74% expenses.
Templeton Emerging Markets Balanced (TAEMX), which must have at least 25% each in stocks and bonds but which is currently 65/30 in favor of stocks. 5.75% front load, 1.54% expenses.
While the options for no-load, low-cost investors remain modest, they’re growing – and growing in a useful direction.
Launch Alert (and an interview): Seafarer Overseas Growth and Income
 In my February 2012 Commentary, I highlighted the impending launch of Seafarer Overseas Growth and Income (SFGIX and SIGIX). I noted
In my February 2012 Commentary, I highlighted the impending launch of Seafarer Overseas Growth and Income (SFGIX and SIGIX). I noted
The fund will be managed by Andrew Foster, formerly manager of Matthews Asia Growth & Income (MACSX) and Matthews’ research director and acting chief investment officer.
The great debate surrounding MACSX was whether it was the best Asia-centered fund in existence or merely one of the two or three best funds in existence. Here’s the broader truth within their disagreement: Mr. Foster’s fund was, consistently and indisputably one of the best Asian funds in existence.
The launch provoked three long, thoughtful discussion threads about the prospects of the new fund, the Seafarer prospectus was our most downloaded document in the month of February and Chip, our sharp-eyed technical director, immediately began plotting to buy shares of the fund for her personal portfolio.
Mr. Foster and I agreed that the best way to agree potential investors’ questions was, well, to address potential investors’ questions. He read through many of the comments on our discussion broad and we identified these seven as central, and often repeated.
Kenster1_GlobalValue: Could he tell us more about his investment team? He will be lead manager but will there be a co-manager? If not, then an Assistant Manager? How about the Analysts – tell us more about them? Does he plan to add another analyst or two this year to beef up his team?
He’s currently got a team of four. In addition to himself, he works with:
Michelle Foster, his wife, CFO, Chief Administrator and partner. She has a remarkable investing resume. She started as an analyst with JP Morgan, was a Principal at Barclay’s Global Investors (BGI) where she developed ETFs (including one that competed directly with Andrew’s India fund), and then joined investment advisory team at Litman/Gregory Asset Management.
William Maeck, his Associate Portfolio Manager and Head Trader. William was actually Foster’s first boss at A. T. Kearney in Singapore where Andrew worked before joining Matthews. Before joining Seafarer, he worked with Credit Suisse Securities as an investment advisor for high net worth individuals and family offices. For now, William mostly monitors trading issues for the fund and has limited authority to execute trades at Foster’s direction. With time, he should move toward more traditional co-manager responsibilities.
Kate Jaquet, Senior Research Analyst and Chief Compliance Officer. Kate brings a lot of experience in fixed-income and high-yield investing and in Latin America. She began her career in emerging markets in 1995 as an economic policy researcher for the international division of The Adam Smith Institute in London. In 1997, she joined Credit Suisse First Boston as an investment banking and fixed-income analyst within their Latin America group. In 2000, she joined Seneca Capital Management in San Francisco as a senior research analyst in their high yield group. She worked on high yield and distressed issuers, the metals & mining, oil & gas, and utilities industries, emerging market sovereigns and select emerging market corporate issuers.
AndyJ : I’m still mildly curious about the context of his leaving Matthews. Simply “pursuing other opportunities” might be the whole story, or it might not – even if perfectly true, there’s likely a context that would be interesting to know about.
Good and fair question. Mr. Foster has a deep and abiding respect for Matthews and a palpable concern for his former shareholders. When he joined Matthews in 1998, the firm managed $180 million. It had grown a hundredfold by the time he left. As a long-time member of the team, sometime chief investment officer, chief research officer and portfolio manager, he’d made a huge and rewarding commitment to the company. About his leaving Mr. Foster made two points:
- A fund like this has been on his mind for a decade. It wasn’t clear, ten years ago, whether Matthews would remain purely Asia-focused or would broaden its geographic horizons. As part of those deliberations, Paul Matthews asked Andrew to design a global version of MACSX. He was very excited about the potential of such a fund. After a long debate, Matthews concluded that it would remain an Asia specialist. He respects their decision (indeed, as manager, helped make it pay off) but never gave up the dream of the broader fund and knew it would never fit at Matthews.
- He did not leave until he was sure that his MACSX shareholders were in good hands. He worked hard to build “an extremely capable team,” even celebrating the fact that he only hired “people smarter than me.” He became convinced that the fund was in the hands of folks who’d put the shareholders first. In order to keep it that way, he “made sure I didn’t do anything to advance [Seafarer] at the expense of Matthews.” As a result, his current team is drawn from outside Matthews and he has not sought to aggressively recruit former shareholders out of the prior fund so as to drive growth in the new one.
Kenster1_GlobalValue: What does he see as potentially the top 3 countries in the fund if he were investing & managing the Seafarer fund right now? As an example – Indonesia looks great but what are his thoughts on this country? How would he rate it? Would he be lightly invested in Indonesia because he feels it might be too growthy at this time?
While he didn’t address Indonesia in particular, Mr. Foster did highlight six markets that were “particularly interesting.” They are:
- Vietnam
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Turkey
- Poland
- South Africa
He argues that there are substantial political and cultural challenges in many of these countries, and that that turmoil obscures the fundamental strength of the underlying economy. While it’s possible to conclude that you’d have to be nuts to sink your money in broken countries, Andrew notes that “broken can be good . . . the key is determining whether you’re experiencing chaos or progress, both raise a lot of dust.” His general conclusion, having lived through generations of Asian crisis, “I’ve seen this story before.”
Maurice: I’d be interested in what Mr. Foster brings new to the table. Why would I not if invest new dollars with Matthews?
He thinks that two characteristics will distinguish Seafarer:
- The Fund can provide exposure to multiple asset classes, as its strategy allows for investment in equities, convertible bonds, and fixed income.
- The Fund has a broad geographical mandate. It’s not just broader than Asia, it’s also broader than “emerging markets.” SFGIX / SIGIX is pursuing exposure to emerging and frontier markets around the world, but Mr. Foster notes that in some instances the most effective way to gain such exposure is through the securities in neighboring countries. For example, some of the best access to China is through securities listed in Singapore and Hong Kong; Australia plays a similar role for some Asian markets.
MikeM : It seems to me that if you are looking for Asian exposure, this may not be your fund. This fund is not supposed to be an Asian concentrated fund like his previous fund at Matthews, MACSX.
Yes and no. Mr. Foster can invest anywhere and is finding a lot of markets today that have the characteristics that Asia had ten years ago. They’re fundamentally strong and under-recognized by investors used to looking elsewhere. That said, he considers Asia to be “incredibly important” (a phrase he used four times during our conversation) and that “a large portion of the portfolio, particularly at the outset” will be invested in the Asian markets with which he’s intimately acquainted.
AndyJ: It’s danged expensive. There’s a closed-end fund, FEO, from the long-successful people at Aberdeen, which has a proven track record using a “balanced” EM strategy and costs the same as the investor shares of the Foster fund will. So, I’m not totally sure that Seafarer as a brand new entity is worthier of new $ at this point than FEO.
His response: “I hear you.” His money, and his family’s, is in the fund and he wants it to be affordable. The fund’s opening expense ratio is comparable to what Matthews charged when they reached a billion in assets. He writes, “I view it as one of the firm’s central duties to ensure that expenses become more affordable with scale, and over time.” Currently, he can’t pass along the economies of scale, but he’s committed to do so as soon as it’s economically possible. His suspicion is that many funds get complacent with their expense structure, and don’t work to aggressively pursue savings.
fundalarm — it’s almost exclusively about pay. If you’re a star, and your name is enough to attract assets, why would you want to share the management fee with others when you can have your own shop. Really. Very. Simple. Answer.
While Mr. Foster didn’t exactly chuckle when I raised this possibility, he did make two relevant observations. First, if he were just interested in his own financial gain, he’d have stayed with Matthews. Second, his goal is to pursue asset growth only to the degree that it makes economic sense for his shareholders. By his estimation, the fund is economically sustainable at $100-125 million in assets. As it grows beyond that level, it begins accumulating economies of scale which will benefit shareholders. At the point where additional assets begin impairing shareholder value, he’ll act to restrict them.
Seafarer represents a thoughtfully designed fund, with principled administration and one of the field’s most accomplished managers. It’s distinctive, makes sense and has been under development for a decade. It’s worthy of serious consideration and will be the subject of a fund profile after it has a few months of operation.
Launch Alert: Wasatch Frontier Emerging Small Countries Fund (WAFMX)
Just as one door closes, another opens. Wasatch closed their wildly successful Emerging Markets Small Cap Fund (WAEMX) to new investors on February 24, 2012. The fund gathered $1.2 billion in assets and has returned 51% per year over the three years ending 2/29/2012. They immediately opened another fund in the same universe, run by the same manager.
Wasatch Frontier Emerging Small Countries Fund (WAFMX) became available to retail investors on March 1, 2012. It has been open only to Wasatch employees for the preceding weeks. It will be a non-diversified, all-cap fund with a bias toward small cap stocks. The managers report:
In general, frontier markets and small emerging market countries, with the exception of the oil-producing Persian Gulf States, tend to have relatively low gross national product per capita compared to the larger traditionally-recognized emerging markets and the world’s major developed economies. Frontier and small emerging market countries include the least developed markets even by emerging market standards. We believe frontier markets and small emerging market countries offer investment opportunities that arise from long-term trends in demographics, deregulation, offshore outsourcing and improving corporate governance.
The Fund may invest in the equity securities of companies of any size, although we expect a significant portion of the Fund’s assets to be invested in the equity securities of companies under US$3 billion at the time of purchase.
We travel extensively outside the U.S. to visit companies and expect to meet with senior management. We use a process of quantitative screening followed by “bottom up” fundamental analysis with the objective of owning the highest quality growth companies tied economically to frontier markets and small emerging market countries.
The manager is Laura Geritz. She has been a portfolio manager for the Wasatch Emerging Markets Small Cap Fund since 2009 and for the Wasatch International Opportunities Fund since 2011. The minimum investment is $2000, reduced to $1000 for accounts with an automatic investing plan. The expense ratio will be 2.25%, after waivers. We will, a bit after launch, try to speak with Ms. Geritz and will provide a full profile of the fund.
Fidelity is Thinking Big
 (May God have mercy on our souls.)
(May God have mercy on our souls.)
Despite the ironic timing – they simultaneously announce a bunch of long overdue but still pretty vanilla bond funds at the same time they trumpet their big ideas – Fido has launched its first major ad campaign which doesn’t involve TV. Fidelity is thinking big.
In one of those “did they have the gang at Mad Magazine write this?” press releases, Fido will be “showcasing thought-provoking insights” which “builds on Fidelity’s comprehensive thought leadership” “through an innovative new thought leadership initiative.”
Do you think so?
So what does “thinking big” look like? At their “thinking big” microsite, it’s a ridiculous video that runs for under three minutes, links that direct you to publishers websites so that you can buy three to five year old books, and links to articles that are a year or two old. The depth and quality of analysis in the video are on par with a one-page Time magazine essay. It mixes fun facts (it takes 635 gallons of water to make one pound of hamburger), vacuous observations (water shortages “could further exacerbate regional water issues”) and empty exhortations (“think about it. We do.”).
According to the Boston Business Journal, the campaign “was created by Fidelity’s internal ad agency, Fidelity Communications and Advertising. Arnold Worldwide, the mutual fund firm’s ad agency of record, did not work on the campaign.” It shows. While the VP for communications described this as “the first campaign where we’ve actually attempted to create a viral program without a large supporting TV effort,” he also adds that Fidelity isn’t taking a position on these issues, they’re just “stating the facts.”
Yep. That’s the formula for going viral: corporate marketing footage, one talking head and a “just the facts” ethos.
A quick suggestion from the guy with a PhD in communication: perhaps if you stopped producing empty, boilerplate shareholder communications (have you read one of your annual reports?) and stopped focusing on marketing, you might actually educate investors. A number of fund companies provide spectacularly good, current, insightful shareholder communications (T. Rowe Price and Matthews Asia come immediately to mind). Perhaps you could, too?
The Best of the Web: A new Observer experiment
This month marks the debut of the Observer’s “best of the web” reviews. The premise is simple: having a million choices leaves you with no choices at all. When you’ve got 900 cable channels, you’ll almost always conclude “there’s nothing on” and default to watching the same two stations. It’s called “the paradox of choice.” Too many options cause our brains to freeze and make us miserable.
The same thing is true on the web. There are a million sites offering financial insight; faced with that daunting complexity, we end up sticking with the same one or two. That’s comforting, but may deny you access to helpful perspectives.
One solution is to scan the Observer’s discussion board, where folks post and discuss a dozen or more interesting topics and articles each day. Another might be our best of the web feature. Each month, based on reader recommendations and his own evaluations, contributing editor Junior Yearwood will post reviews for three to five related sites. Each is a page long and each highlights what you need know: what’s the site about, what does it do well, what’s our judgment?
The debut issue features fund rating sites. Everyone knows Morningstar, but how many folks have considered the insights available from, and strengths or weaknesses of, its dozen smaller competitors? Take the case of a single splendid fund, Artisan International Value (ARTKX). Depending on who you ask, it’s seen as somewhere between incredibly excellent (for our money, it is) and utterly undistinguished. Here’s the range of assessments from a variety of sites:
- BarCharts.com: 96% buy
- Morningstar: Five stars, Gold
- FundMojo: 89/100, a Master
- Lipper: 24 of 25 possible points, a Leader
- U.S. News: 8.1/100
- FundReveal: less risky, lower return
- MaxFunds 79/100, good
- TheStreet.com: C-, hold
- Zacks: 3/5, hold.
After a month of reading, Junior and I identified three sites that warranted your time, and named eight more that you probably won’t be bookmarking any time soon.
If you’re wondering “what do those mean?” Or “does Zacks know something that Morningstar doesn’t?” – or even if you’re not – we’re hoping you’ll check out “the best of the web.”
Numbers that you really shouldn’t trust
Claymore/Mac Global Solar Energy Index ETF (XTANX) is up 1120% YTD!
(Source: BarCharts.com, YTD Leaders, as of 2/29/2012)
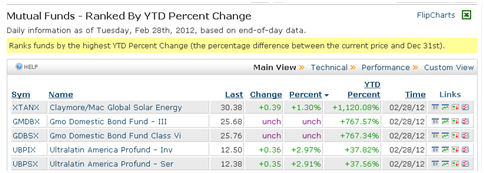
Or not. First, it’s a Guggenheim ETF now. Second, there was a 10:1 reverse split on February 15. BarCharts has a “strong buy” rating on the shares.
GMO Domestic Bond III (GMBDX) is up 767%!
(Same source)
Uhh. No. 9:1 reverse split on January 17.
There are 77 T. Rowe Price funds that waive the investment minimum for investors with an automatic investing plan!
(Source: Morningstar premium fund screener, 2/29/2012)
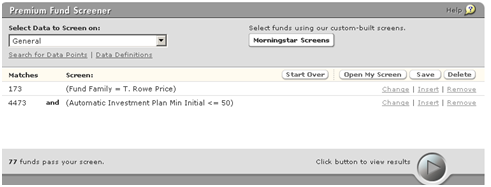
Uhh. No. T. Rowe discontinued those waivers on August 1, 2011.
The “real” expense of running Manning & Napier Dividend Focus (MNDFX) is 5.6%.
(Source: Manning and Napier website, 2/29/2012)
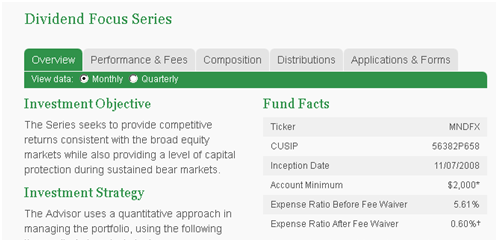
Likewise: no. An M&N representative said that the figures represented the fund’s start-up state (high expenses, no shareholders) but that they weren’t allowed to change them yet. (???) The actual e.r. without an expense waiver is 1.05%, but they have no intention of discontinuing the waiver.
NorthRoad International is a five-star fund that offers tiny beta and huge alpha
(Source: Morningstar profile, 2/29/2011)
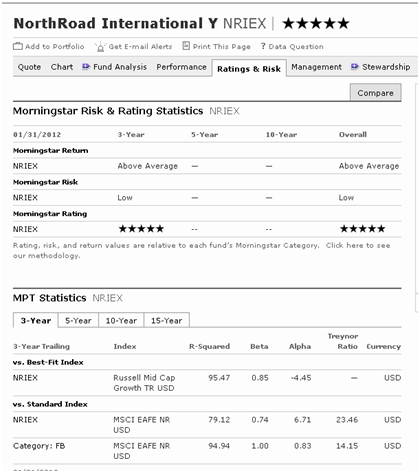
Uhh. No. Not even a little. Why not? Because until June 30, 2011, this was the Madison Mosaic Small/Mid-Cap Fund. Because US smaller stocks were bouncing back from the bloody meltdown from October 2007 – March 2009, this fund returns that were great by international large cap standards and those returns have been folded seamlessly into Morningstar’s assessment.
In NorthRoad’s defense: the fund’s own publicity material makes the change very clear and refuses to include any comparisons that precede the fund’s new mandate. And, since the change, it has been a distinctly above-average international fund with reasonable fees. It’s just not the fund that Morningstar describes.
Any three-year performance number. The market reached its bottom in the first week of March, 2009 and began a ferocious rally. We are now entering the point where the last remnants of a fund’s performance during the market downturn are being cycled-out of the three-year averages. As of 3/01/2012, there are 18 funds which have returned more than 50% per year, on average for the past three years. Half of all funds have three-year returns above 21% per year. Forester Value (FVALX), the great hero of 2008 and the recipient of a ton of money in 2009, now has three-year returns that trail 99% of its peers.
Two funds and why they’re worth your time . . .
Really, really worth your time.
Each month we provide in-depth profiles of two funds that you should know more about, one new and one well-established.
Matthews Asia Strategic Income (MAINX): most US investors have little or no exposure to Asian fixed-income markets, which are robust, secure and growing. Matthews, which already boasts the industry’s deepest corps of Asia specialists, has added a first-rate manager and made her responsible for the first Asian income fund available to U.S. retail investors.
GRT Value (GRTVX): what do you get when you combine one of the best and most experienced small cap investors, a corps of highly professional and supportive partners, a time-tested, risk-conscious strategy and reasonable expenses? GRTVX investors are finding out.
Briefly noted:
T. Rowe Price Real Assets (PRAFX) opened to retail investors in December, 2011. The fund invests in companies that own “stuff in the ground.” The fund was launched in May 2011 but was only available for use in other T. Rowe Price funds. A 5% allocation to real assets became standard in their target-date funds, and might represent a reasonable hedge in most long-term portfolios. The fund’s opening to retail investors was largely unexplained and unnoticed.
Wasatch Microcap Value (WAMVX) has reopened to new investors through Schwab, Fidelity, TD Ameritrade, and other intermediaries.
Talented managers with good marketers attract cash! What a great system. The folks at Grandeur Peaks passed $100 million in assets after four months of operation. The exceedingly fine River Park /Wedgewood Fund (RWGFX) just passed $200 million. When I first profiled the fund, July 2011, it had $200,000 in assets. Dave Rolfe, the manager, estimates that the fund’s strategy can accommodate $5 billion.
Vanguard finally put Vanguard Asset Allocation out of its misery by merging it into Vanguard Balanced Index fund (VBINX) on 2/10/2012. Last fall the Observer identified Vanguard Asset Allocation as one of the fund universe’s 12 worst funds based on its size and its wretched consistency. We described funds on the list this way:
These funds that have finished in the bottom one-fourth of their peer groups for the year so far. And for the preceding 12 months, three years, five years and ten years. These aren’t merely “below average.” They’re so far below average they can hardly see “mediocre” from where they are.
RiverNorth DoubleLine Strategic Income (RNSIX) will close to new investors on March 30, 2012. The fund, comanaged by The Great Gundlach, gathered $800 million in its first 14 months.
Wells Fargo will liquidate Wells Fargo Advantage Social Sustainability (WSSAX) and Wells Fargo Advantage Global Health Care (EHABX) by the end of March, 2012. It’s also merging Wells Fargo Advantage Strategic Large Cap Growth (ESGAX) into Wells Fargo Advantage Large Cap Growth (STAFX), likely in June.
Bridgeway is merging Bridgeway Aggressive Investors 2 (BRAIX) into Bridgeway Aggressive Investors 1 (BRAGX) and Bridgeway Micro-Cap Limited (BRMCX) into Bridgeway Ultra-Small Company (BRUSX). Bridgeway had earlier announced a change in BRUSX’s investment mandate to allow for slightly larger (though still tiny) stocks in its portfolio. In hindsight, that appears to have been the signal of the impending merger. BRUSX, which closed when it reached just $22.5 million in assets, is a legendary sort of fund. $10,000 invested at its 1994 launch would now be worth almost $120,000 against its peers $50,000.
Invesco Small Companies (ATIIX) will close to new investors on March 5, 2012. That’s in response to an entirely-regrettable flood of hot money triggered by the fund’s great performance in 2011. Meanwhile, Invesco also said it will reopen Invesco Real Estate (IARAX) to new investors on March 16.
Delaware Large Cap Value (DELDX) is merging into Delaware Value (DDVAX), itself an entirely-respectable large cap value fund with noticeably lower expenses.
Likewise Lord Abbett is merged Lord Abbett Large-Cap Value (LALAX) into Lord Abbett Fundamental Equity (LDFVX).
Proving the adage that nothing in life is certain but death and taxes, State Street Global Advisors will kill its Life Solutions funds on May 15. Among the soon-to-be decedents are Balanced, Growth and Income & Growth. Also going are SSgA Disciplined Equity (SSMTX) and Directional Core Equity (SDCQX).
Speaking of death, the year’s second mass execution of ETFs occurred on February 17 when Global X took out eight ETFs at once: Farming, Fishing, Mexico Small Caps, Oil, Russell Emerging Markets Growth, Russell Emerging Markets Value, and Waste Management. The 17 HOLDRS Trusts, which promised to “revolutionize stock investing” were closed in December and liquidated on January 9, 2012.
Our chief programmer, Accipiter, was looking for a bit of non-investing reading this month and asked folks on the board for book recommendations. That resulting outpouring was so diverse and thoughtful that we wanted to make it available for other readers. As a result, our Amazon store (it’s under Books, on the main menu bar) now has a “great non-investing reads” department. You’ll be delighted by some of what you find there.
Oh, and Accipiter: there will be a quiz over the readings.
Amazon’s time limit
If you’re one of the many people who support the Observer, thank you! Thank you, thank you, thank you! A dozen readers contributed to the Observer this month (thank you!) by mail or via PayPal. That’s allowed us to more than offset the rising costs caused by our rising popularity. You not only make it all worthwhile, you make it all possible.
If you’re one of the many people who support the Observer by using our link to Amazon.com, thank you – but here’s a warning: the link you create expires or can be wiped out as you navigate.
If you enter Amazon using the Observer’s link (consider bookmarking it), or any other Associate’s link, and put an item in your Shopping Cart, the item carries a special code which serves to identify the referring site (roughly: “us”). It appears the link expires about 24 hours after you set it, so if something’s been in your shopping cart for six weeks (as sometimes happens with me), you might want to re-add it.
Which I mention because Amazon just restated their policy.
A WORD OF WARNING BEFORE YOU GO:
We are going try to cull dead accounts from our email list in the next month, since the monthly charge for sending our notice climbs precipitously after we pass 2500 names. Anyone who has subscribed to receive an email notice but who has never actually opened one of them (it looks like more than a hundred folks) will be dropped. We’d feel bad if we inadvertently lost you, so please do be sure to open the email notice (don’t just look at it in a preview pane) at least once so we know you’re still there.
Take great care and I’ll write again, soon.

 Abnormal Returns has a clean, content-focused layout. Across the top there’s the site banner, with a search box and rudimentary site navigation. Below the banner and site navigation links the page is separated into two sections. The left column contains the current content; the right column has the archives and a smattering of ads.
Abnormal Returns has a clean, content-focused layout. Across the top there’s the site banner, with a search box and rudimentary site navigation. Below the banner and site navigation links the page is separated into two sections. The left column contains the current content; the right column has the archives and a smattering of ads.

 RiverPark/Gargoyle Hedged Value Fund pursued a covered call strategy. Here’s how Gargoyle describes their investment strategy:
RiverPark/Gargoyle Hedged Value Fund pursued a covered call strategy. Here’s how Gargoyle describes their investment strategy: Lipper: Your Best Small Fund Company is . . .
Lipper: Your Best Small Fund Company is . . .

 Just as transistors have been succeeding by microchips, a third of all adults and 20% of smartphone users listen to radio via the internet. Half of them take radio in the form of podcasts, portable snippets of radio that they can listen to as they unwind at home (71%) or try to make a commute more pleasant and productive (45%). Some of us (*cough* Snowball *cough*) even use them to make time at the gym more bearable.
Just as transistors have been succeeding by microchips, a third of all adults and 20% of smartphone users listen to radio via the internet. Half of them take radio in the form of podcasts, portable snippets of radio that they can listen to as they unwind at home (71%) or try to make a commute more pleasant and productive (45%). Some of us (*cough* Snowball *cough*) even use them to make time at the gym more bearable.
 On to the weekend!
On to the weekend! An Update: MoneyLife is Here!
An Update: MoneyLife is Here!