Dear friends,
Welcome to the Year of the Dragon. The Chinese zodiac has been the source of both enthusiasm (“Year of the Dragon and the scaly beast’s unmatched potency as a symbol for prosperity and success – as part of China’s own zodiac – promises an extra special 12 months”) and merriment (check the CLSA Asia-Pacific Market’s Feng Shui Report) in the investing community. The Dragon itself is characterized as “magnanimous, stately, vigorous, strong, self-assured, proud, noble, direct, dignified, eccentric, intellectual, fiery, passionate, decisive, pioneering, artistic, generous, and loyal. Can be tactless, arrogant, imperious, tyrannical, demanding, intolerant, dogmatic, violent, impetuous, and brash.”
Sort of the Gingrich of Lizards.
The Wall Street Journal reports (1/30/12) that Chinese investors have developed a passion for packing portfolios with “fungus harvested from dead caterpillars . . . homegrown liquors, mahogany furniture and jade, among other decidedly non-Western asset classes.”
Given that the last Year of the Dragon (2000) was a disappointment and a prelude to a disaster, I think I’ll keep my day job and look for really good sales on cases of peanut butter (nothing soothes the savaged investor quite like a PB&J . . . and maybe a sprinkle of caterpillar fungus).
Morningstar’s Fund Manager of the Year Awards
I’m not sure if the fund industry would be better off if John Rekenthaler had stayed closer to his bully pulpit, but I know the rest of us would have been. Mr. Rekenthaler (JR to the cognoscenti) is Morningstar’s vice president of research but, in the 1990s and early part of the past decade, played the role of bold and witty curmudgeon and research-rich gadfly. I’d long imagined a meeting of JR and FundAlarm’s publisher Roy Weitz as going something like this: 
The ugly reality is that age and gentility might have reduced it to something closer to: 
For now, I think I’ll maintain my youthful illusions.
Each year Morningstar awards “Fund Manager of the Year” honors in three categories: domestic equity, international equity and fixed-income. While the recognition is nice for the manager and his or her marketers, the question is: does it do us as investors any good. Is last year’s Manager of the Year, next year’s Dud of the Day?
One of the things I most respect about Morningstar is their willingness to provide sophisticated research on (and criticisms of) their own systems. In that spirit, Rekenthaler reviewed the performance of Managers of the Year in the years following their awards.
His conclusions:
Domestic Fund Manager of the Year: “meh.” On whole, awardees were just slightly above average with only three disasters, Bill Miller (1998), Jim Callinan (1999 – if you’re asking “Jim Who?” you’ve got a clue about how disastrous), and Mason Hawkins (2006). Bruce Berkowitz will appear in due course, I fear. JR’s conclusion: “beware of funds posting high returns because of financials and/or technology stocks.”
Fixed-Income Manager of the Year: “good” and “improving.” On whole, these funds lead their peers by 50-80 basis points/year which, in the fixed income world, is a major advantage. The only disaster has been a repeated disaster: Bob Rodriquez of FPA New Income earned the award three times and has been mediocre to poor in the years following each of those awards. Rekenthaler resists the impulse to conclude that Morningstar should “quit picking Bob Rodriguez!” (he’s more disciplined than I’d be). JR notes that Rodriquez is streaky (“two or three truly outstanding years” followed by mediocrity and disappointment before taking off again) and that “it’s a tough fund to own.”
International Fund Manager of the Year: Ding! Ding! Ding! Got it right in a major way. As Rekenthaler puts it, “the Morningstar team selecting the International-Stock winners should open a hotline on NFL games.” Twelve of the 13 international honorees posted strong returns in the years after selection, while the final honoree Dodge & Cox International (DODFX) has beaten its peer group but just by a bit.
Rekenthaler’s study, Do the Morningstar Fund Manager of the Year Awards Have Staying Power? is available at Morningstar.com, but seems to require a free log-in to access it.
Fun with Numbers: The Difference One Month Makes
Investors often look at three-year returns to assess a fund’s performance. They reason, correctly, that they shouldn’t be swayed by very short term performance. It turns out that short term performance has a huge effect on a fund’s long-term record.
 The case in point is Matthews Asian Growth and Income (MACSX), a FundAlarm “Star in the Shadows” fund, awarded five stars and a “Silver” rating by Morningstar. It’s in my portfolio and is splendid. Unless you look at the numbers. As of January 27 2011, it ranked dead last – the 100th percentile – in its Morningstar peer group for the preceding three years. Less than one month earlier, it was placed in the 67th percentile, a huge drop in 20 trading days.
The case in point is Matthews Asian Growth and Income (MACSX), a FundAlarm “Star in the Shadows” fund, awarded five stars and a “Silver” rating by Morningstar. It’s in my portfolio and is splendid. Unless you look at the numbers. As of January 27 2011, it ranked dead last – the 100th percentile – in its Morningstar peer group for the preceding three years. Less than one month earlier, it was placed in the 67th percentile, a huge drop in 20 trading days.
Or not, since its trailing three-year record as of January 27 showed it returning 18.08% annually. At the beginning of the month, its three-year return was 14.64%.
How much difference does that really make? $10,000 invested on January 1 2009 would have grown to $15,065 in three years. The same amount invested on January 27 2009 and left for three years would have grown to $16,482. Right: the delay of less than a month turned a $5100 gain into a $6500 one.
What happened? The January 27 calculation excludes most of January 2009, when MACSX lost 3.3% while its peers dropped 7.8% and it includes most of January 2012, when MACSX gained 4.8% but its peers rallied 10.2%. That pattern is absolutely typically for MACSX: it performs brilliantly in falling markets and solidly in rising ones. If you look at a period with sharp rises – even in a single month – this remarkably solid performer seems purely dreadful.
Here’s the lesson: you’ve got to look past the numbers. The story of any fund can’t be grasped by looking at any one number or any one period. Unless you understand why the fund has done what it has and what it supposed to be doing for your portfolio, you’re doomed to an endless cycle of hope, panic and missteps. (From which we’re trying to save you, by the way.)
Looking Past the Numbers, Part Two: The Oceanstone Fund
Sometimes a look past the numbers will answer questions about a fund that looking dowdy. That’s certainly the case with MACSX. In order instances, it should raise them about a fund that’s looking spectacular. The Oceanstone Fund (OSFDX) is a case in point. Oceanstone invests in a diversified portfolio of undervalued stocks from micro- to mega-cap. Though it does not reflect the fund’s current or recent portfolio, Morningstar classifies it as a “small value” fund. And I’ve rarely seen a fund with a more-impressive set of performance numbers:
| Percentile rank, Small Value Peers |
|
| 2007 | Top 1% |
| 2008 | Top 1% |
| 2009 | Top 1% |
| 2010 | Top 13% |
| 2011 | Top 8% |
| 2012, through 1/31 | Top 2% |
| Trailing 12 months | Top 5% |
| Trailing 36 months | Top 1% |
| Trailing 60 months | Top 1% |
In the approximately five years from launch through 1/30/2011, Oceanstone’s manager turned $10,000 into $59,000. In 2009, powered by gains in Avis Budget Group and Dollar Thrifty Automotive (1,775 percent and 2,250 percent respectively), the fund made 264%. And still, the fund has only $17 million in assets.
Time to jump in? Send the big check, and wait to receive the big money?
I don’t know. But you do owe it to yourself to look beyond the numbers first. When you do that, you might notice:
1. that the manager’s explanation of his investment strategy is nonsense. Here’s the prospectus description of what he’s doing:
In deciding which common stocks to purchase, the Fund seeks the undervalued stocks as compared to their intrinsic values. To determine a stock’s intrinsic value (IV), the Fund uses the equation: IV = IV/E x E. In this equation, E is the stock’s earnings per share for its trailing 4 quarters, and a reasonable range of its IV/E ratio is determined by a rational and objective evaluation of the current available information of its future earnings prospects.
Read that formula: IV = IV divided by E, times E. No more than a high school grasp of algebra tells you that this formula tells you nothing. I shared it with two professors of mathematics, who both gave it the technical term “vacuous.” It works for any two numbers (4 = 4 divided by 2, times 2) but it doesn’t allow you to derive one value from the other. If you know “the stock’s earnings” and are trying to determine it’s “investment value,” this formula can’t do it.
2. that the shareholder reports say nothing. Here is the entire text of the fund’s 2010 Annual Report:
Oceanstone Fund (the Fund) started its 2011 fiscal year on 7/1/2010 at net asset value (NAV) of $28.76 per share. On 12/27/2010, the Fund distributed a short-term capital gain dividend of $2.7887 per share and a long-term capital gain dividend of $1.7636. On 6/30/2011, the Fund ended this fiscal year at NAV of $35.85 per share. Therefore, the Fund’s total return for this fiscal year ended 6/30/2011 is 42.15%. During the same period, the total return of S&P 500 index is 30.69%.
For portfolio investment, the Fund seeks undervalued stocks. To determine a stock’s intrinsic value (IV), the Fund uses the equation IV = IV/E x E, as stated in the Fund’s prospectus. To use this equation, the key is to determine a company’s future earnings prospects with reasonable accuracy and subsequently a reasonable range for its IV/E ratio. As a company’s future earnings prospects change, this range for its IV/E ratio is adjusted accordingly.
Short-term, stock market can be volatile and unpredictable. Long-term, the deciding factor of stock price, as always, is value. Going forward, the Fund strives to find at least some of the undervalued stocks when they become available in U.S. stock market, in an effort to achieve a good long-term return for the shareholders.
One paragraph reports NAV change, the second reproduces the vacuous formula in the prospectus and the third is equally-vacuous boilerplate about markets. What, exactly, is the manager telling you? And what does it say that he doesn’t think you deserve to know more?
3. that Oceanstone’s Board is chaired by Rajendra Prasad, manager of Prasad Growth (PRGRX). Prasad Growth, with its frantic trading (1300% annual turnover), collapsing asset base and dismal record (bottom 1% of funds for the past 3-, 5- and 10-year period) is a solid candidate for our “Roll Call of the Wretched.” How, then, does his presence benefit Oceanstone’s shareholders?
4. the fund’s portfolio turns over at triple the average rate, is exceedingly concentrated (20 names) and is sitting on a 30% cash stake. Those are all unusual, and unexplained.
You need to look beyond the numbers. In general, a first step is to read the managers’ own commentary. In this case, there is none. Second, look for coverage in reliable sources. Except for this note and passing references to 2009’s blistering performance, none again. Your final option is to contact the fund advisor. The fund’s website has no email inquiry link or other means to facilitate contact, so I’ve left a request for an interview with the fund’s phone reps. They seemed dubious. I’ll report back, in March, on my success or failure.
And Those Who Can’t Teach, Teach Gym.
Those of us who write about the investment industry occasionally succumb to the delusion that that makes us good investment managers. A bunch of funds have managers who at least wave in the direction of having been journalists:
- Sierra Strategic Income Fund: Frank Barbera, CMT, was a columnist for Financial Sense from 2007 until 2009.
- Roge Partners: Ronald W. Rogé has been a guest personal finance columnist for ABCNews.com.
- Auer Growth: Robert C. Auer, founder of SBAuer Funds, LLC, was from 1996 to 2004, the lead stock market columnist for the Indianapolis Business Journal “Bulls & Bears” weekly column, authoring over 400 columns, which discussed a wide range of investment topics.
- Astor Long/Short ETF Fund: Scott Martin, co-manager, is a contributor to FOX Business Network and a former columnist with TheStreet.com
- Jones Villalta Opportunity Fund: Stephen M. Jones was financial columnist for Austin Magazine.
- Free Enterprise Action Fund: The Fund’s investment team is headed by Steven J. Milloy, “lawyer, consultant, columnist, adjunct scholar.”
Only a handful of big-time financial journalists have succumbed to the fantasy of financial acumen. Those include:
- Ron Insana, who left CNBC in March 2006 to start a hedge fund, lost money for his investors, closed the fund in August 2008, joined SAC Capital for a few months then left. Now he runs a website (RonInsanaShow.com) hawking his books and providing one minute market summaries, and gets on CNBC once a month.
- Lou Dobbs bolted from hosting CNN’s highly-rated Moneyline show in 1999 in order to become CEO of Space.com. By 2000 he was out of Space and, by 2001, back at CNN.
- Jonathan Clements left a high visibility post at The Wall Street Journal to become Director of Financial Education, Citi Personal Wealth Management. Sounds fancy. Frankly, it looks like he’s been relegated to “blogger.” As I poke around the site, he seems to write a couple distinctly mundane, 400-word essays a week.
- Jim Cramer somehow got rich in the hedge fund world. Since then he’s become a clown whose stock picks are, by pretty much every reckoning, high beta and zero alpha. And value of his company, TheStreet.com’s, stock is down 94.3% since launch.
- Jim Jubak, who writes the “Jubak’s Picks” column for MSN Money, launched Jubak Global Equity (JUBAX), which managed to turn $10,000 at inception into $9100 by the end of 2011 while his peers made $11,400.
You might notice a pattern here.
The latest victim of hubris and comeuppance is John Dorfman, former Bloomberg and Wall Street Journal columnist. You get a sense of Dorfman’s marketing savvy when you look at his investment vehicles.
Dorfman founded Thunderstorm Capital in 1999, and then launched The Lobster Fund (a long-short hedge fund) in 2000. He planned launch of The Oyster Fund (a long-only hedge fund) and The Crab Fund (short-only) shortly thereafter, but that never quite happened. Phase One: name your investments after stuff that’s found at low tide, snatched up, boiled and eaten with butter.
He launched Dorfman Value Fund in 2008. Effective June 30, 2009, the fund’s Board approved changing the name from Dorfman Value Fund to Thunderstorm Value Fund. The reason for the name change is that the parent firm of Thunderstorm Mutual Funds LLC “has decided the best way to promote a more coherent marketing message is to rebrand all of its products to begin with the word ‘Thunderstorm’.”
Marketers to mutual fund: “Well, duh!”
Earth to Dorfman: did you really think that naming your fund after a character in Animal House (Kent Dorfman, an overweight, clumsy legacy pledge), especially one whose nickname was “Flounder,” was sharp to begin with? Name recognition is all well and good . . . . as long as your name doesn’t cause sniggering. I can pretty much guarantee that when I launch my mutual fund, it isn’t going to be Snowball Special (DAVYX).
Then, to offset having a half-way cool name, they choose the ticker symbol THUNX. THUNX? As in “thunks.” Yes, indeed, because nothing says “trust me” like a vehicle that goes “thunk.”
Having concluded that low returns, high expenses, a one-star rating, and poor marketing aren’t the road to riches, the advisor recommended that the Board close (on January 17, 2012) and liquidate (on February 29, 2012) the fund.
Does Anyone Look at this Stuff Before Running It?
They’re at it again. I’ve noted, in earlier essays, the bizarre data that some websites report. In November, I argued, “There’s no clearer example of egregious error without a single human question than in the portfolio reports for Manning & Napier Dividend Focus (MNDFX).” The various standard services reported that the fund, which is fully invested in stocks, held between 60 – 101% of its portfolio in cash.
And now, there’s another nominee for the “what happens when humans no longer look at what they publish” award. In the course of studying Bretton Fund (BRTNX), I looked at the portfolios of the other hyper-concentrated stock funds – portfolios with just 10-15 stocks.
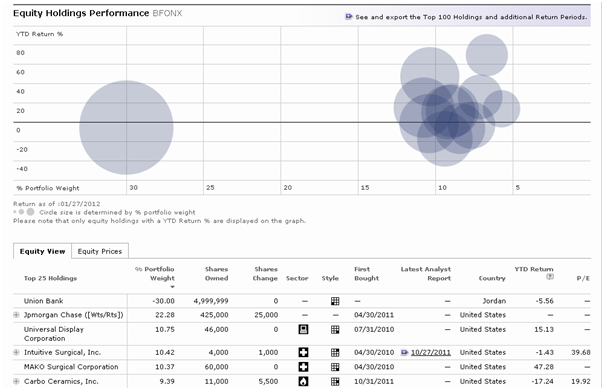
One such fund is Biondo Focus (BFONX), an otherwise undistinguished fund that holds 15 stocks (and charges way too much). One striking feature of the fund: Morningstar reports that the fund invested 30% of the portfolio in a bank in Jordan. That big gray circle on the left represents BFONX’s stake in Union Bank.
There are, as it turns out, four problems with this report.
- There is no Union Bank in Jordan. It was acquired by, and absorbed in, Bank Al Etihad of Amman.
- The link labeled Union Bank (Jordan) actually leads to a report for United Bankshares, Inc. (UBSI). UBSI, according to Morningstar’s report, mostly does business in West Virginia and D.C.
- Biondo Focus does not own any shares of Union or United, and never has.
- Given the nature of data contracts, the mistaken report is now widespread.
Joe Biondo, one of the portfolio managers, notes that the fund has never had an investment in Union Bank of Jordan or in United Bankshares in the US. They do, however, use Union Bank of California as a custodian for the fund’s assets. The 30% share attributed to Union Bank is actually a loan run through Union Bank, not even a loan from Union Bank.
The managers used the money to achieve 130% equity exposure in January 2012. That exposure powered the portfolio to a 21.4% gain in the first four weeks of January 2012, but didn’t offset the fund’s 24% loss in 2011. From January 2011 – 2012, it finished in the bottom 1% of its peer group.
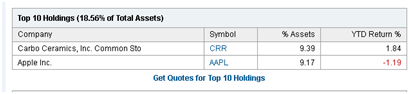
Google, drawing on Morningstar, repeats the error, as does MSN and USA Today while MarketWatch and Bloomberg get it right. Yahoo takes error in a whole new direction when provides this list of BFONX’s top ten holdings:
Uhhh, guys? Even in daycare the kids managed to count past two on their way to ten. For the record, these are holdings five and six.
Update from Morningstar, February 2
The folks at Biondo claimed that they were going to reach out to Morningstar about the error. On February 2, Alexa Auerbach of Morningstar’s Corporate Communications division sent us the following note:
We read your post about our display of inaccurate holdings for the Biondo Focus fund. We’ve looked into the matter and determined that the fund administrator sent us incomplete holdings information, which led us to categorize the Union Bank holding as a short-equity position instead of cash. We have corrected our database and the change should be reflected on Morningstar.com soon.
Morningstar processes about 50,000 fund portfolios worldwide per month, and we take great pride in providing some of the highest quality data in the industry.
Point well-taken. Morningstar faces an enormous task and, for the most part, pulls it off beautifully. That said, if they get it right 99% of the time, they’ll generate errors in 6,000 portfolios a year. 99.9% accuracy – which is unattested to, but surely the sort of high standard Morningstar aims for – is still 600 incorrect reports/year. Despite the importance of Morningstar to the industry and to investors, fund companies often don’t know that the errors exist and don’t seek to correct them. None of the half-dozen managers I spoke with in 2011 and early 2012 whose portfolios or other details were misstated, knew of the error until our conversation.
That puts a special burden on investors and their advisers to look carefully at any fund reports (certainly including the Observer’s). If you find that your fully-invested stock fund has between 58-103% in cash (as MNDFX did), a 30% stake in a Jordanian bank (BFONX) or no reported bonds in your international bond fund (PSAFX, as of 2/5/2012), you need to take the extra time to say “how odd” and look further.
Doesn’t Anyone at the SEC Look at their Stuff Before Posting It?
The Securities and Exchange Commission makes fund documents freely available through their EDGAR search engine. In the relentless, occasionally mind-numbing pursuit of new funds, I review each day’s new filings. The SEC posts all of that day’s filings together which means that all the filings should be from that day. To find them, check “Daily Filings” then “Search Current Events: Most Recent Filings.”
Shouldn’t be difficult. But it is. The current filings for January 5, 2012 are actually dated:
- January 5, 2012
- October 14, 2011
- September 2, 2011
- August 15, 2011
- August 8, 2011
- July 27, 2011
- July 15, 2011
- July 1, 2011
- June 15, 2011
- June 6, 2011
- May 26, 2011
- May 23, 2011
- January 10, 2011
For January 3rd, only 20 of 98 listings are correct. Note to the SEC: This Isn’t That Hard! Hire A Programmer!
Fund Update: HNP Growth and Preservation
We profiled HNP Growth and Preservation (HNPKX) in January 2012. The fund’s portfolio is set by a strict, quantitative discipline: 70% is invested based on long-term price trends for each of seven asset classes and 30% is invested based on short-term price trends. The basic logic is simple: try to avoid being invested in an asset that’s in the midst of a long, grinding bear market. Don’t guess about whether it’s time to get in or out, just react to trend. This is the same strategy employed by managed futures funds, which tend to suffer in directionless markets but prosper when markets show consistent long-term patterns.
Since we published our profile, the fund has done okay. It returned 3.06% in January 2012, through 1/27. That’s a healthy return, though it lagged its average peer by 90 bps. It’s down about 5.5% since launch, and modestly trails its peer group. I asked manager Chris Hobaica about how investors should respond to that weak initial performance. His reply arrived too late to be incorporated in the original profile, but I wanted to share the highlights.
Coming into August the fund was fully invested on the long term trend side (fairly rare…) and overweight gold, Treasuries and real estate on the short term momentum side. . . Even though the gold and Treasuries held up [during the autumn sell-off], they weren’t enough to offset the remaining assets that were being led down by the international and emerging assets. Also, as is usually the case, assets class correlations moved pretty close to 1.
Generally though, this model isn’t designed to avoid short-term volatility, but rather a protracted bear market. By the end of September, we had moved to gold, treasuries and cash. So, the idea was that if that volatility continued into a bear market, the portfolio was highly defensive.
While we are never happy with negative returns, we explain to shareholders that the model was doing what it was supposed to do. It became defensive when the trends reversed. I am not worried by the short term drop (I don’t like it though), as there have been many other times over the backtest that the portfolio would have been down in the 8-10% range.
Three Funds, and why they’re worth your time
Really worth it. Every month the Observer profiles two to four funds that we think you really need to know more about. One category is the most intriguing new funds: good ideas, great managers. These are funds that do not yet have a long track record, but which have other virtues which warrant your attention. They might come from a great boutique or be offered by a top-tier manager who has struck out on his own. The “most intriguing new funds” aren’t all worthy of your “gotta buy” list, but all of them are going to be fundamentally intriguing possibilities that warrant some thought. This month we’ll highlight three funds with outstanding heritages and fascinating prospects:
Bretton Fund (BRTNX): Bretton is an ultra-concentrated value fund managed by the former president of Parnassus Investments. It has shown remarkable – and remarkably profitable – independence from style boxes, peers and indexes in its brief life.
Grandeur Peak Global Opportunities (GPGOX): here’s a happy thought. Two brilliantly-successful managers who made their reputation running a fund just like this one have struck out on their own, worrying about a much smaller and more-nimble fund, charging less and having a great time doing it.
Matthews Asia Strategic Income (MAINX): Matthews, which already boasts the industry’s deepest corps of Asia specialists, has added a first-rate manager and made her responsible for the first Asian income fund available to U.S. retail investors.
Launch Alert: Seafarer Overseas Growth and Income
 Seafarer Overseas Growth and Income (SFGIX) is set to launch in mid-February, 2012. The fund’s final prospectus is available at SeafarerFunds.com. The fund will be managed by Andrew Foster, formerly manager of Matthews Asia Growth & Income (MACSX) and Matthews’ research director or acting chief investment officer.
Seafarer Overseas Growth and Income (SFGIX) is set to launch in mid-February, 2012. The fund’s final prospectus is available at SeafarerFunds.com. The fund will be managed by Andrew Foster, formerly manager of Matthews Asia Growth & Income (MACSX) and Matthews’ research director or acting chief investment officer.
The great debate surrounding MACSX was whether it was the best Asia-centered fund in existence or merely one of the two or three best funds in existence. Here’s the broader truth within their disagreement: Mr. Foster’s fund was, consistently and indisputably one of the best Asian funds in existence. That distinction was driven by two factors: the fund’s focus on high-quality, dividend-paying stocks plus its willingness to hold a variety of securities other than common stocks. A signal of the importance of those other securities is embedded in the fund’s ticker symbol; MACSX reflects the original name, Matthews Asian Convertible Securities Fund.
Those two factors helped make MACSX one of the two least volatile and most profitable Asian funds. Whether measured by beta, standard deviation or Morningstar’s “downside capture ratio,” it typically incurs around half of the risk of its peers. Over the past 15 years, the fund’s returns (almost 11% per year) are in the top 1% of its peer group. The more important stat is the fund’s “investor returns.” This is a Morningstar calculation that tries to take into account the average investor’s fickleness and inept market timing. Folks tend to arrive after a fund has done spectacularly and then flee in the midst of it crashing. While it’s an imperfect proxy, “investor returns” tries to estimate how much the average investor in a fund actually made. With highly volatile funds, the average investor might have earned nothing in a fund that made 10%.
In the case of MACSX, the average investor has actually made more than the fund itself. That occurs when investors are present for the long-haul and when they’re in the habit of buying more when the fund’s value is falling. This is an exceedingly rare pattern and a sign that the fund “works” for its investors; it doesn’t scare them away, so they’re able to actually profit from their investment.
Seafarer will take the MACSX formula global. The Seafarer prospectus explains the strategy:
The Fund attempts to offer investors a relatively stable means of participating in a portion of developing countries’ growth prospects, while providing some downside protection, in comparison to a portfolio that invests purely in the common stocks of developing countries. The strategy of owning convertible bonds and dividend-paying equities is intended to help the Fund meet its investment objective while reducing the volatility of the portfolio’s returns.
Mr. Foster writes: “I hope to marry Asia Pacific with other ‘emerging markets,’ a few carefully-selected ‘frontier’ markets, alongside a handful of ‘developed’ countries. I am excited about the possibilities.”
The fund’s minimum investment is $2500 for regular accounts and $1000 for IRAs. The initial expense ratio is 1.60%, an amount that Mr. Foster set after considerable deliberation. He didn’t want to charge an unreasonable amount but he didn’t want to risk bankrupting himself by underwriting too much of the fund’s expenses (as is, he expects to absorb 0.77% in expenses to reach the 1.6% level). While the fund could have launched on February 1, Mr. Foster wanted a couple extra weeks for finish arrangements with some of the fund supermarkets and other distributors.
Mr. Foster has kindly agreed to an extended conversation in February and we’ll have a full profile of the fund shortly thereafter. In the meantime, feel free to visit Seafarer Funds and read some of Andrew’s thoughtful essays on investing.
Briefly Noted
Fidelity Low-Priced Stock (FLPSX) manager Joel Tillinghast has returned from his four-month sabbatical. It looks suspiciously like a rehearsal for Mr. Tillinghast’s eventual departure. The five acolytes who filled-in during his leave have remained with the fund, which he’d managed solo since 1989. If you’d had the foresight to invest $10,000 in the fund at inception, you’d have $180,000 in the bank today.
Elizabeth Bramwell is retiring in March, 2012. Bramwell is an iconic figure who started her investment career in the late 1960s. Her Bramwell Growth Fund became Sentinel Capital Growth (SICGX) in 2006, when she also picked up responsibility for managing Sentinel Growth Leaders (SIGLX), and Sentinel Sustainable Growth Opportunities (CEGIX). Kelli Hill, her successor, seems to have lots of experience but relatively little with mutual funds per se. She’s sometimes described as the person who “ran Old Mutual Large Cap Growth (OILLX),” but in reality she was just one of 11 co-managers.
Fidelity has agreed to pay $7.5 million to shareholders of Fidelity Ultra-Short Bond fund (FUSBX) (and their attorneys) in settlement of a class action suit. The plaintiffs claimed that Fidelity did not exercise reasonable oversight of the fund’s risks. Despite being marketed as a low volatility, conservative option, the fund invested heavily in mortgage-backed securities and lost 17% in value from June 2007 – May 2008. Fidelity, as is traditional in such cases, “believes that all of the claims are entirely without merit.” Why pay them then? To avoid “the cost and distraction” of trial, they say. (Court Approves a $7.5 Million Settlement, MFWire, 1/27/12).
Fidelity is changing the name of Fidelity Equity-Income II (FEQTX) to Fidelity Equity Dividend Income fund. Its new manager Scott Offen, who took over the fund in November 2011, has sought to increase the fund’s dividend yield relative to his predecessor Stephen Peterson.
Bridgeway Ultra-Small Company (BRUSX) is becoming just a little less “ultra.” The fund has, since launch, invested in the tiniest U.S. stocks, those in the 10th decile by market cap. As some of those firms thrived, their market caps have grown into the next-higher (those still smaller than microcap) decile. Bridgeway has modified its prospectus to allow the fund to buy shares in these slightly-larger firms
Invesco has announced the merger of three more Van Kampen funds, which follows dozens of mergers made after they acquired Morgan Stanley’s funds in 2010. The latest moves: Invesco High Income Muni (AHMAX) will merge into Invesco Van Kampen High Yield Municipal (ACTFX). Invesco US Mid Cap Value (MMCAX) and Invesco Van Kampen American Value (MSAJX), run by the same team, are about to become the same fund. And Invesco Commodities Strategy (COAIX) disappears into the more-active Invesco Balanced Risk Commodity Strategy (BRCNX). The funds share management teams and similar fees, but Invesco Commodities Strategy has closely tracked its Dow-Jones-UBS Commodity Total Return Index benchmark, while Invesco Van Kampen Balanced Risk Commodity Strategy is more actively managed.
DWS Dreman Small Cap Value (KDSAX), which is already too big, reopened to all investors on February 1, 2012.
Managers Emerging Markets Equity (MEMEX) will liquidate on March 9, 2012. The fund added a bunch of co-managers three years ago, but it’s lagged its peer group in each of the past five years. It’s attracted $45 million in assets, apparently not enough to making it worth the advisor’s while.
On March 23, 2012, the $34 million ING International Capital Appreciation (IACAX) will also liquidate, done in by performance that was going steadily from bad to worse.
I’d missed the fact that back in mid-October, RiverPark Funds liquidated their RiverPark/Gravity Long-Biased Fund. RiverPark has been pretty ruthless about getting rid of losing strategies (funds and active ETFs) after about a year of weakness.
The Observer: Milestones and Upgrades
The folks who bring you the Observer are delighted to announce two milestones and three new features, all for the same reasonable rate as before. Which is to say, free.
On January 27, 2012, folks launched the 2000th discussion thread on the Observer’s lively community forum. The thread in question focused on which of two Matthews Asia funds, Growth and Income (MACSX) or Asia Dividend (MAPIX), was the more compelling choice. Sentiment seemed to lean slightly toward MAPIX, with the caveat that the performance comparison should be tempered by an understanding that MACSX was not a pure-equity play. One thoughtful poster analogized it to T. Rowe Price’s stellar Capital Appreciation (PRWCX) fund, in that both used preferred and convertible shares to temper volatility without greatly sacrificing returns. In my non-retirement account, I own shares of MACSX and have been durn happy with it.
Also on January 27, the Observer attracted its 50,000th reader. Google’s Analytics program labels you as “unique visitors.” We heartily agree. While the vast majority of our readers are American, folks from 104 nations have dropped by. I’m struck that we’re had several hundred visits from each of Saudi Arabia, Israel, France, India and Taiwan. On whole, the BRICs have dispatched 458 visitors while the PIIGS account for 1,017.
In March the Observer will debut a new section devoted to providing short, thoughtful summaries and analyses of the web’s best investment and finance websites. We’ve grown increasingly concerned that the din of a million cyber voices is making it increasingly hard for folks to find reliable information and good insights as they struggle to make important life choices. We will, with your cooperation, try to help.
The project team responsible for the effort is led by Junior Yearwood. Those of you who’ve read our primer on Miscommunication in the Workplace know of Junior as one of the folks who helped edit that volume. Junior and I met some years ago through the good offices of a mutual friend, and he’s always proven to be a sharp, clear-eyed person and good writer. Junior brings what we wanted: the perspectives of a writer and reader who was financially literate but not obsessed with the market’s twitches or Fidelity’s travails. I’ll let him introduce himself and his project:
It’s rare that a 19-year-old YouTube sensation manages to sum up the feelings of millions of Americans and people the world over. But Tay Zonday, whose richly-baritone opening line is “are you confused about the economy?” did. “Mama, Economy; Make me understand all the numbers” explains it all.
The fact is we all could use a little help figuring it all out. “We” might be a grandmother who knows she needs better than a zero percent savings account, a financial adviser looking to build moats around her clients’ wealth, or even me, the former plant manager and current freelance journalist. We all have something in common; we don’t know everything and we’re a bit freaked out by the economy and by the clamor.
My project is to help us sort through it. The idea originated with the estimable Chuck Jaffe MarketWatch. I am not a savvy investor nor am I a financial expert. I am a guy with a sharp eye for detail and the ability to work well with others. My job is to combine your suggestions and considered analysis with my own research, into a monthly collection of websites that we believe are worth your time. David will oversee the technical aspects of the project. I’ll be reaching out, in the months ahead, to both our professional readership (investment advisers, fund managers, financial planners, and others) and regular people like myself.
Each month we will highlight and profile around five websites in a particular category. The new section will be launching in March with a review of mutual fund rating sites. In the following months we’ll look at macro-level blogs run by investment professionals, Asian investing and many of the categories that you folks feel most interested in. I’d be pleased to hear your ideas and I can be reached at [email protected]
A special word of thanks goes out to Chuck. We hope we can do justice to your vision.
Finally, I remain stunned (and generally humbled) by the talent and commitment of the folks who daily help the Observer out. I’m grateful, in particular, to Accipiter, our chief programmer who has been both creative and tireless in his efforts to improve the function of the Observer’s discussion board software. The software has several virtues (among them, it was free) but isn’t easy to scan. The discussion threads look like this:
MACSX yield 3.03 and MAPIX yield 2.93. Why go with either as opposed to the other?
14 comments MaxBialystock January 27| Recent Kenster1_GlobalValue3:54PM Fund Discussions
Can’t really see, at a glance, what’s up with the 14 comments. Accipiter wrote a new discussion summary program that neatly gets around the problem. Here’s that same discussion, viewed through the Summary program:
MACSX yield 3.03 and MAPIX yield 2.93. Why go with either as opposed to the other? By – MaxBialystock viewed (468)
- 2012-01-28 – scott : I was going to say MACSX is ex-Japan, but I guess it isn’t – didn’t it used to …
- 2012-01-28 – MaxBialys : Reply to @scott: Yes, it’s SUPPOSED to be…….
- 2012-01-28 – scott : Reply to @MaxBialystock: Ah. I own a little bit left of it, but I haven’t looke…
- 2012-01-28 – MikeM : If you go to their web, site, they have a compare option where you can put the…
- 2012-01-28 – InformalE : Pacific Tigers, MAPTX, is ex-Japan. I don’t think MACSX was ever ex-Japan.In re…
- 2012-01-28 – msf : You can’t put too much stock in the category or benchmark with these funds. M…
- 2012-01-28 – MaxBialys : Lots of work, thought and information. And CLEARLY expressed. MACSX is still ab…
- 2012-01-28 – catch22 : Hi Max, Per your post, it appears you are also attempting to compare the dividen…
- 2012-01-28 – Investor : I recently sold all of MACSX and reinvested most in MAPIX. I just did not feel …
- 2012-01-28 – fundalarm : Reply to @Investor: as mentioned before, i have done the same at the end of Dec…
- . 07:27:27 . – msf : Reply to @fundalarm: Though figures show long term performance of MAPIX to be b…
- 2012-01-28 – MaxBialys : Ya, well, I kinda hogtied myself. I got 11 X more in MAPIX than MACSX, and MACS…
The Summary is easy to use. Simply go to the Discussions page and look at the gray bar across the top. The menu options are Discussions – Activity – Summary – Sign In. Signing up and signing in are easy, free and give you access to a bunch of special features, but they aren’t necessary for using the Summary. Simply click “Summary” and, in the upper right, the “comments on/off” button. With “comments on,” you immediately see the first line of every reply to every post. It’s a fantastic tool for scanning the discussions and targeting the most provocative comments.
In addition to the Summary view, Chip, our diligent and crafty technical director, constructed a quick index to all of the fund profiles posted at the Observer. Simply click on the “Funds” button on the top of each page to go to the Fund’s homepage. There you’ll see an alphabetized list of the fifty profiles (some inherited from FundAlarm) that are available on-site. Profiles dated “April 2011” or later are new content while many of the others are lightly-updated versions of older profiles.
I’m deeply grateful to both Accipiter and Chip for the passion and superb technical expertise that they bring. The Observer would be a far poorer place without. Thanks to you both.
In closing . . .
Thanks to all the folks who supported the Observer in the months just passed. While the bulk of our income is generated by our (stunningly convenient!) link to Amazon, two or three people each month have made direct financial contributions to the site. They are, regardless of the amount, exceedingly generous. We’re deeply grateful, as much as anything, for the affirmation those gestures represent. It’s good to know that we’re worth your time.
In March, there’ll be a refreshed and expanded profile of Matthews Asia Strategic Income (MAINX), profiles of Andrew Foster’s new fund, Seafarer Overseas Growth and Income (SFGIX) and ASTON/River Road Long-Short Fund (ARLSX) and a new look at an old favorite, GRT Value (GRTVX).
As ever,



 2.
2.  3.
3. 